Esophageal pain
Synonyms
- Esophageal pain
- Esophageal cancer
- Reflux heartburn
- throat
- Esophageal cancer
Medical: Esophagus
English: Esophagaus, esophagus
introduction
The causes of pain in and on the esophagus depend on the respective clinical picture. Below are a number of causes of the esophagus that cause pain.

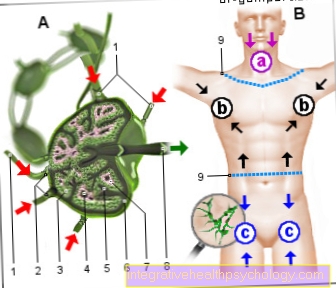
Illustration pain and anatomy of the esophagus

Pain in the esophagus
- Esophagus -
Esophagus - Mucous membrane -
Tunica mucosa - Diaphragm -
Diaphragm - Stomach entrance -
Ostium cardiacum - Gastric juice (stomach acid)
- Stomach body -
Corpus gastricum
Causal diseases:
A - Reflux disease
(Heartburn) -
Backflow of gastric juice
B - achalasia -
Sphincter of the esophagus
not at the transition to the stomach
fully open
C - esophageal cancer
(Esophageal carcinoma) -
Sequelae of reflux disease
D - esophageal diverticulum -
pathological protuberances
the esophageal wall
E - esophagitis
(Esophagitis) - mostly through
Causes reflux disease
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations

- esophagus
(Neck section) -
Esophagus, pars cervicalis - Nasal cavity - Cavitas nasi
- Oral cavity - Cavitas oris
- Windpipe (approx. 20 cm) - Trachea
- esophagus
(Chest section) -
Esophagus, pars thoracica - esophagus
(Abdominal section) -
Esophagus, pars abdominalis - Stomach entrance -
Cardia - Stomach body -
Corpus gastricum - Throat -
Pharynx - Thyroid -
Glandula thyroidea
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Causes and other symptoms

It can be one of the causes of esophageal pain Variety of causes give. In order to draw conclusions about the underlying disease, it is therefore all the more important to find more Symptoms to pay attention.
The most common diseases include:
- Reflux disease (Synonym: reflux esophagitis, heartburn)
- Achalasia
- Tumors of the esophagus (Esophageal carcinoma)
- Esophageal diverticulum
- Narrowing of the esophagus
- Esophagitis
diagnosis
The most important section in diagnosing esophageal pain is the detailed one Doctor-patient conversation (anamnese). During this conversation it should be clarified when the pain in the esophagus mainly occurs and whether there is a connection to it Ingestion gives. In addition, the doctor asks the patient about other symptoms such as fever, Difficulty swallowing, sensation of a foreign body, secretion of blood and general complaints. Regular use of Medicines should be disclosed at this time.
This is followed by a physical examination for example the size and displacement of the thyroid is checked (enlargement of the thyroid tissue can also lead to pain in the esophagus and difficulty swallowing). If the findings are unclear, imaging procedures can then be initiated.
The diagnosis of pain in the esophagus applies reflection of esophagus and stomach an important role. During this procedure, changes in the mucous membranes can be detected and, if necessary, tissue samples can be taken.
In addition, a so-called pH-metry should be carried out. This way it is possible Concentration of stomach acid Measure around the esophagus.
The mobility of the esophagus and the density of the lower sphincter can be determined by manometry. If the presence of one is suspected Achalasia with pain should be a X-ray of the esophagus be effective.
therapy
Therapy for pain in the esophagus is directed according to the underlying disease. In the case of reflux esophagitis, the gastric acid concentration and thus its ascent into the esophagus must be reduced. For this purpose, so-called Acid blockers (Proton pump inhibitors) used. Usually the affected patient needs these medicines lifelong take in.
In addition, a operative correction of the lower esophageal sphincter. Patients with diverticulum-induced esophageal pain can only do one surgical removal of the wall protuberances help in the long term. The aim of treating achalasia is to dilate the lower esophageal sphincter. This can be done through local injections or surgical dilation.
forecast
The forecast of esophageal pain depends on the causal disease. Either Reflux disease, as well as Achalasia can be treated well. Patients who malicious changes those suffering from esophagus have a rather poor prognosis.
