Tibia, tibia
Synonyms
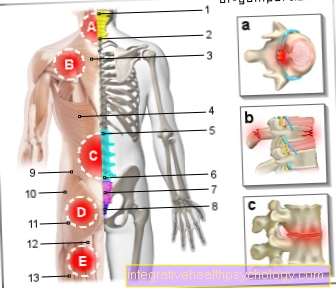
Tibia, tibial plateau, tibial tuberosity, medial malleolus (maleolus medialis), tibial head, tibial head
English: shin, tibia
anatomy
The Shinbone (tibia) forms with the Fibula the bony part of the lower leg.
The fibula is found on the outside of the lower leg, while the shin is on the Knee joint located in the middle (see also the X-ray images below)
The shin widens towards the knee joint Tibial head (= Tibial head). The tibial head has two small depressions on its upper side, in which the articular knots (= condyles) of the Thighbone (= Femur) are included.
A slight elevation of the bone can be felt on the front of the shin just below the knee joint. This bone elevation is medically called Tibial tuberosity designated. On the tibial tuberosity the Kneecap tendon (= Patellar tendon) at.
The shin shaft is triangular.
To the Ankle joint towards the end the tibia widens and forms the major part of the articular surface of the upper ankle and the medial malleolus.
Function of the tibia
But what is this bone used for anyway? Is the shin indispensable for the human physique? The apparent function of the tibia is to connect Thigh about the knee and foot about the Ankle joint. As the larger part of the two lower leg bones, the shin is an important one Support and support pillars of the leg axis without which we could neither stand nor walk. To a much greater extent than the second lower leg bone, that Fibula, gives the shin stability and at the same time serves as a firmer Anchor point for muscles that run along the lower leg and towards the foot.
Figure shin and knee joint
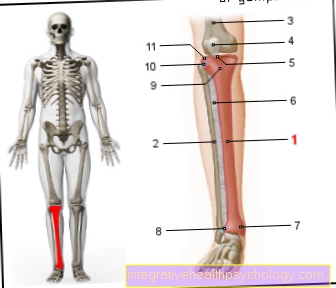
- Shin community -
Corpus tibiae - Calf community -
Corpus fibulae - Thigh shaft -
Corpus femoris - Kneecap -
patella - Inner articular knot -
Medial condyle - Interbone membrane
of the lower leg -
Membrana interossea cruris - Shin bones -
Medial malleolus - Shin and fibula tape adhesive -
Syndesmosis tibiofibularis - Tibial tuberosity -
Tibial tuberosity - Tibia-fibula joint -
Articulatio tibiofibularis - External articular knot -
Lateral condyle
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
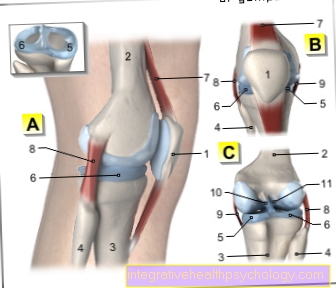
A - Right knee joint from the left
B - Right knee joint from the front
C - Right knee joint from behind
- Kneecap - patella
- Femur - Femur
- Shin - Tibia
- Fibula - Fibula
- Inner meniscus -
Medial meniscus - Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Kneecap ligament -
Patellar ligament - Outer band -
Ligament collaterale fibulare - Inner band -
Ligament collateral tibial - Posterior cruciate ligament -
Ligament cruciatum posterius - Anterior cruciate ligament -
Ligament cruciatum anterius
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Pain in the shin
Pain in the shin area can have a number of other causes in addition to the fatigue fracture described below and the shin splint syndrome, which occurs almost exclusively in runners and therefore only in exceptional cases as a cause of pain in non-runners. However, pain almost always goes in some way overload back. Pulled muscles are just as conceivable as a trigger as a Tendinitis or one Nerve irritation.
Also Malpositions of the feetthat should actually be corrected with the help of insoles can, after some time, radiate as pain to the shin. Correct, high-quality shoes and, if necessary, insoles are then essential. Nonetheless, in the event of pain - regardless of whether it is exertion-dependent and only during exercise or persistently - a doctor should be consulted, who can usually quickly differentiate between harmless and more serious injuries and irritations optimal therapy will recommend.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of and work as an orthopedist at Lumedis.
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me live every 6 weeks on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is not enough time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of all treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.
Diseases of the shin
The most common disease of the shin bone is osteoarthritis of the knee joint (= osteoarthritis of the knee, knee osteoarthritis).
The inner ankle fracture is also a common disease that is almost always combined with a fracture of the outer ankle (= fibular fracture; Weber fracture).
Another combination injury is the Volkmann injury or Volkmann Dreick. This breaks the rear edge of the shin at the upper ankle.
A tibial joint fracture (= tibial shaft fracture) is relatively rare, but like a tibial head fracture (= tibial head fracture) it must be reconstructed with precise axis, since fracture-related misalignments can lead to subsequent problems such as osteoarthritis.
A fracture of the tibia can often be seen in athletes. Usually there is a so-called fatigue fracture of the shin (stress fracture).
