Heel bone pain
definition
Heel pain is one of the foot complaints that occur frequently and can lead to a significant reduction in quality of life for those affected.
Heel spur, inflammation of the Achilles tendon, plantar warts or inflammation of the bursa mainly leads to pain in the heel bone.
In addition, excessive athletic stress, excessive body weight, unsuitable or unsuitable footwear or misalignment of the feet often play a role.
causes
Heel pain, which is also known in medical jargon as Tarsalgia can have very diverse causes.
It is important to distinguish between one, also for the diagnosis lower or plantar Heel pain and one upper or dorsal Heel pain.
The lower or plantar heel pain is localized under the heel, whereas the upper or dorsal heel pain represents pain at the insertion of the Achilles tendon. The various causes of heel pain are briefly discussed below.
This list includes the most important triggers for heel pain.
Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is an inflammatory disease of the Tendon plate the sole of the foot (Plantar aponeurosis), as well as the ending -itis in the term "Plantar fasciitis“Suggests.
Plantar fasciitis is the leading cause of heel pain. Plantar fasciitis is around 10% of the population, and women are generally more likely to experience it than men.
In addition, the frequency of this clinical picture also increases with the Age and the Body mass index (BMI) or the weight.
Standing or walking professions and runners, as well as people with foot anomalies, such as one Flat foot or different leg lengths are more likely to suffer from plantar fasciitis. In athletes, however, there is no association with the occurrence of plantar fasciitis and body weight.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
Athletes (joggers, soccer players, etc.) are particularly often affected by diseases of the foot. In some cases, the cause of the foot discomfort cannot be identified at first.
Therefore, the treatment of the foot (e.g. Achilles tendonitis, heel spurs, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of foot diseases.
The aim of every treatment is treatment without surgery with a complete recovery of performance.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Foot abnormalities
Congenital or acquired foot abnormalities, such as a Knuckle, flat or flat foot are also a cause of heel pain.
Even surplus bones (accessory bones) on the foot, like the so-called Os trigonum can be a cause of heel pain in some cases.
Atrophy of the heel fat pad
In medical jargon, atrophy is one Tissue shrinkage.
As you get older, this can also manifest itself on the heel, where the heel fat pad normally acts as a natural shock absorber.
You can also use injections cortisone lead to a shrinkage of the heel fat pad in this area.
Also anorexia (Anorexia nervosa) can cause the heel fat pad to shrink.
Over time, the bursa located below the heel bone becomes irritated and / or a heel spur develops in this area.
Heel spur
A so-called heel spur is one thorn-like bone growth on the calcaneus.
You can choose between the rarer upper (posterior, dorsal) and a lower (plantar) Differentiate heel spurs.
A lower heel spur, together with an inflammation of the tendon plate of the sole of the foot (Plantar fasciitis) occur.
Heel spurs are also quite common, although a heel spur does not necessarily have to cause discomfort.
A great way of depicting a calcaneal spur is one X-ray.
Haglund exostosis
Haglund's exostosis is a congenital one Shape variant of the heel cusps of the calcaneus, with the lateral and rear portions being particularly prominent. This different shape of the heel is called the Haglund heel according to the original description.
Bone cyst
Cysts are fluid-filled cavities that can occur in different areas of the human body, including in the bones, or especially in the heel bone.
It should be noted, however, that the calcaneus is a rather rare location for the appearance of a bone cyst.
These benign changes in the bone can mostly be seen in people under the age of twenty.
Often times, the bone cysts are under a Heel fracture diagnosed, whereby the fracture in these cases was mostly promoted by the existing bone cyst.
Bone tumors
Benign (benign) and malicious (malignant) Tumors (Tumors) develop. It should be noted that bone tumors on the heel bone are real rarity acts.
Fatigue fracture of the calcaneus
A fatigue fracture can occur when repetitive Overuse of the heel bone, for example in marathon runners or extensive marches.
A previously diseased bone promotes the occurrence of such fractures. An example to be mentioned is that osteoporosis, which by a decreased bone density is marked.
Calcaneal apophysitis
This clinical picture can especially occur in active children and adolescents in the growth phase (approximately eight to sixteen years of age), with girls usually falling ill earlier than boys. This leads to a softening of the apophysis of the calcaneus.