Causal diseases
Reflux disease and esophagitis
Under the term "reflux disease" (synonyms: reflux esophagitis, heartburn, gastroesophageal reflux disease) is understood in medical jargon as a disease in which it becomes a pathologically increased reflux of acidic gastric juice gets into the esophagus. Since the Mucous membranes the esophagus have a completely different structure than the gastric mucosa, it is not very resistant to the acidic properties of the gastric fluid. As a result, it can become too over time Development of inflammatory processes come in the esophagus. There is also the possibility that the mucous membrane cells accept structural changes due to the permanent irritation. In most cases, gastroesophageal reflux disease is caused by a dysfunction of the lower sphincter of the esophagus. In addition, they were important Risk factorsthat promote the development of reflux disease. The main risk factors are:
- fatty foods (e.g. chocolate)
- hot spices
- peppermint
- alcohol
- coffee
- nicotine
- Obesity
- various drugs (e.g. aspirin).
The symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease are quite clear in most cases. Typically, the affected patients feel the pain in the esophagus just behind the sternum. The esophageal pain felt by the patient usually decreases after larger mealsincreases in intensity when bending and lying down.
Achalasia
In the Achalasia it is a disease in which the lower esophageal sphincter is at the junction with the stomach not fully open can be. In most cases, the mobility is also the Esophageal muscles (Motility) highly limited. Reasons for the occurrence of this condition can be malignant changes in the esophageal tissue be. In addition, it is now assumed that different forms of achalasia by Autoimmune processes can be triggered. Also the emergence through viral pathogens (mainly by: Varicella zoster virus, Measles virus and human papillomavirus) is possible.
Typical symptoms of achalasia are pronounced pain of the esophagusthat mainly as Pain behind the sternum and in the middle upper abdomen be perceived. In addition to the pain, many of the affected patients report of difficulties swallowing (Dysphagia). As food intake due to the severe pain and pronounced Impairment of the swallowing process is significantly reduced by most patients in the early stages of the disease, they suffer from one significant weight loss and one Malnutrition. This problem occurs especially in children who suffer from achalasia with pain in the esophagus and difficulty swallowing.
Esophageal diverticulum
Even patients who are under Esophageal diverticula sufferers develop severe pain in the esophagus. In contrast to achalasia, however, the localization of this pain is in most cases upper to middle section the esophagus. An esophageal diverticulum is pathological protuberances the esophageal wall. In principle, diverticula can develop anywhere in the esophagus. Nevertheless, most patients show such a wall protuberance in the area of the upper and / or middle esophagus.
Reasons for the development of an esophageal diverticulum with severe pain can, for example Changes in cell architecture and a increased pressure be inside the esophagus. While smaller diverticula are perfect in most cases asymptomatic remain, so the affected patient does not feel any pain, large wall protuberances show through quite early pronounced symptoms. At the beginning, the affected patients usually do not complain of pain, but do complain pronounced foreign body sensation. In addition, it can already occur at the onset of the disease difficulties swallowing come. Pronounced esophageal diverticula cause severe pain in the esophagus, especially in the course of the disease in the neck and behind the sternum be perceived. Since food deposits often form in the area of the wall sacs while eating, most of those affected suffer from one before the first pain occurs bad smelling halitosis (Foeter ex ore).
Narrowing of the esophagus
A narrowing of the esophagus causes the esophagus to narrow, usually in the lower area. As a result, the food can no longer be transported to the stomach as usual.
The narrowing can have various causes, such as heartburn or inflammation of the esophagus.
Esophageal diverticulum
As an esophageal diverticulum (Esophageal diverticulum) refers to pain caused by sagging of the esophageal wall, of which two different forms can be distinguished: real divertricula (Traction diverticulum) and false diverticula (Pulsation or pseudodivertricle), depending on which wall layers are affected. The most common form is 70% of the Zenker's diverticulum. This is what is known as a pulsation diverticulum.
Further information can be found under our topic: Esophageal diverticulum
Esophagitis (inflammation of the gullet)
Most esophagitis and the resulting pain in the esophagus are caused by the Reflux disease caused. Otherwise there are mechanically iriitative, thermal, chemical infectious ones (e.g .: the yeast Candida albicans) Causes. The pain in swallowing is the main symptom of these diseases.
Esophageal cancer (esophageal cancer)
Of the Esophageal cancer arises almost entirely from one Beret - esophagus and can therefore also be a secondary disease of Reflux disease are designated. Of the Esophageal cancer metastasizes early and causes no or only unspecific complaints for a long time. Because it is recognized late as a result, the survival prognosis for patients with this tumor disease is usually poor.