Inflammation in the area of the shin can also occur if there is inflammation of the tendons in this area. This is mostly the case due to excessive and incorrect loads.
Read more on the subject below: Tendinitis on the shin.
Fatigue fracture of the tibia
A fatigue fracture of the tibia, also called a so-called Stress fracture or pathological fracture known, joins prolonged overload of the shin - classically at Athleteswho are preparing for a big competition. Almost exclusively athletes who have very large training volumes are at risk (for example marathon runners) and are also highly motivated and ambitious.
Smaller ones Body's warning signals are often ignored and Regeneration phases sometimes shortened or left out entirely. So many add up over a longer period of time smallest injuries both in the bone structure itself and in the surrounding tissue. As a result, the shin can no longer be properly protected and stabilized and at the same time it is itself more susceptible to injuries.
Sooner or later it comes to fracture of the bone. Unlike a "normal“- so-called acute - bone fracture, the accompanying pain does not have to set in suddenly and with high intensity. A shin fatigue fracture can initially only make itself felt during training light pain to make noticable. Later come often Pain at rest in addition, which in the following often remain permanently noticeable.
The consequence of such a fatigue fracture is possibly a simple one Lower leg cast as one would use it for other bone fractures as well. As a rule, however, the Relief of the affected lower leg helpful. It remains the be-all and end-all in the further course of treatment.
In more complicated cases, splinting on its own is unfortunately sometimes not sufficient: If that is the case, a operative fixation the break is necessary. The corresponding operation is carried out in the same way as the operative treatment of an acute fracture of the tibia.
For more information, please also read our page: Fatigue fracture on the shin
Shin splints
Another disease of the shin that almost exclusively affects ambitious runners is that Shin splints, which deals with Pain and one Feeling of pressure expresses in the shin. At the beginning, the above complaints only occur during specific stress situations and quickly disappear again after the end of the training. Due to this very characteristic constellation, unfortunately, many sufferers do not go to the doctor immediately because they perceive their own complaints as strange but tolerable.
Gradually, however, the symptoms of the shin splints get worse, so that under certain circumstances Training sessions canceled Need to become. Typically, the affected athletes come to the point at some point where the pain and the uncomfortable feeling also occur in peace stay. This is often the moment when those affected see a doctor for the first time.
The problem with this temporal course is, however, obvious: ever later an affected person with the symptoms of "Shin splints“, As the tibial splint syndrome is also called in English, goes to medical treatment, the more longer the subsequent healing process can continue.
The cause of the pain with this type of overload reaction is the Irritation of the muscle attachment on the shin bone. If the muscle is overtrained, it becomes inflamed and irritated. The point of attachment that lies directly on the bone can then hurt like hell due to the extreme sensitivity of the periosteum to pain. An early visit to the doctor can help consistent sports break and the Relief of the affected structures.
The shin splints must heal completely. In this phase itself is supposedly "loose" To run absolutely taboo. Physiotherapy can aid the healing process as well Strengthening and stretching exercises. In order to avoid shin splints from the outset, it is important not to train too much, too fast or too ambitiously. Every body needs time to get used to stress and to build muscle. Conscientious Regeneration breaks are just as important as the actual training itself.
Please also read our page Shin splints.
Osgood Schlatter disease
According to the doctors Dr. Osgood and Dr. Disease named Schlatter belongs to the large group of the so-called aseptic osteochondrosis and only affects the shin. Aseptic osteochondrosis is understood as a Bone death, which is not due to an infection with pathogens but by a Blood deficiency supply of the corresponding area is triggered. Since simply too little blood arrives in certain areas of the shin, the bone structure is disturbed. Individual pieces of bone can even split off.
In addition, almost all those affected observe the development of a at a certain point on the shin just below the knee joint thickeningthat is very sensitive to touch and pressure.
The direct cause of Osgood Schlatter's disease cannot yet be conclusively explained. It is very likely that it was due to a mechanical overload of the tibia to that blood undersupply and thus to the disturbances of the bone metabolism. Interestingly, Schlatter is almost exclusively from Osgood's disease male children or adolescents aged 10 to 15 years affected. After the suspected diagnosis has been confirmed with the help of an X-ray in the worst case scenario, a absolute relief of the diseased shin is important. For the patient, this usually means no sport and, in severe cases, running with forearm crutches ("crutches“) For complete relief. As a rule, this conservative therapy is sufficient as a treatment measure and at the latest after the last growth spurt of puberty, the ghost is just as suddenly over as it appeared.
You can find more information on our website Osgood Schlatter disease.
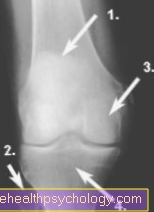
Right knee x-ray
(taken from the front):
- Femur (Femur)
- Fibular head of the fibula
- Inner joint roller (medial condyle)
- Shin (Tibia)
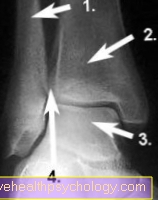
Right upper ankle x-ray
(taken from the front):
- Fibula (Fibula)
- Shin (Tibia)
- Ankle bone (Talus)
- Syndesmosis