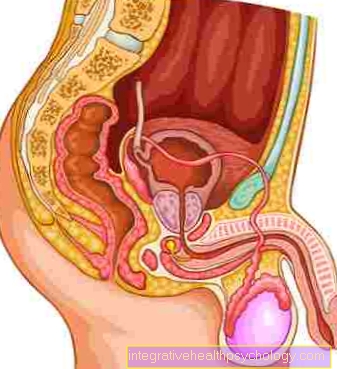
Pain in the testicle
Definition
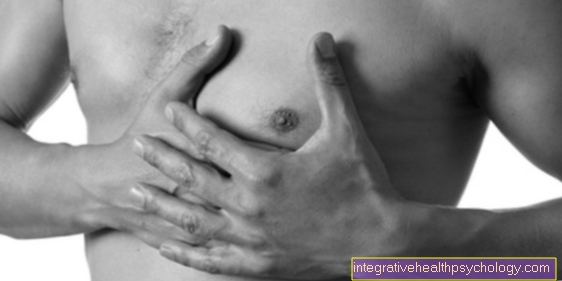
Pain at the Testicles are first of all a very general symptom which can have various causes. Initially, the pain can have different characters.
They can appear as a drag in the testicle pressure or Sting in the testicle respectively Scrotum (scrotum) noticeable and in doing so up to the Groin region radiate. Doing so can reduce the pain in their Duration, intensity and Strength vary and turn out very differently depending on your own feelings. However, one cannot draw conclusions about the severity or type of the disease or the cause from the severity of the pain.
Also read: Pulling in the testicle - what can it be?
Cause of pain in the testicles
The causes of testicular pain can be very diverse and range from traumatic experiences (i.e. accidents or injuries) to diseases of the urogenital tract or the testicle itself
Testicular pain after accidents
One of the most common causes of painful testicles is previous accidents. This resulted in a direct injury like one bruise, Prospecting or bruise of the testicle. In the context of this injury, a "Annihilation pain“Spoken, an acute pain of the highest pain level. It can even lead to a "Testicular dislocation“Come, so one Relocation of the testicle out of the scrotum in the groin or perineum area. For clarification, the course of the accident should be reconstructed and the testicles examined. In addition, a Ultrasound of the testicle to be carried out around Fluid in the testicle to prove or a bruise (Hematoma) in the scrotum to identify.
- therapy
The forms of therapy differ depending on the extent of the injury. At minor injuries should the testicle something elevated such as chilled become. To relieve the pain you can Pain medication be taken. Did the accident result in a bruise (Hematoma) of the testicle or one Testicular torsionso this represents an indication to a operative therapy If there is a bruise, the testicle is relieved. As part of a Testicular torsion becomes the testicle relocated back and reattached. It came to one complete bruising and Destruction of the testicular tissue, removal of the testicle may be indicated (Orchiectomy).
Testicular pain with inflammation

An inflammation of the testicles (orchitis) can be caused by various pathogens, most of which have caused a general infection, in the course of which the testicles are also inflamed. Examples are the mumps viruses (mumps orchitis), but testicular inflammation can also occur with mononucleosis (Ebstein-Barr virus), a Coxsackie virus infection, varicella and others. A previous trauma can also result in inflammation. Antibodies against sperm and testicular tissue can also cause inflammation of the testicular tissue.
Read more about this in our main article: What are the causes of testicular inflammation?
- Symptoms
Symptoms of orchitis are sudden onset of pain, which mainly radiates into the groin and back. In addition, the testicles swell up and are very red (reddening of the scrotal skin) and the fever may rise. In the special case of mumps orchitis, the first inflammation of the parotid gland (salivary gland) and a somewhat delayed (3-4 days) inflammation of the testicles, which occurs in 10% on both sides.
- diagnosis
The diagnosis is made through a detailed medical history and urological examination. In addition, an ultrasound of the testicle can be done to rule out a possible abscess. An increased number of leukocytes (so-called leukocytosis, an increase in white blood cells) can be found in the blood and, in the case of mumps orchitis, antibodies against the mumps virus.
- therapy
Bed rest and pain relievers are recommended as therapy. In adults with mumps orchititis, alpha interferons and glucocorticoids can also be administered to combat inflammation and the immune response. If abscesses occurred as part of the inflammation, they can be surgically opened and emptied.
