Pain in the navel
introduction
Come for pain in the navel area various causes into consideration. Besides mostly harmless causes, like growing pains or psychological causes, but can also be a Umbilical hernia or one Appendicitis stand behind the pain.
causes
Navel pain can have many different causes.
In general, gastrointestinal complaints can manifest themselves in the area of the belly button.
This includes, for example, an inflammation of the stomach lining or an incorrect / one-sided diet.
In this case, alcohol and nicotine should definitely be avoided, as both are considered to be convulsive.
Other causes can be a pinched nerve in the area of the navel or increased stress. Inflammation with a navel piercing can also be responsible. In women, gynecological causes can also be considered.
In rare cases, the pain can also be due to a chronic disease such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, or chronic inflammation of the pancreas (Pancreatitis). If the pain persists over a long period of time and cannot be overcome with simple home remedies, a doctor should be consulted for diagnostic clarification. If the pain is accompanied by red spots on the navel, other causes may also be possible.
Read more about this under Red spots on the navel.
Causes of pain above the belly button
Pain above the belly button can have different causes.
From an anatomical point of view, there are different structures above the navel that can cause pain. On the one hand, there can be a gap in the abdominal wall above the navel, through which the bowels can bulge outwards. This clinical picture is known medically as a hernia.
The epigastric region is also located above the navel. An inflammation of the lining of the stomach or a stomach ulcer can cause pain in this area.
The pancreas can also cause upper abdominal pain in the case of inflammation. In the case of inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), these are typically described as belt-shaped and thus pull around the upper abdomen on both sides towards the back.
Last but not least, symptoms of the liver, gall bladder and spleen can cause pain above the navel. Therefore, if the complaints persist, a medical clarification is advisable, as this is the only way to rule out serious causes of the pain.
Causes of pain below the belly button
Various clinical pictures can be responsible for pain under the navel. Often the causes are harmless in nature and the pain goes away on its own within a very short time. However, there can also be serious causes behind the pain.
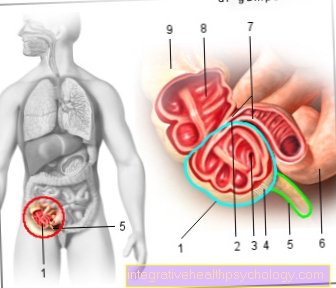
In the area below the navel there are various organs that can cause pain. On the one hand, changes in the intestinal area can be the cause, for example colon inflammation (colitis), appendicitis or masses in the intestinal area such as intestinal tumors.
In women, pain below the navel is often caused by diseases within the internal genital organs. Uterine infections, uterine tumors, ovarian infections or tumors, and ectopic pregnancies can be the cause.
If the pain is located well below the belly button, it can also be a bladder infection. In addition, there is typically a burning sensation when urinating and tenderness over the bladder.
Since there are many different clinical pictures that can explain pain under the navel, a doctor is recommended if the pain persists and / or is very severe.
Read more on the topic: Lower abdominal pain- what are the causes?
Causes of pain to the right or left of the belly button
Pain to the right or left of the belly button can have different causes.
Often the reasons for this lie in the intestinal area. Gas formation in the intestine can temporarily lead to abdominal pain, which will subside when the air is released. A minor injury to the abdominal muscle can also cause pain. However, there can also be other causes behind it. Pain to the left of the belly button may indicate an inflammatory disease of the colon.
In the elderly, sigmoid diverticulitis is a typical clinical picture. In the process, small protuberances form in the intestinal wall in which stool is deposited. This can lead to inflammation of these protuberances, which then manifests itself as left-sided abdominal pain.
However, chronic inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis can also cause such abdominal pain. However, there are usually other symptoms such as severe diarrhea as well as mucus and blood leakage.
On the right side of the navel, the most typical clinical picture that could explain the symptoms is appendicitis (appendicitis). Often the symptoms begin with pain in the upper abdomen / navel area and then shift over time to the right lower abdomen. A strong pressure pain at this point is typical for the disease.
Appendicitis must be treated by a doctor, otherwise there is a risk of serious complications. Persistent complaints should therefore be taken as a reason to see a doctor.
Inflammation of the belly button as a cause of pain in the belly button
An infection of the belly button can be very painful. Small injuries in the area of the belly button can cause germs to penetrate the skin and cause an infection with an inflammatory reaction. This is often visible through reddened, overheated and possibly swollen skin in the navel area. It can also lead to weeping wound surfaces. There is also pain.
