Cosmetic surgery
Plastic surgery usually involves changes to the face, chest, abdomen and hips. Below is an overview of the most common cosmetic surgeries:

The most common cosmetic surgeries
- Eyelid correction
- Ear correction
- Rhinoplasty
- Lip correction
- Breast surgery (breast lift, breast augmentation, breast reduction)
- Liposuction
- Hair transplant
- Wrinkle treatment / lifting
- Tightening of the abdomen, legs, arms
Facial surgery
Eyelid correction (eyelid tightening, eyelid plastic surgery, blepharoplasty)
This method is one of the most common cosmetic surgery procedures for 40 to 60 year-old patients and is used in particular for drooping eyelids.
To tighten the eye area on the upper or lower eyelid, excess skin as well as excess fat and muscle tissue is removed. The procedure is usually carried out on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia (local anesthesia) and takes about 1-3 hours. The rest of the tissue is closed again with fine seams.
The risks of this intervention are low.
A rare but serious complication is injury to the eyelid lifter muscle, which can subsequently lead to dry eyes. However, this can usually be remedied by conservative measures without additional surgery. Bleeding and swelling usually recede by themselves, wound infections rarely occur.
You can find more information about eyelid lift at: Eyelid lift
Ear correction (ear plasty, otoplasty)
Ear correction is the reduction in size of the auricle or the creation of protruding ears. While an auricle that is too large is rare and should only be corrected after growth is complete, the protruding ear is a common malformation in the head area.
During otoplasty, the skin is first partially detached from the cartilaginous auricle, so that the underlying cartilage can be thinned or incised. Once the desired cartilage shape has been achieved, the result is fixed with the help of certain sutures and additionally supported by a head bandage for about three days.
After the treatment, a headband must be worn for a few weeks so that correct healing can take place.
The formation of hematomas (formation of bruises) and wound infections are possible but rare complications of this plastic surgery.
Further information can be found under our topic: Big ears
Rhinoplasty (nose surgery, rhinoplasty)
The outer shape of the nose is changed by enlarging, reducing or changing the shape of the bridge of the nose, turbinates or nasal entrance.
In addition to rhinoplasty as part of cosmetic surgery, this procedure can also be required to improve nasal breathing or facial deformities.
The cartilaginous and bony nasal skeleton and, in some cases, the nasal septum are corrected. First, the mucous membrane or skin must be detached from the structures before cartilage and bones can be modulated to the desired shape.
The operation is usually performed under general anesthesia, which is why a short stay in the clinic of 1-2 days is recommended.
Packing both nostrils stabilize the new shape of the nose after the operation.
Bleeding or secondary bleeding are possible complications of this procedure, and corrections may also be necessary. The final healing can take up to a year, during which there may still be small changes in shape.
Read more on this topic at: Rhinoplasty
Hair transplant (own hair transplantation)
During this operation, bald spots on the head or other parts of the body are filled with hair roots from the back of the head / neck area, so that hair grows again after about 3 months. First, the hair roots are exposed through a small incision in the nape of the neck before they are planted individually or in groups of 2-3 roots in the desired location in tubules. The removal point is sewn. It can take up to 3 months for the hair roots to regenerate at the new location and for subsequent hair growth. This operation takes 2-4 hours and is performed under local anesthesia. The risk of infection is reduced by giving antibiotics during the procedure. In addition, this plastic surgery involves few risks.
Further information on this topic can be found at: Hair transplant
Lip correction (lip plasty, cheiloplasty)
Lip plasty is used for cleft lip and palate, but is also often offered as a cosmetic operation, especially on the upper lip.
A distinction is made between pulling up the upper lip (lip lift), reducing and enlarging the lip.
To pull up the upper lip, an incision is made above the red lip and a narrow strip of skin is removed above the lip. Then the skin that has been loosened from the red lips is pulled up and fixed with thin threads.
Enlargement of the lip can be achieved through padding. Autologous fat, connective tissue, biological or plastic materials are used as material that is brought into the tissue through an incision or a syringe in order to increase the volume.
When reducing the size of the lip, an incision is made on the inside of the lip, where a piece of mucous membrane with underlying connective tissue is removed and the two edges of the wound are then closed.
Any cosmetic surgery on the lip carries the risk of visible scarring and deformation and a feeling of numbness. In addition, especially when the padding is used, infections can be carried over into the wound. These interventions are usually carried out on an outpatient basis and take up to an hour.
Read more on this topic at: Lip correction
Wrinkle treatment

