Foamy diarrhea
What is frothy diarrhea?
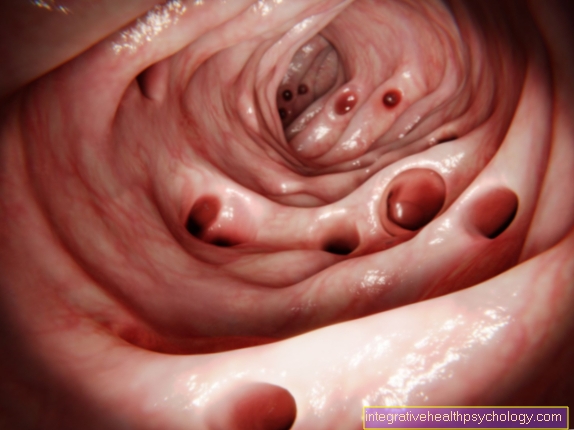
Foamy diarrhea is a sub-classification of diarrhea. The following changes in bowel movements are classified as diarrhea: One speaks of diarrhea if there are more than three bowel movements per day or the bowel movement has a water content of at least 75% or the weight of the bowel movement exceeds 250g. Foamy diarrhea usually occurs in connection with particularly thin stool. In addition to the usual soft to liquid consistency, there are foamy deposits on the stool. In addition, the color and smell of the stool may be changed in foamy diarrhea.

What are the causes of frothy diarrhea?
Foamy diarrhea occurs mainly with infectious changes in the gastrointestinal tract. The changes in the composition of the intestinal bacteria are usually responsible for changes in bowel movements. For example, a bacterial or viral infection of the digestive tract can lead to an imbalance in the intestinal bacteria. This can cause frothy diarrhea. In addition, symptoms such as stomach pain, nausea and vomiting can occur. Read more on the subject at: Gastrointestinal infection
Fungi and parasites can also change the intestinal flora and cause foamy diarrhea. In particular, the pathogens from the yeast species can cause foamy diarrhea through fermentation reactions in the digestive tract. Chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract can also be accompanied by foamy diarrhea. The reason for this can also lie in a changed composition of the bowel movements.
If the body can only process and absorb certain components of the food poorly, these components are excreted in larger quantities. If liquid stool occurs together with a high protein (protein) content, this can make the diarrhea frothy.
fermentation
Fermentation is a form of converting food components into energy that is often used by bacteria. By definition, no oxygen is required for this type of metabolism. Many bacteria in the intestine can use fermentation for digestion and energy production. Especially when pathogenic (disease-causing) bacteria get into the digestive tract, the proportion of digestion that takes place through fermentation increases. This often leads to a liquefaction of the stool, and foamy deposits can often also occur.
Can that be an indication of cancer?
Foamy diarrhea initially speaks for a change in the gastrointestinal tract. Diarrhea can result from a variety of causes, but foamy diarrhea occurs in most cases in connection with an altered intestinal flora (intestinal bacteria). In most cases, this change is due to an infectious cause. But other diseases can also affect bowel movements. These include, for example, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases such as ulcerative colitis, which can increase the risk of colon cancer. Foamy diarrhea, along with a variety of other symptoms, can therefore be an indication of cancer.
How is frothy diarrhea diagnosed?
In the case of foamy diarrhea, the diagnosis consists of a large number of individual steps. First of all, the person concerned should be interviewed (anamnesis) by the doctor. Many important clues as to a cause of the complaints can be found. Then the abdomen is listened to and palpated. Depending on the suspected cause, imaging procedures (initially ultrasound, possibly X-ray, MRI, CT) can then be performed. Laboratory tests of the blood and, if necessary, of the stool can also provide diagnostic information (for example, on inflammation, pathogens in the stool, etc.).
If the symptoms persist without a cause being found, invasive examinations such as a stomach or colonoscopy are carried out.
Which symptoms are pathological?
Foamy diarrhea does not necessarily have to have a pathological cause. For example, the stool can change temporarily due to certain foods, so that foamy diarrhea can occur even without a specific disease value.
Symptoms that indicate that the frothy diarrhea is pathological include persistent abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. The timing of frothy diarrhea is of particular importance. Complaints that only last for a few hours or one or two days and then go away on their own are generally of no disease value. However, if the symptoms appear over a longer period of time or repeatedly, one should think of a pathological cause of the foamy diarrhea.