Apophyses are a peculiarity of the child's skeleton. These bone nuclei are located in the area of the growth plate (Epiphysis) and later mature into bony protrusions that serve as a starting point for muscles and ligaments.
Read more about the topic here: Calcaneal apophysitis
Changes in the Achilles tendon
Chronic inflammation of the Achilles tendon (Achilles tendinitis) is in most cases caused by constant exposure.
In addition, one naturally occurs with age Deterioration in tissue quality, that is, to a natural decline of tissue (degeneration).
Through the Tendinitis Tissue damage and partial tears of the Achilles tendons can gradually occur.
If the tendon is acutely overloaded, inflammation can also develop.
In extreme cases it comes to Tendon rupture, that means to tear the Achilles tendon. In the case of acute as well as chronic overstrain, stress with jumping, running and sprinting performance plays a role.
A complete rupture, so one Torn Achilles tendon, is the second most common location for tendon tears after tendon tears on the shoulder.
The Achilles tendon can tear in different sections, but most often this happens at mid-level of the tendon.
On the other hand, cracks occur less frequently in the upper and lower areas. In special cases, an avulsion breakout on the heel bone or tears at the junction between the muscle and tendon can occur.
The main reason for an Achilles tendon tear are sporting loads with high intensity. If the quality of the tissue is reduced, the Achilles tendon can tear under normal loads.
Finally, a kick or push against the tense Achilles tendon or Cortisone injections be responsible for a tear injury in the case of tendon problems.
Skin changes and other causes
Also changes in the skin, like Calluses or Warts can be seen as a cause of heel pain.
Calluses typically form on highly stressed areas of the skin, such as the heel. The occurrence of calluses is promoted by inadequate footwear, excess bones, foot anomalies and other causes.
Warts occur mainly in children and can also be seen on the soles of the feet. The cause of a wart is infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), this virus can get into the skin thanks to small cracks or injuries.
Heel pain can also be caused outside the musculoskeletal system and skin. For example, you can also Metabolic diseases, as the gout (Hyperuricemia) or one Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) cause foot or heel pain.
Symptoms

Plantar fasciitis
People with plantar fasciitis typically complain of pain that is most pronounced in the morning after getting up or after a long period of rest.
The symptoms usually improve after a short period of time, although they can return during the day after prolonged exposure. The symptoms can become so severe that they can even lead to the inability to walk.
Foot abnormalities
Foot anomalies, such as flat feet or a buckling and sagging combination, can be recognized by the shape deviation of the foot.
They too can be a cause of heel pain. In addition, they usually make themselves felt through other complaints, such as restrictions in mobility.
The os trigonum, an extra foot bone on the talus (Talus) tends to cause pain behind the outer ankle, but these complaints can also radiate into the heel and Achilles tendon.
Atrophy of the heel fat pad
The shrinkage of the heel fat pad causes heel pain, which is mainly located in the middle below the heel and occurs when walking.
Heel spur
Another common disease that causes heel pain is heel spur.
Affected people often feel as if there is a nail in the sole of their feet when they step on it. This means that the pain that occurs with a heel spur is usually stabbing or burning and has a particularly high intensity in the morning during the first steps after getting out of bed.
After a certain period of exposure, the pain intensity usually decreases again.
Experience has shown that the pain can also be triggered by pressure on the affected area. With the more common lower heel spur, pressure pain occurs on the sole of the foot below the heel.
In the case of an upper heel spur, the pressure on the insertion of the Achilles tendon in the upper back of the heel causes pain. The affected area may also show swelling and redness.
Haglund exostosis
The congenital Haglund exostosis does not necessarily lead to symptoms. These typically occur through external pressure, for example through the pressure of the shoes.
In addition, Haglund's exostosis can cause swelling at the attachment point of the Achilles tendon.
Reddening of the skin or inflammation of the bursa can also add to the heel pain.
Bone cyst
The fluid-filled cavity in the heel bone can be asymptomatic.
However, when exercising, there may be discomfort. Occasionally a swelling can develop. A bone cyst promotes the occurrence of a fracture.
Bone tumors
The symptoms of a bone tumor depend on the respective shape. The benign osteoid osteomas typically cause severe pain at night, but they respond extremely well to painkillers such as acetylsalicylic acid, or ASA for short.
A tumor in the bone also promotes the occurrence of a break.