Facelift
Facelifting (face lifting, face tightening) is intended to rejuvenate the appearance of the face by up to 12 years. For this purpose, a multi-layer surgical method is usually used to avoid changes in facial expression or facial expressions by simply tightening the skin layer. In addition to the skin itself, the deeper layers (muscles, connective and fatty tissue) are exposed and tightened.
In the cheek area, mainly The sunken cheek fat is raised and the muscles for lifting the mouth are tightened, in the neck area the neck muscles are tightened over a large area.
The face lift is often combined with the forehead lift, where the sunken eyebrows are raised again. The cut for this goes along the border between forehead and hair, either in front of or behind the auricle and ends in the hairy neck area, which should avoid noticeable scars.
The cosmetic surgery can be performed under general or local anesthesia as part of a hospital stay.
Risks such as secondary bleeding or nerve damage rarely occur.
Read more on this topic at: Facelift, face lift
Tummy tuck
As part of a tummy tuck, the skin of the upper abdomen is pulled down and excess tissue is removed. Then the navel is replanted before the skin flaps are sutured. A tummy tuck creates a visible scar that runs between the two iliac crests. This is a major operation with the risk of major blood loss, which is why the patient must be sufficiently healthy.
You will find more information on this topic here: Tummy tuck
Arm lift
The upper arm lift is often combined with liposuction (liposuction) on the upper arm to remove slack tissue. After liposuction, excess tissue is removed, whereby the size and shape of the scar varies greatly.
You will find more information on this topic here: Arm lift
Thigh lift
Tightening the thigh removes excess tissue; partly fat is also sucked off for this purpose. The size and shape of the scar are different and are adapted to the shape of the thigh.
Liposuction
This plastic surgery is mostly performed on the buttocks, abdomen or thighs.
First, liquid is injected into the surgical area in order to fill the subcutaneous fatty tissue. Then fatty tissue is sucked out through a cannula. The scar is only closed with a plaster and the remaining fluid and blood residues are drained away for a few days using a drain. In addition, a bodice must be worn in the appropriate place for some time to support the formation of scar tissue. The scarring causes the excess skin to shrink.
The procedure is very stressful for the cardiovascular system, which is why a short stay in the clinic should be planned after the plastic surgery. The complications are skin irregularities and abnormal sensations in the operating area, and there is also an increased risk of infection. The cosmetic result can only be finally assessed after 3-4 months.
Read more on this topic at: Liposuction
Breast surgery

Breast enlargement (breast augmentation)
In order to enlarge the breast, implants with a silicone sleeve are usually inserted, which are filled with saline solution or silicone gel.
To do this, an incision is made in the armpit, in the crease in the breast or in the area of the areola.
The implant can be placed either directly under the mammary gland or under the pectoral muscle.
This plastic surgery is performed under general anesthesia. A support bra must be worn for 6 weeks after the procedure.
In addition to the general surgical risks, capsular contracture can occur more frequently in the context of breast augmentation. This causes scar tissue to form around the silicone implant, which can lead to hardening, deformation and pain in the breast. This complication can still occur a few years after the operation, which may require another operation.
Read more on this topic at: Breast augmentation, breast implants
Breast reduction
Breast reduction can be performed both as a cosmetic operation and therapeutically. General anesthesia is required for the operation.
The cut depends on the breast; usually the incision goes along the areola and from there down to the breast fold. Glandular and adipose tissue and excess skin are removed before the nipple and areola are re-placed. In addition to the general risks, wound healing disorders (especially in the area of the nipple) and visible scars are particular complications of this method.
You will find more information on this topic here: Breast reduction
Breast lift (mastopexy)
A breast lift lifts sagging, sagging breasts and reshapes them. The nipples are reinserted higher, which looks more youthful.
Depending on the patient's wishes, the breast can also be made smaller or larger. However, if the pregnancy continues, the breast may sag again.
Read more on this topic at: Breast lift
Operations in the genital area
Labia reduction
With a labia minora reduction, the inner labia are shortened surgically or with the help of a laser treatment.
Further information on this topic can be found at: Shrink the labia
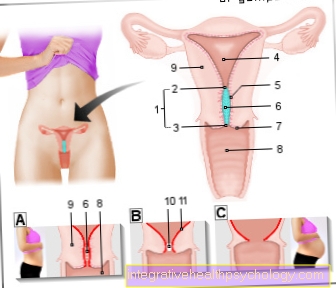
Hymen reconstruction
A hymen reconstruction is understood as the operative restoration of the hymen.
Read more on this topic at: Hymen reconstruction