Good hygienic wound care of the navel is essential to contain the inflammation. Antibiotic treatment may be necessary. In many cases, however, it is sufficient to disinfect the wound area and clean the navel. Sterile bandages are applied and must be changed regularly. In this way, the umbilical inflammation can heal well in most cases.
Early pregnancy as a cause of navel pain
In addition to childhood, pregnancy is also a typical phase in which pain in the navel area can occur.
This pain occurs mainly in the first trimester of pregnancy and is a sign that the child and, accordingly, the pregnant woman's belly is growing.
As the child grows, the abdominal wall is stretched further and further and with the abdominal wall also the navel. As part of this growth, the depression of the belly button often disappears and the navel emerges.
This type of pain is harmless pain that is normal during pregnancy, but not necessarily experienced by every pregnant woman.
However, if at the same time as the pain there is a bulge in the area of the navel, which is not the navel itself, this indicates an umbilical hernia, for which there is an increased risk during pregnancy, as the abdominal wall is weakened by the stretch (you can find more information on this below on this page).
Pain in the navel when urinating
If there is severe pulling pain in the area of the belly button when urinating, it may be a bladder infection.
In this case, a doctor should definitely be consulted for clarification, who will arrange for a urine test for further diagnosis.
In the case of a bladder infection, the pain gets worse, especially towards the end of urination. Often, those affected have to urinate much more often than normal, with only a small amount of urine secretion occurring in each case.
Women in particular are often affected by cystitis because their urethra is shorter and pathogens can enter the bladder more easily.
Read more on the subject at: Cystitis
Pain in the navel when defecating
Pain in the belly button when defecating may indicate an umbilical hernia. In the case of an umbilical hernia, there is a gap in the abdominal wall through which - in the case of smaller hernias - fatty and connective tissue, - in the case of larger hernias - loops of the intestine bulge.
These so-called hernial sacs are usually visible or palpable as protrusions in the area of the navel. The hernial sacs bulge, especially when the pressure in the abdomen increases. This is the case with coughing, sneezing, laughing, but also with bowel movements, as the pressure in the abdomen is increased by pressing. Therefore, the pain can occur especially in these situations.
In this case, a medical examination is advisable, as the hernial port may have to be closed surgically to avoid complications. In the worst case, the intestine may otherwise become trapped with subsequent intestinal obstruction or the trapped intestinal area may die.
Pain in the belly button from a piercing
Belly button pain can be caused by a navel piercing.When piercing, a ring or metal pin is passed through the skin on the navel to be left there as a piece of jewelry. The piercing itself can be painful due to the sensitivity of the skin. But even after the sting, the piercing can cause pain for a long time until the wound surface has healed sufficiently.
Inadequate disinfection and poor care of the navel piercing can lead to inflammation of the piercing in the navel, which can be very painful. Sometimes the piercing has to be removed. Getting caught on the piercing can also tear the skin or, in the worst case, tear the piercing out completely. Such larger injuries may have to be treated medically or even sewn to prevent infections and unsightly scarring.
Read more on the topic: My belly button is inflamed - what can I do?
Umbilical hernia as a cause of pain in the navel
Also an umbilical hernia (Umbilical hernia) can cause pain in the belly button. An umbilical hernia is a protrusion of the intestine through a weak point in the abdominal wall in the area of the navel.
This hole in the abdominal wall can either be congenital or, for example, caused by a weak connective tissue.
Read more on the topic: Umbilical hernia
The so-called hernial sac, which bulges out, is surrounded by peritoneum and contains intestines and fatty tissue.
In addition to the pain, which can but do not have to occur in the context of an umbilical hernia, a small to larger protrusion of the skin that can be seen from the outside is characteristic, so that the diagnosis is relatively easy to make.
Usually there is no pain at rest, but if there is an increased pressure load in the abdomen, stinging symptoms can occur in the navel area. This can occur, for example, in connection with strong pressure during bowel movements.
Read more on the topic: Symptoms of an umbilical hernia
However, if the pain is stronger and the protruding hernia becomes reddish to brownish discoloration at the same time, an emergency doctor should be consulted, as the hernial sac may become trapped.
In technical terms, one speaks of a so-called incarceration of the umbilical hernia. This can sometimes be accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting and constipation.
As a result of the entrapment, the intestinal tissue can no longer be supplied with blood containing oxygen and nutrients, so that the tissue threatens to die.
As the disease progresses, blood poisoning or even more dangerous peritonitis can occur.
Causes of pain in the belly button in children
Children in particular can experience pain in the navel area as they grow. This pain occurs mainly between the ages of three and five years.