Fatigue fracture of the calcaneus
Indications of a fatigue fracture of the heel usually result from questioning the patient (anamnese), in which known bone diseases and sporting activities should be taken into account. In addition, heel pain gradually develops, which increases in intensity with exercise. Swelling of the heel area can also be observed.
Calcaneal apophysitis
Calcaneal apophysitis can be seen as the most common cause of heel pain in the growth phase.
This pain usually worsens with exertion. A limp after straining the heel bone can also be observed. The heel region may also be sensitive to external pressure and show reddening and swelling.
Pathological changes in the Achilles tendon
Acute inflammation of the Achilles tendon leads to sharp pain, especially when exerted, as well as swelling in the area of the tendon.
Chronic changes in the Achilles tendons tend to cause discomfort with the first steps in the morning, which then decrease with further stress.
Only overuse or rest lead to a renewed increase in the intensity of the pain.
The Achilles tendon can be painful on pressure at certain points and also have thickening.
Fine tears of the tendon are usually asymptomatic, whereas patients with a complete tear of the Achilles tendon (Achilles tendon rupture) report severe pain.
Achilles tendon rupture (Achilles tendon rupture)
Most of the time, those affected report a whip-crack-like noise that occurred during the trauma. There is also a palpable gap in fresh cracks, most often a few centimeters above the tendon attachment on the heel bone.
The affected area will be bloodshot and swollen after a while. Walking on tiptoe is difficult or no longer possible for patients with a torn Achilles tendon.
Skin changes
Calluses, which are actually a protective barrier, can also be a reason for heel pain. A wart can either be superficial (so-called mosaic warts) or in depth.
Especially the deep-penetrating plantar warts can cause heel pain when walking.
Heel pain when stepping on
Heel pain when it occurs can have various causes. First of all, a distinction must be made whether the pain is superficial or deep.
In the case of superficial pain, the cause is usually in the skin. For example, shoes that are too tight and incorrectly cut can cause skin irritation, blisters and pressure points. The complaints can be on the outside and inside of the heel bone as well as behind or below.
Do you have blisters on your feet? - Then find out here what works best against it: Blisters on the foot
Pain that comes from deeper body layers usually has other structural causes. For example, insufficiently padded shoes can cause irritation below the heel bone. There are tendon attachments that can become inflamed. In addition, there are several bursae on the heel bone that can become infected.
Do you suspect you have bursitis on your heel? - Then read our article: Bursitis on the heel
Could a tendinitis be behind your symptoms? - Then you might be interested in the following articles:
- Tendonitis on the sole of the foot
- Inflammation of the heel
In the case of traumatic events, heel pain can also be triggered by sprains or fractures. What all these diseases have in common is that they usually hardly cause any complaints when you are at rest. Only when it occurs does pressure and strain come on the structures, which makes the pain noticeable.The symptoms can also be caused by bony changes such as a heel spur.
Pain under the calcaneus
Pain under the calcaneus is usually caused by excessive strain while walking. Traumatic injuries such as fractures rarely occur when, for example, one lands on one's feet from a great height.
Pain due to overuse is mostly of an inflammatory nature. Increased stress repeatedly causes irritation of the tendons that attach below the heel bone. The plantar tendon, for example, is often affected.
Would you like to know more about inflammation of the plantar tendon? - Then read our related article: Inflammation of the plantar tendon
The irritation leads to small inflammatory reactions, which can be felt in the form of pain. In the long run, the irritated tendons can become calcified, which can lead to the formation of a heel spur.
Pain in the back of the calcaneusIf there is pain in the back of the heel bone, you should first check the shoes to see whether they are too hard in the back heel area. This can cause blisters on the surface, but also irritate deeper structures in the long term.
Do you have blisters on your feet? - Then read our article about Blisters on the foot
In addition, the Achilles tendon attaches to the rear calcaneus. If this is stressed, for example, when jogging or due to a misaligned foot, it can lead to pain, especially in the area where it is attached. An irritation of the bursa lying under the Achilles tendon can also be the cause of the pain in the posterior heel bone.
Do you have problems with the Achilles tendon? - Read the following articles:
- Achilles tendon pain
- Achilles tendon inflammation - treatment and duration
Pain in the inner calcaneus
The tendons that are responsible for the flexion of the toes run on the inner calcaneus. Overloading can lead to inflammatory or degenerative changes, which are noticeable in pain.