Further information can be found under our topic:
- Esophageal cancer
- Therapy esophageal cancer
Esophageal pain - what to do?

Many patients who suffer from long-lasting or constantly recurring pain in the esophagus often ask themselves what can be done against this problem.
In principle, it should be noted in this context that prolonged or frequent pain the esophagus of the urgent medical evaluation and the Initiate appropriate treatment need.
If the pain in the esophagus appears for the first time, there are some tips and assistance that can help against the symptoms.
Is it the pain in the esophagus? classic heartburn, should be the first analyzed own diet become. Frequent consumption of sweets or fatty foods and excessive consumption of alcohol can cause stomach acid to rise up into the esophagus and cause pain. For this reason, affected patients can already relieve the symptoms through a targeted change of the menu alleviate.
Patients for whom this measure does not lead to the desired success either wonder what exactly helps against the pain in the esophagus.
In some cases they show up simple home remedies extremely effective in treating harmless esophageal pain. Of the regular consumption of chamomile tea helps, for example, to calm the stomach and that Curb acid production. As a result, less stomach acid can rise and the pain in the esophagus decreases. The helps in a similar way Enjoyment of fennel tea relieve pain in the esophagus. Another home remedy that helps with this problem is ginger. Ginger juice can be bought in the form of ready-made preparations or obtained from a ripe tuber. If you soak the tuber in mineral water for a few hours or add the ready-made juice directly to some tea, the distortion can help to inhibit gastric acid production. Other home remedies that can help relieve harmless pain in the esophagus include:
Caraway seed
linseed
Mallow blossom
Marshmallow root
Healing earth
- Base mixtures of potassium, sodium and calcium
When does the pain occur?
Esophageal pain - after radiation
The irradiation is a Cornerstone in the treatment of malignant tumors. You irradiate the affected area with harmful rays from the outside and direct the rays as well as possible towards the cancer. The Cell DNA damaged so the cells perish and the cancer shrinks.
At Cancers of the throat irradiation can also be used. In particular, these are possible Carcinoma of the esophagus or thyroid gland. Especially parts of the The mucous membrane of the esophagus is affected by the radiation. The mucous membrane can largely recover from this, but the long-term consequences of the damage can be serious. The Esophagitis by irradiation is one common side effect. It occurs a few weeks after the first exposure. The typical symptoms are Chest pain with difficulty swallowing and a foreign body sensation in the esophagus.
Pain in the esophagus - when drinking
If a patient feels pain in the area of the esophagus while drinking, this can also have various causes. In this context, the question arises whether it is at Drinking hot or cold beverages the emergence of the complaints or whether just that Drink acidic liquids (for example: lemonade, cola or fruit juice) leads to pain.
Possible causes for the development of pain in the area of the esophagus, which occur when drinking or are aggravated by the fluid intake Lesions of the esophageal mucosa. In this case, burning pain occurs, especially when drinking acidic drinks.
Esophageal pain - alcohol

Regular consumption of alcohol represents one Risk factor for a variety of diseases In addition to the damage in the area of the Cardiovascular system and the liver can cause excessive consumption of alcohol also cause lasting damage to the esophagus. Both smoking and excessive consumption of alcohol represent the most important risk factor for the development of the so-called "Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus“ (Esophageal cancerAbove all, the simultaneous consumption of nicotine and alcohol increases the risk many times over. Furthermore Alcohol has been shown to increase gastric acid production. This in turn can lead to persistent and / or frequently recurring reflux (heartburn; stomach acid rising up the esophagus). In both cases, the affected patients feel severe pain in the area of the esophagus, which typically increases in intensity during and after the consumption of alcohol. This phenomenon is due to one by the Alcohol induced irritation of the esophageal mucosa return.
Pain in the esophagus - when eating
Pain in the esophagus that especially when eating occur, can be a key symptom of various diseases.
The actual cause that leads to the occurrence of pain when eating (rather during the swallowing process) in all relevant diseases Movement disorders of the esophageal muscles or mechanical obstacles.
The most common mechanical obstacle that leads to the development of pain in the esophagus, especially when eating, is the so-called Esophageal diverticulum. This symptom is the presence small bulges which block the esophagus.
When eating, the still relatively firm chyme has to pass these bulges and causes severe pain due to the tightness. In addition, membranes, constrictions caused by scar tissue or foreign bodies can obstruct the esophagus and cause pain, especially when eating.