Sometimes the pain is so strong that the children scream and hunch over in a relieving position.
These pains come about because the child's stomach grows in different directions: in width, in length, and forwards.
This results in a stretching of the scar tissue of the navel, which can be painful. The growth-related navel pains in children are often linked to food intake.
The pain often occurs about half an hour after a meal, as the abdomen spreads particularly strongly forwards during this period.
The pain correlates with the amount of food you eat: the more you eat, the stronger the pain.
If the children move around a lot after eating, the symptoms improve or stay away completely, because in this case the food that has been thickened is better distributed.
Another cause can be a so-called umbilical colic in the child.
This usually occurs between the ages of four and twelve years. Girls are more likely to be affected.
The characteristic of colic is that the pain occurs at intervals, i.e. a phase of severe pain is followed by a painless phase.
Even if umbilical colic manifests itself with severe pain, so that the parents are often very worried, the colic is not based on an organic disease.
The cause is psychological, triggered for example by stressful situations such as exams or general excessive demands. T
If you had nausea and / or vomiting accompanying the navel pain, you should definitely consult a pediatrician for clarification.
A common disease in children and adolescents is also one Appendicitis. In this case, the pain is only in the initial phase in the area of the navel, while it is then in the further course of the diseaseafter a few hours migrate to the right lower abdomen. Typical of appendicitis are very severe painso that the child is a curved posture occupies. That is also characteristic Defense tension and Sensitivity to touch of the abdomen in the child. Even light touches, such as caressing, can lead to severe pain, and reactively to a hardening of the abdomen. In addition to the pain symptoms, you can still Accompanying complaints, how Fever, diarrhea, nausea, inheritance, increased sweat production and an increased pulse occur. These complaints do not necessarily have to be present. If you notice these symptoms, the child should definitely directly to the pediatrician or to the hospital to be brought. In the event of appendicitis, the child's appendix is usually removed prophylactically to prevent possible complications.
Furthermore, a Inflammation of the belly button as a cause. This is expressed by a reddened, swollen and overheated umbilical skin. Sometimes it can also be a festering wound come, which is accompanied by an unpleasant odor. A Inflammation of the belly button in the baby mostly occurs when the belly button is after birth not properly maintained / cleaned but can also be traumatic. Belly button inflammation usually occurs during the first week of life, but an infection can also develop years later Inflammation of the belly button in the child come.
An incarceration is one life threatening emergency, which must be operated on immediately. According to the underlying cause of an umbilical hernia, the name "umbilical hernia" is a bit misleading.
Since in Period after birth The tissue of the abdominal wall is not yet fully developed, it often occurs immediately after birth to a Umbilical hernia in the infant.
Premature babies are more often affected than "punctual" babies.
Around 1/5 of all babies have an umbilical hernia after birth.
But umbilical hernia can not only occur in newborns, but also in adults who have increased pressure in the abdomen. This is the case with, for example obese people, at heavy sports loads, the Lifting heavy objects, strong cough and one existing pregnancy.
Another cause can be a congenital connective tissue weakness which makes it easier for a hernia to develop.
In most cases, an umbilical hernia in infants resolves on its own after one to two years as the abdominal muscles become increasingly stronger. At Adult An umbilical hernia does not resolve on its own and even if there are no accompanying symptoms Umbilical hernia surgically relocatedto prevent further complications such as fracture entrapment.
Concomitant symptoms
Pain in the belly button can be accompanied by different symptoms, depending on the cause of the discomfort.
Umbilical inflammation can be associated with reddening, swelling and overheating of the region as well as oozing wound surfaces.
In the case of an umbilical hernia, you will usually see a bulge in the area of the navel, as this is where the intestines bulge through a weak point in the abdominal wall. In some cases this hernia is only visible when the pressure in the abdomen increases - for example when coughing or pressing.
Pain in the umbilical area can also occur with appendicitis. Accompanying symptoms can then be, for example, fever, nausea and stool irregularities. Further symptoms should give rise to a medical examination in order to rule out serious causes for the symptoms.
Drawing pain in the navel
If the pain on the belly button is tugging and rather dull, certain, special causes may be considered.
Read more on the subject at: Pulling in the navel - what can it be?
diagnosis
Pain in the belly button can easily be diagnosed if the patient describes the typical symptoms to the doctor.
A physical examination is then carried out to clarify the cause, during which the doctor carefully inspects the umbilical region. If there are no obvious signs of inflammation or the like, the doctor will also palpate the navel and check it for pain and other abnormalities.
