Pain in the left arm as a sign of a heart attack
introduction
A heart attack is a serious and possibly life-threatening disease. Pain in the left arm can be a sign of this, but it usually doesn't happen on its own. With a heart attack, there is usually a feeling of pressure over the chest or even pain behind the sternum and shortness of breath.
An EKG and a blood test can rule out or confirm the suspicion of a heart attack. If there is a heart attack, the closed coronary artery should be reopened as soon as possible.
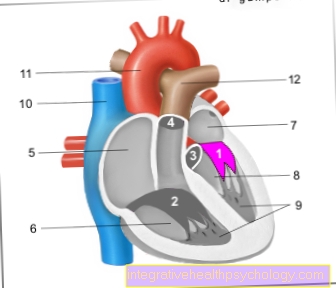
General information about heart attacks
A heart attack is a serious and possibly life-threatening disease. It comes about when the vital Coronary arteriesthat supply the heart with oxygenated blood, locked and as a result an adequate amount of blood cannot be pumped into the heart muscle. With the associated undersupply of the heart muscle cells, the heart muscle cells in the affected area die. The person concerned notices this by means of Sudden severe chest painthat can also radiate into the left arm. Furthermore, it can also be an unpleasant one Sensation of pressure in the chest area have preceded. Very often the so-called annihilation pain is indicated by the patient, that of Sweats can be accompanied. A fulminant heart attack always goes with a feeling of Fear of death hand in hand. A painful radiation to the left arm is also reported relatively often. About the Half of all patients becomes a painful pulling in the course of a heart attack in the arm or jaw reported.
You can find more information on this topic here: Symptoms of a heart attack
Cause of arm pain in a heart attack
Today almost everyone knows that a referred pain in the left arm with a heart involvement in the sense of a Angina pectoris- Seizure (vascular narrowing in the heart) or a heart attack (vascular obstruction in the heart). And although in most cases of left-sided pain radiating into the arm there is a muscular problem and leads to these complaints, the heart must always be examined as wellso as not to miss a heart attack. A EKG must therefore be carried out in any case with such a symptom.
More information can be found here: Diagnosis of a heart attack
In the event of a heart attack, one or more coronary arteries close up, preventing the heart muscle from being adequately supplied with oxygenated blood. The chest pain typical of a heart attack comes from this Undersupply conditions. The shortness of breath and the rapid pulse are mostly due to a reaction of the heart to the reduced oxygen supply. (see also Cause of a heart attack)
How pain is radiated into the left arm is still today not quite sure. It is assumed, however, that nerve pathways that run in the area of the left arm are connected to nerves that also run in the area near the heart. The pains in the left arm are thus in the sense of a unspecific transmission of pain to evaluate. The reason why a heart attack usually only affects the left arm and not the right arm could be because the tip of the heart, which is otherwise in the center of the chest, points to the left and thus becomes one Transmission of pain to the left half of the body can come. If treatment is initiated immediately, pain in the left arm will disappear very quickly, also in combination with the other complaints.
Heart attack pain can spread not only to the left arm, but also to the Jaw, neck, back and even the upper abdomen.
If the patient has subjected his left arm to unusual movement or overloaded it a few days before the pain began, heart disease is also unlikely to be the cause. In some cases, a Tendinitis of the forearm lead to a radiation up to the shoulder, which can also trigger a suspicion of a heart attack. It should be noted, however, that the pain of tendinitis in almost all cases start over the wrist and then pull up.
Please also read our article on this Tendonitis on the wrist.
If the symptoms were caused by involvement of the heart, the pain is almost always im upper third of the humerus localized. The arm is supplied with numerous, mostly well-pervaded blood vessels. Sometimes calcification of the vessel walls can lead to a narrowing of the blood vessels, which then leads to a Circulatory disorder in the area of the upper arm has the consequence. The symptoms of this so-called arteriosclerosis The blood vessels can have an uncomfortable drag in the left arm as well Numbness be in the area of the upper arm and shoulder. A circulatory disorder in the arm can therefore be one of the reasons that there is pain in the area of the left arm and that there is no heart problem behind it. After a heart attack has been ruled out diagnostically, the Finding the cause The patency of the blood vessels in the upper arm must also be checked. An ultrasound examination is used for this. Also called Vascular doppler The designated examination method shows the vascular flow of the upper arm and can show constrictions in the shoulder and upper arm area. In the case of a vasoconstriction, either conservative blood-thinning drugs treated, or else a Stent be placed in the affected vessel.
There are still numerous neurological causes that can lead to left arm pain. As a rule, however, it is very rare to find out the exact cause. The so-called nerve conduction velocity would definitely be measured as an examination method. This checks how quickly the nerve impulses cross certain nerve pathways. If there is a delay in the transmission of stimuli, there is usually a constriction or nerve damage in the area of the upper arm. Sometimes the bottleneck can also be in the elbow area. Nerve bottleneck syndromes can cause pain to radiate into the hand and shoulder, but also to numbness in the fingers of the affected hand. Treatment is primarily conservative, i.e. through physiotherapy, but it can also be done through surgical relief surgery.
