Pain in the heel of the hand - What do I have?
introduction
Painful balls of the hands can be attributed to various causes. Often the symptoms are caused by harmless causes, such as by simply overloading the hand muscles by repeatedly performing the same movement (writing, certain sports, etc.). However, diseases can also cause pain in the palm of the hand. The following are possible causes of the symptoms.

Pain in the palm of the hand
If pain occurs on the inside of the heel of the hand, this affects the ball of the little finger (Hypothenary). This can be caused by irritation of nerves or tendon sheaths due to overloading.
Read more on the subject at: Tendinitis in the thumb
An entrapment of the ulnar nerve (elbow nerve) within the Guyon Lodge be
Please also read our main article on this: Loge de Guyon syndrome
Since the little finger is the weakest finger, a sudden increase in stress, such as learning to play the guitar, can tire the muscles of the little finger, which is then reflected in pain in the ball of the little finger. The muscles are best trained gradually.
Read more about this below: Pain in the little finger
Arthrosis in the area of the little finger ball, i.e. cartilage wear in the joint between two carpal bones, can also cause pain in the little finger ball, so that the affected patient can no longer lean on the hand without pain, for example.
Please also read our main article on this: arthrosis
Appointment with a hand specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me at:
- Lumedis - orthopedics
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, appointments can only be made with private health insurers. I ask for understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Lumedis - Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Pain in the palm of the hand
Pain in the palm of the hand, at the Ball of the thumb (Thenar), usually occur in connection with a so-called adducted Thumb up, speak when the thumb inside is pulled.
The thumb can often be relieved when pain occurs no longer spread.
There are many in the ball of the thumb short muscles of the thumb, which are necessary for almost all activities, as they occasionally bring the thumb to the fingers.
This movement is called opposition designated.
Pain in the ball of the thumb often occurs monotonously repetitive activities as part of a Tendinitis on (typical example: frequent use of the computer mouse.
Often there is one Arthrosis of the thumb saddle joint, which is located in the ball of the thumb, causes a painful ball of the thumb. The Saddle thumb joint is for the opposition of the thumb.
Please also read our main article on this: Thumb saddle joint osteoarthritis
Illustration causes of pain in the heel of the hand
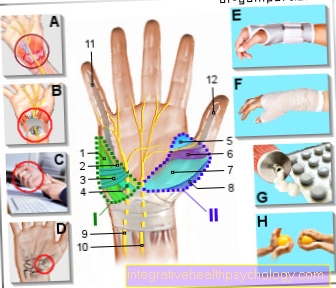
Pain ball of the hand
I - little finger pads - Hypothenary (green)
inner palm
II - ball of the thumb - Thenar (blue)
outer heel of the hand
- Little finger spreader -
Abductor digiti minimi muscle - Short little finger flexor -
M. flexor digiti minimi brevis - Short palm tendon tensioner -
Muscle palmaris brevis - Little finger counteracting device -
M. opponens digiti minimi - Thumb pull -
Muscle abductor pollicis - Short thumb flexor -
Muscle flexor pollicis brevis - Short thumb spreader -
Muscle abductor pollicis brevis - Thumb counter -
Muscle opponens pollicis - Ellen's nerve - Ulnar nerve
- Median arm nerve - Median nerve
- Common tendon sheath
the finger flexor -
Vagina communis tendinum
musculorum flexorum - Tendon sheath of the long
Thumb flexors -
Vagina tendinis musculi
flexoris pollicis longi
Causes:
A - tendonitis -
(Tendovaginitis)
Movements, such as long writing,
tap computer keys and
Throwing Sports
B - carpal tunnel syndrome
(Compression syndrome)
C - Rheumatic Diseases
(such as rheumatoid arthritis)
D - arthrosis of the thumb saddle joint
(Rhizarthrosis)
Therapy of pain
E - splints, plaster splints
F - Stabilizing bandages
G - anti-inflammatory creams,
pain reliever as well
anti-inflammatory drugs
H - Physiotherapeutic and
physiotherapy exercises
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
causes
Causes of a sore palm can be one Tendinitis be, as well as a Carpal tunnel syndromesince the Median nerve Sensitive care for the palm of the hand within the carpal tunnel.
Also rheumatic diseases, as the Rheumatoid arthritis can for example through a Joint inflammation cause discomfort in the ball of the thumb or ball of the thumb in the thumb saddle joint.
In addition, there is a cause Arthrosis of the thumb saddle joint, technically as Rhizarthrosis referred to.