A diagnosis can usually be made quickly in this way.
therapy

It is about growth-related pain in the child, it is helpful to the child especially after eating to let romp around or to animate it to move. This can also be done preventively in susceptible children.
General helps with Pain in the abdomen, the Application of heat, for example in the form of grain pillows or hot water bottles, as well as a light one Abdominal massage. Abdominal massage has a double effect on children in particular.
Duration
The duration of pain in the belly button area depends largely on the underlying cause.
With adequate therapeutic treatment, pain can usually be quickly brought under control. Umbilical inflammation should subside within a few days of initiating therapy.
However, an umbilical hernia must be treated surgically. After such an operation, the surgical treatment will leave the area painful for a few days. However, freedom from pain can usually be achieved within a few weeks.
The same applies to appendicitis, which must be treated surgically. Functional complaints in the area of the navel, for which there is no specific cause that requires treatment, usually resolve themselves within a short time.
forecast
The prognosis for pain in the belly button is good, as it often does not conceal any causes that require treatment.
Even if there are more serious causes behind the complaints, such as an umbilical hernia or an umbilical inflammation, the prognosis is still very good, as these causes can usually be treated medically.
In general, the prognosis of the pain depends on the cause, but can be assessed as very positive overall.
On the one hand, the gentle movements calm the intestines, on the other hand, the children feel secure through the care, which can also improve the symptoms.
For the massage, slightly warmed oil (fennel or chamomile oil are particularly suitable) can be used, which is spread gently clockwise, whereby the drawn circles should become larger and larger.
Is there a Umbilical colic the parents should ensure that the child is at home in a quiet, stress free atmosphere growing up and that there is not too much pressure on the child or that too much is being asked of the child.
In addition to heat and massage applications, they are also suitable for harmless navel pain natural remedies, such as Flaxseed wrap.
For this, a cup of flaxseed is boiled in a pot and the finished seeds are wrapped in a kitchen towel and the wrap is then placed on the belly button for about two hours until the flaxseed has become cold.
In addition to the calming flaxseed, other herbs such as chamomile, Caraway seed or fennelwhich can be used as a tea or as a local tincture.
Can pain in the belly button be a sign of pregnancy?
Abdominal pain is not uncommon in early pregnancy. However, specific pain in the belly button is not a typical sign of pregnancy, as it can have many different causes.
Umbilical pain typically only occurs later in pregnancy, when the growing child is putting increasing pressure on the mother's abdominal wall. The stretching and strain on the abdominal wall can then lead to pulling pains in the navel area and bulging of the belly button.
Theoretically, belly button pain is therefore conceivable as a sign of pregnancy, but in no way to be regarded as specific. Pregnancy tests should be done to be sure.
Is belly button pain dangerous during pregnancy?
Pain in the belly button during pregnancy is usually not dangerous. Most women experience these symptoms at times during pregnancy. The growing child increasingly exerts pressure on the abdominal wall. This leads to the belly button protruding over time. This is normal and not a cause for concern. Due to the unusual strain, the navel can also hurt to a greater or lesser extent.
However, the pressure can also lead to an umbilical hernia. Tissue emerges through a gap in the abdominal wall and becomes visible and / or palpable as a protrusion. In the case of small fractures, only a little fat and connective tissue protrudes; larger fractures can lead to loops of intestine penetrating. Larger fractures usually require treatment, as there is a risk of entrapment of intestinal loops, which could result in death. Since this is a threatening complication, the gap in the abdominal wall must be surgically closed in such a case. This can usually be done without any problems during pregnancy. Small fractures often do not require any therapy and can be remedied naturally after pregnancy by training the abdominal muscles.
In most cases, however, the pregnant woman does not have to worry about umbilical pain. However, in the event of persistent and severe complaints, a medical clarification is advisable.
What can be done about pain in the belly button during pregnancy?
There is usually not much that can be done about pain in the belly button during pregnancy. The pain is mostly caused by the pressure of the growing baby on the abdominal wall. When the abdominal wall has adapted to the new load and has stretched, the pain usually subsides again.
Sometimes the symptoms can be relieved by gently massaging the abdominal wall or applying heat. It is important, however, that an umbilical hernia is excluded as the underlying cause. In the case of a larger fracture, which has already led to the passage of parts of the intestine, surgical treatment is often necessary to prevent complications. In the case of small breaks, you can usually wait. A medical examination is therefore definitely recommended in order to be able to initiate any necessary therapy for the symptoms.











.jpg)