The inner ligaments of the ankle also extend into the area of the heel bone. If the ligament is twisted, it can cause overstretching, tears and tears in the ligaments, which, in addition to pain, also causes severe swelling.
You can find more detailed information on this in the following articles:
- Ligament stretch at the ankle
- Torn ligament at the ankle
Pain in the outer calcaneus
In the area of the outer calcaneus, there are mostly muscles that are used to abduce the foot, that is, to spread the foot outwards. These are guided along the ankle in a long tendon sheath.
Excessive stress, especially in athletes, can lead to inflammation or even sticking of the tendons in the tendon sheaths. If there is pain in the outer heel bone, the shoes should also be checked to see how much external pressure they put on the heel bone.
Pain in the heel bone after getting up / after resting
Heel bone pain that occurs at rest or immediately after getting up tends to argue against a degenerative cause of the symptoms.
So one should rather assume an acute inflammation of a bursa or a tendon, for example. These complaints also usually get worse with exertion, but in acute phases they can cause pain even at rest.
This is usually accompanied by swelling, reddening and overheating of the area. Rheumatic diseases can also make themselves felt on the heel bone. Bechterew's disease, for example, leads to a stiffening of the joints, which is most pronounced in the morning.
If there is a reduced blood flow due to vascular disease and thus a poorer supply of the calcaneus, small defects can arise in the bone. Over time, these expand so that they weaken the bony structure. This can also lead to pain in the heel bone.
In the case of pain after getting up or at rest, it is not uncommon for disorders of the nerve fibers to be the cause of the complaints. This causes damage to the nerves so that they incorrectly transmit pain signals to the brain.
diagnosis
At the beginning of the approach to the possible diagnosis there is always a detailed survey of the medical history by questioning the patient (anamnese).
This should be followed by a physical examination of the person concerned, with the examiner especially the posture, the anatomy and the Course of the body axes Pay attention.
In addition, the Joint mobility, the Muscle strength, the Reflexes, Further Nerve functions and the Gait pattern to be examined.
There are a few simple but expressive movement tests for the function of the Achilles tendon.
Depending on which diagnosis the examining doctor comes up with, he will initiate further special examinations.
The survey of certain ones should be mentioned here Blood work, as well as imaging procedures, such as X-rays or Ultrasound examinations.
Furthermore, in the case of special questions, or before a planned operation, a Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or one Computed tomography (CT) come into question.
A nuclear medicine examination method (Scintigraphy) can sometimes be useful.
The gait pattern can be achieved with the help of a Pedography can be examined more closely.
This is a scientifically recognized method for representing forces that act on the foot while standing and moving.
The measurements are taken while standing (that is static), as well as when walking or running (that means dynamic) performed.
With the help of a video analysis, incorrect loads on the body axes can also be revealed.
Last but not least, a Jointoscopy (Arthroscopy, if the Achilles tendon is reflected, also tendoscopy) help with the diagnosis as well as with the therapy itself.
therapy
The therapeutic approach to heel pain depends on the specific diagnosis and ranges from simple conservative Activities (that means not operational) to various Operations.
Plantar fasciitis
Are suitable for plantar fasciitis Stretching exercises the thigh and calf muscles as well as the soles of the feet, which should be learned at the beginning with professional support.
Also Cold and heat applications and anti-inflammatory or analgesic drugs can be used for heel pain caused by plantar fasciitis.
Intense sporting loads should be avoided in the period of acute irritation. In addition, a Silicone cushion, which is incorporated into an insert, can help by cushioning the heel.
In the conservative therapy of plantar fasciitis, however, patience is required, as this over one to two years can drag.
Surgical therapy can only be considered in exceptional cases.
Foot abnormalities
Corrective insoles, shoe adjustments and foot gymnastics can be used for foot anomalies.
Again, surgery may be required as a therapeutic approach.
This can be considered if the symptoms do not improve with the measures just listed, if there is an excess foot bone or in children with a restricted range of motion.
Atrophy of the heel fat pad
If the heel fat pad shrinks, which causes heel pain, a anti-inflammatory and pain reliever ointment be used.
Soft heel pads can also provide relief for those affected.
Heel spur
Heel spur, a common cause of heel pain, is mainly treated conservatively.
Conservative treatment includes an arsenal of options physical therapylike the local Heat or cold application, as well as setting Sound stimuli.
In addition, the training should be adapted, or the Load reduced and physiotherapy exercises are performed.