By Cartilage wear it is particularly important gripping movements to pain. Also Ruptured muscle fibers or Nerve damage in the context of trauma or the like can cause pain in the palm of the hand.
In the following we have compiled the most important causes for you in more detail.
Tendinitis
In the case of tendinitis, the long finger tendons are usually irritated due to incorrect or excessive strain. These run in tendon sheaths that allow the tendons to slide onto the hand bones. If the same movement is carried out over a longer period of time, so that the tendons and their tendon sheaths are overloaded, an inflammatory reaction can occur.
Depending on which tendon sheaths are affected, the inflammation manifests itself in differently localized pain. The tendon sheath of the thumb tendon is most commonly affected. In most people, this is connected to the tendon sheath of the little finger, so that the inflammation can quickly spread to this tendon sheath. Affected patients feel sharp pain that radiates from the wrist to the thumb and little finger. Pain also occurs in the ball of the thumb, as the tendon sheath of the thumb runs along there and can be painful over its entire course. Pressure can often make the pain worse.
Tendonitis can also be caused by bacteria. This can happen after injuries to the hand, when bacteria get through the wound to the tendon sheaths. Since the thumb and little finger tendon sheaths are connected in a V-shape in many people, bacterial inflammation can also spread along these tendon sheaths to the other tendon sheath. This form of bacterial tendonitis is also called V phlegmon. Movements that can typically lead to tendonitis include long typing, typing on computer keyboards (cramped hands), and throwing sports.
Therapy: For most tendinitis, it is sufficient to first immobilize the joint with a Velcro bandage or a plaster splint so that the tendon sheaths can calm down again. If the symptoms persist, taking anti-inflammatory pain relievers or injecting cortisone into the inflamed area can help. Sometimes it may be necessary to surgically split the stuck tendon sheaths in a small operation.
Muscle or nerve injury
Just like tendinitis, incorrect or overloading of the hand can also injure the muscles or nerves. Musculature and nerve damage can also be caused by strong force exerted on the ball of the thumb as part of a sports injury or an accident. Muscle fiber tears can be very painful. The muscle fiber tear often shows itself through reduced strength in the affected muscle, severe pain and swelling, and often a bruise in the tissue. The area should be immediately cooled and immobilized.
Thumb saddle joint osteoarthritis
The thumb saddle joint is the thumb joint that is closest to the wrist and flexibly connects the thumb and wrist. The joint has a large range of motion and is very important for daily gripping. However, since it is exposed to a lot of stress, it is also prone to wear and tear and develop osteoarthritis. The osteoarthritis in the thumb saddle joint will also Rhizarthrosis called.
Typically, load-dependent pain in the ball of the thumb initially occurs, which gets worse over time. At some point, the affected person's ability to grip is limited, and pain occurs, especially when trying to spread the thumb. Even at rest without stress, pain occurs as the wear and tear progresses.
Therapy: This is what is treated Rhizarthrosis initially through targeted heat and / or cold therapy, as well as the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs. Alternatively, a cortisone injection can be made directly into the affected joint. In the case of very severe and therapy-resistant symptoms, surgical therapy may be indicated. E.g. Parts of the joint are removed or the entire joint stiffened, which leads to a certain loss of function, but also to lasting freedom from pain.
rheumatism
With rheumatic changes in the fingers and wrists, discomfort in the ball of the thumb can also occur. The affected joints are often swollen and overheated and the muscles of the ball of the thumb and little finger can be noticeably regressed. Since this reduces the padding of the ball of the thumb, straining this region can quickly cause pain. In addition, the inflammation of the joints also affects the surrounding tissue and can result in tenderness and decreased mobility in the thumb area. In addition, rheumatoid arthritis can also lead to inflammation of the tendon sheaths, which can also be expressed by discomfort in the ball of the thumb.
Therapy: The therapy is mainly based on the severity and severity of the rheumatic disease. Among other things, anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, cortisone injections, but also non-drug therapy forms. A balanced diet for the patient as well as specific movement exercises to keep the affected joints flexible play a major role.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
The carpal tunnel is a tunnel-like structure on the wrist through which various structures are led from the forearm to the hand. This carpal tunnel can narrow, especially when the wrists are exposed to long-term stress, and the structures in it, such as the flexor tendons of the hand and the median nerve, are crushed. This causes pain in the heel of the hand, which can affect the fingertips due to the involvement of the median nerve.