Furthermore can inflammatory processes inside the esophagus or Ulcers / tumors cause pain when eating. Due to the close anatomical relationship to the esophagus, Thyroid ulcers from external pressure cause esophageal pain especially when eating or drinking.
Also one Reflux disease or heartburn can cause esophageal pain after eating.
Pain in the esophagus - when swallowing
If there is pain in the esophagus during the swallowing process, acid-related esophagitis cannot be assumed. The exact time of the pain and any accompanying symptoms are important for making a diagnosis. It is coming in addition to the pain behind the sternum to a Choking the food or too frequent swallowing, one speaks of a "dysphagia". This is the Inability to swallowOften found when the muscles of the esophagus are tight or are constipated from eating too much.
A common problem that doesn't have to be an indication of an illness is an acute stabbing one Pain after swallowing of a big bite. There is a brief obstruction of the esophagus with severe pain and eventually the food is choked up. If the esophagus is permanently narrowed, such a pain occurs when swallowing even with normal food intake. The cause can be medication, infections, diverticula but also malignant changes in the esophagus. The mobility and the swallowing process of the esophagus are severely impaired. A narrowing of the esophagus with subsequent pain when swallowing can also be a long-term consequence of reflux disease. The inflammation is so advanced that scarring changes in the wall of the esophagus cause the pain.
You might also be interested in the following topic: Pain when swallowing
Esophagus of pain - after vomiting

The mucous membrane lining the esophagus is compared to the gastric mucosa very sensitive to chemical stimuli concerns. The permanent rise of stomach acid (for example, due to chronic reflux) can cause lasting damage to the esophageal mucosa.
There is also one during vomiting direct contact between esophageal mucosa and gastric acid. This irritates the esophagus and can cause pain.
This is mainly done after prolonged and pathological vomiting (e.g. Bulimia nervosa) to a extensive damage to the esophagus. In most cases, the affected patients develop persistent pain in the area of the esophagus which increases significantly in intensity after vomiting.
Also read our topic: Larynx pain after vomiting
Pain in the esophagus - when coughing
A cough does not only occur with infections and inflammations of the airways. In rare cases it can Cough that accompanies reflux disease be. A cough that persists for a long time and is only suspect with burning pain behind the sternum occurs without accompanying infectious disease.
The cause of this cough is a simple one Nerve irritation. The affected nerves are located at the junction of the esophagus and the stomach and are irritated by acid reflux. In addition to inflammation of the lining of the lower esophagus, the nerves can trigger a cough through the brain. In addition to coughing, there are also hoarseness, sore throats and increased mucus formation. What sounds like a typical infection is, however, a symptom of the esophagus.
At severe acid reflux the esophagus can cause it to Belching of gastric juice and porridge come out of the stomach. If the person concerned is lying there, the gastric juice that has been pushed up can get into the larynx and incorrectly flow into the lungs. Severe cough is the acute consequence. About pathogens can thereby Inflammation of the lungs and airways arise. Bronchitis via this route is not uncommon.
You might also be interested in this topic: Larynx pain when coughing
Pain in the esophagus radiating to the back
Some cause esophageal diseases Pain that radiates into the back. The most common diseases that cause back pain are Cracks and perforations in the esophagus. Although the esophagus is a fairly stable muscle tube, you can Changes in the wall structure or traumatic events affect their stability.
There are generally tears and ruptures in the esophagus that can cause pain in the sternum and down the back rather seldom.
A typical reason that can lead to a rupture of the esophagus is that A foreign object gets stuck.
You can also therapeutic feeding tubes which persist in the lumen of the esophagus for too long a period lead to its breakthrough with pain in the sternum that radiates into the back. In these cases one speaks of a so-called "Perforation of the esophagus“ (Rupture of the esophagus).
If a patient's esophagus is previously damaged, it can be done while a endoscopic examination (for example a Gastroscopy) injure the muscle tube.
A tear or rupture of the esophagus can in most cases appear entirely classic symptoms detect. If there is a tear in the upper area, affected patients notice sudden onset of pain in the area of Neck or des Neck.
It can also be significant Skin reactions and Swelling (Cutaneous emphysema). This is especially seen when the upper esophagus has been damaged. The swelling is caused by air leaking out of the esophagus and spreading through the tissues.