Symptoms such as alternating constipation and diarrhea can also indicate that the diarrhea has pathological causes. If there are other changes in the stool, such as blood deposits, the foamy diarrhea can also be pathological. Read more about this at: Blood in the stool
Flatulence
Flatulence is a sign that a particularly large number of bacteria are active in the gastrointestinal tract. This can be both naturally occurring bacteria and special pathogens. The bacteria can produce gases when the food is digested, which is reflected in a bloated stomach and flatulence. In addition, with the help of gases and liquid, small bubbles can form in the stool, which can be noticeable as foamy deposits.
Read more on the subject at: Flatulence
stomach pain
Abdominal pain is a very common symptom, so it can indicate a variety of different medical conditions. It is not uncommon for abdominal pain to occur without a specific disease value. If, on the other hand, foamy diarrhea occurs in combination with the symptom of abdominal pain, a disease of the digestive tract can be assumed. The abdominal pain can become noticeable as discomforts occurring at certain points. Diffuse abdominal pain that cannot be assigned to a specific point on the abdomen should also not occur. The abdominal pain can become noticeable even before the stool changes.
Read more on the subject at: Abdominal pain and diarrhea
constipation
Constipation is an interesting phenomenon in combination with frothy diarrhea. Often the two symptoms alternate, so that constipation occurs for a few days, then diarrhea and then constipation again. This often speaks for a change in the intestinal bacteria, which have different effects on the bowel movement and thus alternately cause constipation and foamy diarrhea.
Anyone who suffers from chronic constipation (which is particularly common in children) can also suffer from what is known as "overflow diarrhea". This actually means that there is constipation, so that more and more stool accumulates. This means that only particularly liquid parts of the stool can pass the end of the intestine, resulting in small amounts of particularly liquid diarrhea.
Which frothy diarrhea needs treatment?
Foamy diarrhea, if it occurs for a short time and can be explained by a change in the menu, does not initially require treatment. But especially if the diarrhea lasts for a long time or if there are additional signs of illness, the need for treatment should be considered.
Diarrhea often leads to severe fluid loss, and children and the elderly are particularly at risk. Excessive dehydration should be treated. Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting can also be treated with medication if necessary. One should be clairaudient in the case of foamy diarrhea if the symptoms recur. This suggests a disease that the body cannot fully fight. Therapeutic measures often help to ensure complete healing. In addition, changes in the color of the diarrhea, which indicate blood in the stool, initially require clarification, and in many cases also require treatment. Signs of this can be a dark to black colored stool (evidence of digested blood) or light red blood deposits on the diarrhea.
Foamy diarrhea in the baby
Foamy diarrhea in the baby can, in many cases, be due to the baby's developing digestive tract.Babies typically have very soft to liquid stools, especially in the first few weeks or months of life. This is usually light yellow, often orange or greenish in color. It can also lead to foamy deposits. If changes in bowel movements occur at the same time as other symptoms such as fever, restlessness, increased crying and screaming, abdominal pain, reduced amount of fluids, etc., this can indicate an infection. Babies are sensitive to all kinds of infections, so the symptoms do not necessarily indicate an infection of the digestive tract. For example, an infection of the upper respiratory tract is also conceivable as the cause of the symptoms.
Read more on the subject at: Diarrhea in the baby
Foamy diarrhea in the child
Children are in different phases of physical development depending on their age. Small children in particular have frequent changes in their stool, which means that frothy diarrhea can also occur. Children are particularly vulnerable when their environment changes (new to kindergarten, school, transfer to secondary school, etc.). It is not uncommon for constipation in childhood to be the real cause of frothy diarrhea. If children also frequently complain of abdominal pain and malaise, food intolerance should also be considered.
Read more on the subject at: Diarrhea in toddlers
How long does frothy diarrhea last?
The duration of the foamy diarrhea depends on the cause of the symptoms. Usually symptoms occur that appear over a few days and then heal completely. Chronic bowel disease, on the other hand, can cause recurring symptoms because the body cannot permanently defeat the disease. Food intolerances also persist for longer (often for life). However, the symptoms can be completely avoided by avoiding the triggering foods.