- complication
Complication can be a decrease in sperm quality. Inflammatory destruction of the testicular tissue in particular leads to atrophy (tissue shrinkage) and fibrosis (scarring) of the testicles and in this process, if both testicles are affected, sterility, i.e. infertility. Since this is one of the dangers of mumps orchitis, vaccination against the mumps virus in combination with measles and rubella (MMR) is recommended as a prophylaxis for children. This is administered once at the age of 12-15 months and a second time at the end of the second year of life.
Testicular pain with epididymitis
Inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis) can also cause pain in the testicles.
Most epididymitis comes from ascending infections from the prostate, the vas deferens (see also: Inflammation of the vas deferens) or the urethra. Various bacteria can be pathogenic (chlamydia, gonococci, E.coli, staphylococci). More rarely, the trigger is a spreading infection via the bloodstream or a traumatic experience. A build-up of urine back into the vas deferens to the epididymis can also trigger epididymitis.
- Symptoms
The symptoms are acute severe pain in the scrotal sac, the scrotum. The epididymis swells considerably and the entire scrotal skin is reddened. The pain can also radiate into the groin region and the lower abdomen. There may also be signs of a urinary tract infection and fever.
Read more on this topic at: I recognize epididymitis by these symptoms
- diagnosis
As with orchitis, the diagnosis is made based on the medical history and a urological examination. It is important to ensure that the epididymis can swell so that it can no longer be distinguished from the testicle. The so-called Prehn symbol is considered a pioneering symbol. Here the testicle is raised by the examiner. If the pain decreases, this indicates an inflammation of the epididymis. If the pain persists or if it gets worse, this is considered a differential diagnosis of testicular torsion. Ultrasound can also be performed to reveal possible abscesses. There are more leukocytes in the blood, which indicate the inflammation (leukocytosis).
- therapy
Antibiotics (e.g. Levofloxacin, Tavanic or Ofloxacin) are prescribed as therapy for bacterial epididymitis. Anti-inflammatory drugs can also be taken to reduce inflammation. The testicles should be raised a little and bed rest should be observed.
Testicular pain with testicular torsion
In the case of testicular torsion, the testicle is extremely flexible within its enveloping structures (tunica vaginalis testis) and can thus rotate around the spermatic cord. The venous pampiniformis plexus is compressed and the blood backlog and thus a hemorrhagic testicular infarction can occur.
Testicular torsion is an event that primarily affects children. This occurs predominantly in infants or adolescents between the ages of 15 and 20.
- Symptoms
The main symptom of testicular torsion is the acute onset and very beginning pain in the testicles, which radiate into the groin region and the abdomen. In addition, swelling (edema) and reddening of the testicles can occur. Furthermore, accompanying symptoms can also occur. Such would be nausea and vomiting or possibly shock symptoms.
- diagnosis
To make the diagnosis certain, anamnesis and urological examination are carried out first. In the Brunzel sign, there is a one-sided undescended testicle, as the spermatic cord shortens somewhat due to the rotation. The testicle is also extremely sensitive to pressure and the cremaster reflex is canceled.
Read more on the topic: Cryptorchidism
The Prehn's sign is negative to delimit an inflammatory reaction of the testicle. This means that in comparison with testicular torsion, the pain in the testicles remains the same or may even increase when the testicle is lifted (in the case of epididymis, the pain disappears when the testicle is lifted). In addition, an ultrasound of the testicle can be done. This should always be carried out on both sides, even if the event is one-sided. The differential diagnosis of a hydrocele can be excluded or the blood vessels and blood supply can be visualized using Doppler sonography. In the case of testicular torsion, there is no venous return flow due to the clamping.
Read more on the topic: Doppler sonography
- therapy
Testicular torsion is a urological emergency and requires immediate therapy. You can first try to turn the testicle backwards manually. The doctor turns the left testicle clockwise and the right one counterclockwise to restore the original situation. Afterwards, however, the testicles must always be surgically attached (orchidopexy). Both testicles are attached, including the one that was not affected. This should prevent a recurrence. If testicular torsion cannot be ruled out with certainty, it always requires exposure of the testicle. The operation should generally be performed less than 6 hours after the occurrence of the event, as otherwise the tissue will irreversibly die. It has been proven that after 12 hours without therapy, irreversible necrosis has already occurred in 80%. Therefore, acute and devastating testicular pain always requires rapid clarification and initiation of therapy.
Read more on the topic: Testicular torsion
Testicular pain after ejaculation
As so-called "Cavalier pains“Is referred to when there is after sexual arousal without ejaculation or after a particularly long erection and subsequent ejaculation Pain in the testicle occur. These pains range from uncomfortable Feelings of tension in the testicle up to existing Pain in the testicle. The term is probably coined because the cavalier holds back so long and can delay his orgasm until the partner is sexually satisfied.