Patients who have an oesophageal perforation lower section of the muscle tube suffer classically over complain severe pain in the chest and back. If no prompt treatment is initiated, the esophageal rupture can lead to pain in the back inflammatory processes in the chest area to lead. In these cases one speaks of a so-called "Mediastinitis" with high fever and pronounced symptoms of shock goes hand in hand (palpitations, tremors, sweats).
Treatment of the esophageal perforation with back pain (i.e. a deep perforation) should be Within 24 hours by a reconstructive operation respectively.
Esophageal pain in pregnancy
A large proportion of all pregnant women struggle with esophageal pain during pregnancy. In addition to the already existing physical weakness during pregnancy, the pain appears to be particularly bothersome. All typical causes of esophageal pain are possible in pregnant women, but this is acid-related reflux disease in pregnancy especially likely.
The acid-related irritation and inflammation of the esophagus is caused by a Interplay of hormonal and physical changes in the woman's body. In pregnant women, an always arises as the pregnancy progresses increasing mechanical pressure on the abdominal organs. As the child grows, the uterus presses against some organs and thus also against the stomach and sometimes also causes gastric juice to flow back into the esophagus.
In particular, however, hormonal changes during pregnancy have an impact on reflux disease. In addition to some hormones, the hormone is also used "Progesterone" released in large quantities in pregnant women. It causes smooth muscles to relax in many places in the body. This also applies to the sphincter muscle at the transition from the esophagus to the stomach, which cannot be influenced arbitrarily. The contents of the stomach can more easily get into the esophagus and the stomach acid can trigger an inflammation of the mucous membranes. In addition, due to the hormonal changes, the entire digestion proceeds more slowly and therefore food residues remain in the stomach for a long time after eating. The longer the chyme is in the stomach, the higher the likelihood of acid reflux.
Typical symptom of reflux is the same here burning pain behind the sternumwhich typically occurs a few minutes after drinking or eating. In pregnant women is mainly due to the Diet as a therapeutic measure to pay attention. It is important to avoid typical risk factors such as nicotine, alcohol and caffeine, but also fatty or large meals. Protein-rich food is particularly recommended. For reasons of gravity, you should refrain from lying too straight or lying down after eating. Raising the head at night is gentler on the esophagus.
From drug treatments should be avoided during pregnancy if possible. Some drugs that interfere with gastric acid production or digestion are not without a doubt harmless to the unborn child. On the other hand, agents that bind gastric acid can be used without hesitation. In the case of reflux disease, therapy should always be started early, before severe inflammation develops with possible irreparable damage. After pregnancy, the symptoms usually subside.
Pain in the esophagus and windpipe
A rarer symptom of esophageal pain is a additional pain in the windpipe. Especially with severe reflux disease the windpipe may be affected by backflow of stomach contents. It is also strongly irritated by the highly concentrated acid in the stomach. It can too Coughing attacks and hoarsenessand pain in the larynx and neck. Not infrequently can Inflammation of the airways or the lungs occur this way.
This is an important procedure for a known reflux disease Change of position in bed. Affected people should have a raised headboard or pillows to lift the chest overnight so that gravity does not cause backflow of the stomach contents.
Summary

As part of the digestive tract, the esophagus (lat. Esophagus) the Oral cavity with the Stomach entrance.
The annular esophagus begins at the level of the Larynx and runs from there between windpipe (Trachea) and Spine in the Rib cage.
In humans, the esophagus is usually approximately in length 25 centimeters. At rest, the lower end of the esophagus is so tightly closed that the acid gastric fluid cannot normally rise.During the act of swallowing, the food is produced by continuous, ring-shaped muscle contractions (peristalsis) and the lower esophageal sphincter opened reflexively.
This fact can be proven experimentally. Would the ingested food be pure by the action of gravity in the stomach it would be impossible to drink fluids while standing on the head. However, due to the peristaltic transport, this is possible without any problems.
Due to the anatomical structure and the direct connection to the stomach, Esophageal pain have a variety of causes. In many cases, pain in the esophagus can be caused by harmless Diseases to be triggered. A wrong one nutritionHowever, the consumption of tobacco products and / or the frequent use of medicines can also seriously affect the lining of the esophagus and lead to pain.
In general, if you have frequent complaints, you should consult a specialist immediately before, during or after eating. If therapy is initiated early, the prognosis of the most common diseases that lead to pain in the esophagus can be significantly improved.