Another important component of the therapy are insoles and special shoe adjustments, which reduce the local overload is decreased.
In most cases, conservative therapies for heel spurs can achieve resounding success.
Haglund exostosis
In the case of a heel with a protrusion, i.e. a Haglund exostosis, heel pads with a perforated insert come into question. Specific Shoe adjustments represent a possibility. Physical Protection should be kept for some time.
Furthermore also create anti-inflammatory drugs and cooling measures remedy, as this can reduce the inflammation and reduce the swelling of the tissue.
Physical therapy exercises are also advisable to help with this Calf muscles to stretch.
Also treatment methods of physical therapy, such as a Shock wave treatment can be tested.
However, the therapy costs for shock wave treatment are not borne by health insurance companies.
If there is no improvement in the symptoms within months due to the conservative measures, the protrusion of the bone can also be achieved in the course of a surgery removed.
Of the inflamed bursae is either removed with (so-called bursectomy) or it is preserved and can also recover after damage after removal of the excess bone.
After the operation has been completed, the foot must be carefully accustomed to the strain again with the help of functional treatment. Also orthopedic footwear and physiotherapy are used postoperatively.
Bone cyst
A variety of approaches exist to deal with a bone cyst.
The treatment decision should take into account the potential risk of a broken bone.
If there is an increased risk of a bone fracture, it may be necessary to stabilize the bone with the help of surgical intervention.
Bone tumors
In the presence of a bone tumor, the shape of the tumor is decisive, as there are various therapy concepts for this.
Fatigue fracture of the calcaneus
Compared to purely injury-related fractures, surgical measures are rarely used for fatigue fractures of the heel bone.
A fatigue fracture is an extended one Exercise break inevitable.
The symptoms can be reduced with pain reliever medication. In the case of fatigue fractures of the heel bone, more conservative measures, such as physical therapy or physiotherapy, play a role.
Calcaneal apophysitis
This disease, which occurs in childhood, is also treated conservatively.
The therapeutic concept here includes one Reduction in physical activity for a limited period of about four to six weeks and relief measures, such as shoe heel elevations or heel padding.
Treatment with a anti-inflammatory ointment be soothing. If there is no improvement in the symptoms, a temporary Plaster immobilization become necessary for four to six weeks.
When the growth phase is over, the symptoms usually disappear completely.
Pathological changes in the Achilles tendon
In the acute situation one is recommended several weeks of rest.
Also therapeutic measures from the spectrum of physical therapy, such as the Electrotherapy or cold and heat applications Experience has shown that they are considered beneficial.
In addition, a soft footbed for the heel, a slight heel raised and / or an anti-inflammatory ointment contribute to the reduction of complaints.
Light stretching exercises under professional guidance are also advisable.
Chronic complaints in the Achilles tendon can be improved with physiotherapy and orthopedic aids for the foot.
In the case of extensive damage, usually only one can operational Approach to remedy the situation. Inflamed tendon tissue is removed during an operation and, if necessary, replaced with a piece of the body's own tendon. Postoperatively, the load is increased in small steps up to the normal load.
Achilles tendon tear
A torn Achilles tendon can also be treated conservatively or surgically.
The therapeutic approach to an Achilles tendon rupture also depends on how close the two tendon ends that have diverged are to each other.
The distance between the two tendon ends is measured using Ultrasonic certainly.
If there is good contact between the tendon ends, an Achilles tendon tear can also be treated without surgery.
A so-called "conservative-functional“Therapy that involves the foot with one solid association is immobilized.
After a short phase of pure immobilization, the functional treatment begins, in which the injured limb is first passively and then actively moved under professional supervision.
There are various options for an operation. There is, for example, the possibility of seam possibly also with additional Bonding or the body's own Tendon graft.
An operation is recommended for competitive athletes who need to be ready for action again quickly.
Skin changes
At Callusesthat cause heel pain can be a medical foot care be helpful.
Warts can regress on their own after a while.
In addition, various preparations for self-treatment, such as Icing over or Soften of the area can be purchased in the pharmacy.
In most cases, repeated application is necessary.
If the wart does not work or if the appearance of the wart has changed, a doctor should be consulted to make sure that it is really a wart.
It may be necessary to obtain a tissue sample for this.
The doctor also has a large repertoire in the treatment of warts, such as the curettage with scalpel or sharp spoon in local anesthesia.