When the man is sexually aroused, the blood flows into the genitals, first the penis and then the testicles. The arteries are dilated, but the veins are narrowed (vasoconstriction). This increases blood flow to the genitals, helping to erect the penis and to swell the testicles. The testicles can enlarge by 25-50% of their original volume. Now the reason for the pain may be that the smooth muscles of the seminal ducts become cramped. When orgasm is reached, ejaculation takes place and the vessels return to their original size, causing the penis and testicles to shrink again. If the ejaculation does not occur, the vasoconstriction of the vessels will persist and this can cause a persistent feeling of pressure, discomfort, or pain in the testicles. Similarly, if the condition persists long before ejaculation is achieved. This feeling or this pain can also radiate into the groin.
In and of itself, this pain is not harmful. However, if they persist for a long time, a doctor should be consulted to clarify possible blood flow disorders. The cavalier pain can also be an accompanying symptom of a Permanent erection occur.
- treatment
A treatment must also rarely occur, as the pain is mostly from regress alone. It is stated that after ejaculation, the pain disappears after 30 minutes to 3 hours. One can relieve pain Cooling the testicles with for example one wet, cold towel be. Care must be taken that the cooling done moderately and there is no hypothermia.
Testicular pain in testicular cancer

Nonspecific pain in the testicle can result in an enlargement of the testicle as well as a nodular change in it Testicular cancer indicate. Occasionally a Heaviness of the testicle described, in later stages can add to that Back pain, stomach pain, Weight loss, Loss of appetite, fatigue and reduced performance occur.
- diagnosis
Testicular cancer is after a detailed anamnese (Questioning the patient) and an examination. Likewise, is often a Ultrasonic of the testicle made to possible nodular changes to represent. Further examinations can be connected to a possible metastasis (scattering) of the tumor. That too blood is examined for tumor markers. These can be used for diagnosis and, above all, for progress monitoring. In particular, these would be Alpha fetoprotein (AFP) and the Placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP), the Lactate dehydrogenase(LDH) and the Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG).
- therapy
Various options can be considered as therapy. On the one hand, these would be an operation complete removal of the testicle and lymph nodes. Furthermore, a Radiation or chemotherapy be performed. The treatment concept is based on the age and condition of the patient, the stage of the tumor and microscopic assessment (Seminoma or non-seminoma) chosen. In most cases, surgical removal of the affected testicle is sought first, and subsequent measures may then be taken.
In the follow-up, the Tumor markers determined in the blood and regularly one CT examination (Computed Tomography) carried out in order to detect possible metastases in good time.
Testicular pain with varicocele
A Varicocele describes a abnormal expansion of the venous plexus of the testicle (Pampiniform plexus) in a row of a Insufficiency of the venous valves. About 20% of adult men are affected by a varicocele. The peak of the disease rate is around between the ages of 15 and 25.
- Symptoms
The varicocele can be divided into 3 degrees.
At grade I. is the varicocele only palpable when pressing.
At grade II is the varicocele without provocation like pressing palpable.
At grade III is the Changes in the scrotal veins visible.
A varicocele usually reduces symptoms. However, possibly a Drawing in the testicle as well as a Heaviness the same occur.
- treatment
After the varicocele through inspection (Look at), Palpation (Scan), Ultrasonic and possibly one Spermiogram (about 25% of patients have a limited fearfulness through the venous change and through it Warming of the testicles) has been diagnosed there depending on Degree of expression possible therapy variants.
Is the varicocele painful, the Semen quality decreased or existed cosmetic ailment (the patient finds the appearance of the testicle disturbing) so can a Ligation of the vein be made. Either the Internal testicular vein (Operaton according to Bernardi) or the Spermatic vein (Operation according to Palomo) be prevented (so-called ligature).
Testicular pain after vasectomy
Testicular pain may also occur after a vasectomy. The vasectomy describes the Sterilization of the man, in which the vas deferens are cut, a piece is removed and the two ends are tied off separately from each other. This intervention can be carried out in Local anesthesia carried out because the vas deferens run outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum and are therefore easily accessible. You may experience pain when injecting the local anesthetic; the rest of the procedure is painless.
In hindsight it can be different, however rare complications come. This includes one bruise as well as a Swelling in the area of the scrotum as well as a local inflammation or one Wound infection or even Drawing in the testicle. This can radiate into the groin and occur more frequently in the first few days, but in very rare cases also persist for weeks or months. The pain can usually be overcome local and moderate cooling alleviate. Furthermore can also Painkiller be taken.