It is not uncommon for people who have had carpal tunnel syndrome for a long time to experience additional numbness of the fingers. First of all, the disease can be treated by immobilizing and protecting the wrists. In the process, however, an operation is often necessary in which the constricting ligament is split so that the structures in the carpal tunnel have more space again.
Read more on the topic: Carpal tunnel syndrome
Concomitant syndromes
The accompanying symptoms of pain in the heel of the hand primarily depend on the cause of the complaint. In the event of a fall or another traumatic event, fractures of the carpal or forearm bones can also occur. Sprains and bruises are also possible. There may also be injuries to the muscles and tendons on the wrist. There is also bleeding and bruising, and swelling can also occur. Inflammatory diseases or signs of wear and tear usually affect both hands, and sometimes other joints can also hurt and swell.
deafness
Numbness is a symptom that can occur due to two different mechanisms. One possibility is insufficient blood circulation in the hand, which means that the supply of oxygen and other nutrients to the tissue is no longer guaranteed. This can lead to numbness, similar to a sleepy leg.
Especially in connection with pain in the heel of the hand, numbness often occurs due to nerve damage. Information about touch, pressure, temperature, etc. can no longer be passed on from the nerves to the brain, making it impossible to perceive them.
swelling
In connection with pain in the heel of the hand, swelling is not a rare accompanying symptom. This is often an indication of an inflammatory process in which redness and swelling as well as overheating and limited mobility of the hand occur. The swelling is caused by the many immune cells that the body needs to fight the inflammation. These cells usually also draw a lot of water from the vessels into the tissue, which also leads to fluid retention.
Swelling can also result from trauma to the hand. In this case, tissue fluid can also be the cause of the swelling, and bleeding from a vascular injury can cause the hand to swell. Usually this is accompanied by a bruise.
Also read the article on the topic: Swollen hands
diagnosis
The diagnosis of pain in the ball of the hand is very diverse, as there are many possible causes of the symptoms. In order to rule out some of the possibilities, the doctor responsible should attach great importance to the anamnesis, i.e. the questioning of the person concerned. For example, a traumatic cause can be confirmed or excluded. The diagnostic process is usually followed by imaging using X-rays. If damage to muscles, tendons or joints cannot be ruled out, an MRI is usually necessary. Inflammatory changes that cause pain in the palm of the hand can also be detected in the blood in the laboratory. There you can also find evidence of a rheumatological disease.
Which doctor treats this?
If there is pain in the heel of the hand, you can first see an orthopedic surgeon. This usually arranges for an X-ray of the hand in cooperation with a radiologist, and further imaging using MRI or CT is not infrequently necessary. Once the cause of the discomfort has been clarified and it is a degenerative disease or an acute injury, the orthopedic surgeon can continue to treat the discomfort.
Alternatively, a hand surgeon can be called in. A hand surgeon is usually better trained than an orthopedic surgeon, especially when an operation is necessary. For inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatism, treatment should be in the hands of a rheumatologist.
Treatment / therapy
Therapy for pain in the ball of the hand is initially based on the symptoms. For example, you can take pain medication (e.g. Ibuprofen®) for temporary symptoms, and ointments such as Voltaren® or Doc-Salbe® can also relieve the pain. Additional stabilization of the affected wrist with a bandage or tape is often also helpful. In addition, the therapy should be causal so that the cause of the pain is treated. In the case of trauma with a broken bone, the therapy can consist of immobilization in a cast, for example, a bandage is usually sufficient for sprains and bruises.
Surgical treatment with bone nails or plates is also rarely necessary for more complicated injuries. Pain in the heel of the hand that results from chronic overloading can usually only be treated by prolonged protection and immobilization of the wrist. Surgery can also help with diseases such as carpal tunnel syndrome. Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatism and inflammatory diseases are best treated with medication.
Can a wrist bandage help?
A wrist bandage can reduce the pain in the palm of your hand. The immobilization supports tendons and muscles in their function, and the swelling is somewhat limited by the compression. A wrist bandage can also be used after traumatic injuries; this can protect the wrist when it is subjected to renewed stress. A bandage can also be worn for chronic diseases such as rheumatism.
For more information, see: Wrist bandage
Duration / forecast
The duration of the pain in the heel of the hand can vary greatly depending on the cause. In the case of traumatic events such as broken bones, the symptoms are usually healed after a few weeks with immobilization. Chronic pain caused by rheumatism or carpal tunnel syndrome, for example, can last longer. Rheumatic diseases in particular often accompany affected persons for a lifetime, but can usually be controlled well with medication.