Under no circumstances should you touch warts yourself, as they are infectious and the device or fingernail used can lead to a new wart in another location.
Home remedies
Home remedies that help with heel pain usually aim to cool the affected area in the acute pain phase. Conventional ice packs can be used for this. Cabbage and quark wraps are also well suited to relieve pain by cooling.
Anyone who also has a warm, reddened and / or swollen heel can also use anti-inflammatory agents such as apple cider vinegar. Such compresses contain the inflammation and at the same time cool the affected area.
People who suffer from heel spurs often benefit from relief of the heel, for example through a special sole. Since conventional products often do not work well enough, it may be necessary to lend a hand and cut an additional hole in the insole with small scissors.
Hekla lava
Hekla lava is a homeopathic product that is used in particular for pain due to a heel spur. Hekla lava is extracted from the Hekla volcano in Iceland.
The substance is mainly used for bone and dental diseases and can alleviate both bone-degrading diseases (bone necrosis) and bone-building diseases (heel spur). Pure Hekla lava therapy is not suitable for most diseases, but its use on heel spurs has been tried and tested.
For more information about treating calcaneal spurs with home remedies, see: Home Remedies For Heel Spurs - Which Are The Best?
forecast
The prognosis of heel pain naturally depends on the underlying cause. With careful treatment, however, the result is in most cases promising.
prophylaxis
Problems with the feet can definitely be prevented.
Always beneficial are one Standard weight and a balanced metabolism.
This protects both feet and joints.
Foot care, suitable footwear with breathing textiles and the regular change of shoes and stockings are also good requirements.
In addition, walking barefoot outside of sports halls, swimming pools and saunas is ideal, provided that there are no injuries or illnesses such as Diabetes mellitus or Vascular disease to speak up against.
If calluses are present, they should be removed regularly with a suitable file and then cared for with a cream.
Diabetics should by no means lend a hand, but rather seek professional foot care.
anatomy
The heel bone, which is also known as the calcaneus in Latin, is the largest and longest bone of the Tarsus and must withstand great loads.
The body of the Heel bone Roughly speaking, it has the shape of a cuboid and extends from the rear end of the foot to the front and top to the outside of the foot.
The actual heel of the foot (Calx) is, however, replaced by the Heel hump (Calcaneal tuberosity) located at the rear of the foot.
This is also where the Achilles tendon (Tendo calcanei), which is the strongest tendon in the human body.
It is the common end tendon of the three-headed Calf muscle (Triceps surae muscle) and is therefore a connection between the calf muscles and the heel.
The three-headed calf muscle is made up of the two-headed calf muscle (Gastrocnemius muscle) and the clod muscle (Soleus muscle) together.
There is a bursa between the heel hump and the Achilles tendon (Bursa tendinis calcanei). Two processes originate from the underside of the heel hump, the Processus medialis tuberis calcanei and the Processus lateralis tuberis calcanei.
The clinical picture of Heel spur often starts from one of these processes. Also starting from the heel hump is a connective tissue tendon plate, the so-called sole plate (Plantar aponeurosis) that pulls forward to the ball of the foot.
Due to its fan-shaped arrangement, it stabilizes the arch of the foot together with muscles, ligaments and tendons.
Figure pain ankle
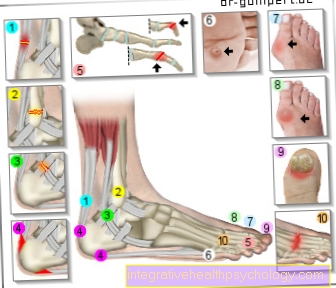
Foot pain
- Achilles tendonitis /
Achilles tendon rupture - Broken bones - toes,
Metatarsus, tarsus
(here outer ankle fracture) - Ligament stretch / torn ligament
at the ankle - Lower and upper heel spurs
Calcaneus spur - Hammer toe and claw toe
(Deformities of the toe bones)
Digitus malleus - Plantar warts
Verrucae plantares - Hallux valgus -
(Deviation of the big toe
in the base joint) - Hallux rigidus -
(Joint wear of the
Metatarsophalangeal joint) - Inflamed nails / nail fungus
- Osteoarthritis / arthritis -
degenerative change of
Joints / inflammation of the joints
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations











.jpg)