Indications that speak against a heart attack
Left arm pain that increased when moving as well as other missing accompanying symptoms suggest a more muscular cause of the pain or a problem that is present in the shoulder or upper arm joint. The pain occurs in the area of the left arm after physical strain and exertionIf the sporting activity was to be carried out without further restrictions, this also indicates a cause in the area of the joint or the muscles, in the sense of a Sore muscles, to. Long-lasting pain in the left shoulder area, which, however, does not increase in frequency and intensity, is most likely not caused by a heart attack. The decision-making process as to whether or not it was a heart attack should also include how old the patient is and whether it has ever had Heart problems for him or in the family and whether the patient has any comorbidities.
Further indications for a heart attack
In the event of a heart attack, it happens seldom only pain in the area of the left arm. Usually associated with this are other complaints that occur either at the same time or slightly offset and that could accompany the left arm pain. There would almost always be an accompanying one pressure-like feeling in the thoracic area. The pressure that is present in almost all heart attacks can occur either at rest or during exertion and provides information on the severity of the vasoconstriction. If the vessels of the heart are almost closed, pressure-like complaints occur even at rest. If the heart is still adequately supplied with blood, but with constricted cardiac artery vessels, symptoms similar to pressure only occur after prolonged physical exertion. Further indicates a rapid and irregular pulse, which accompanies the pulling into the arm on the left side, indicates a heart involvement. Furthermore are mostly strong sweats combined with a narrowed coronary artery or with a heart attack. Very severe pain in the area central chest, which are also referred to as annihilation pain, complete the symptomatic full picture of a heart attack. The most important diagnostic decision as to whether the symptoms of left arm pain are a heart attack is when it occurs. For example, pain in the left arm that is caused by cardiac involvement would not simply go away, but would actually increase in intensity. The pain would be not dependent on movementif it comes from a heart attack and vice versa, the pain would be more likely to be provoked by certain movements if it were a muscular or joint problem. Complaints of any kind would become more and more severe with a heart attack or massive vasoconstriction of the heart muscle under stress. If they even get weaker, heart involvement is more questionable. Those affected should still have complaints such as Chest pressure, shortness of breath, racing heart, or chest pain Do not do a stress test yourself to see if the symptoms go away or not. The only thing you can do is with isolated pain pulling into the left arm without accompanying complaintsforce the arm up, forward, and backward to see if it makes the pain worse. Can through Increased movement sequences the pain in the left arm is increased, the likelihood of heart involvement as the cause is rather low, although not excluded. Even if the examiner presses on the joint space of the shoulder or has the arm raised against resistance, and there is increased pain as a result, this is more likely to indicate a muscular cause.
Racing heart occurs in almost all patients with an acute heart attack. Also very common is a severely increased blood pressure. Both symptoms are an expression of the body's new and life-threatening metabolic situation. Furthermore, the racing heart is also a vegetative sign, because a patient with an acute heart attack is afraid and panics because he realizes that something is wrong. The body then responds with a kind Stress response with an increase in pulse (palpitations) and an increase in blood pressure.
Please also read our topic on this Signs of a heart attack
Other possible causes of left arm pain
In addition to a heart attack, there are also numerous other underlying diseases that can be associated with a pull in the left arm. The most common cause of pulling pain in the left arm is muscular in nature. Particularly in the shoulder-arm area, severe tension can develop over time. Since the upper arm and shoulder are heavily muscled, these would Tension can then also be perceived by pulling pains in the left or right upper arm. If only the left arm is affected, one should always rule out a heart condition in the sense of a heart attack. Degenerative changes of the shoulder joint can also lead to severe pulling pain in the area of the left arm, e.g. also the Osteoarthritis in the shoulder Can cause pain in the shoulder and upper arm area when moving. Another cause of pulling pains in the left shoulder and left arm is Irritation of nerve cordsthat run in the shoulder area. Sometimes you can Calcifications of tendon attachments or muscular indurations (Myogelosis) lead to increased pressure in the area of a passing nerve.
More information can be found here: Left arm pain
Pain in the left arm as a sign of myocarditis?
The Myocarditis is a dreaded disease that must be avoided in any case. Young people are often affected by this disease and, as a rule, they had a severe flu-like infection a few weeks earlier, which was not adequately treated or cured. People who still do sports and exercise when they have an infection can develop heart muscle inflammation. The first signs of an inflammation of the heart muscle are a severe decrease in performance, an irregular pulse, sometimes fever, loss of appetite and nausea. The symptoms typical of a heart attack, such as pressure on the chest or the pain of annihilation, are usually completely absent in heart muscle inflammation. There is also no pain in the arm area, as the heart muscle inflammation is usually painless.
You can read more information about this here: Symptoms of myocarditis
The Diagnosis of myocarditis is performed by means of an EKG, as well as after performing an ultrasound of the heart. A blood test can also indicate the presence of heart muscle inflammation. On the one hand, inflammation levels, but also important cardiac enzymes, are significantly increased in the case of cardiac muscle inflammation.
By Protection and sometimes an accompanying one antibiotic treatmentg an inflammation of the heart muscle can usually be treated adequately. However, if the diagnosis is made too late or if it is a severe and fulminant myocarditis, there is a risk that the heart's strength will be severely restricted forever, resulting in the clinical picture of cardiomyopathy. Patients with cardiomyopathy are no longer productive in the long term, have a greatly increased risk of sudden cardiac death and, depending on the severity and severity of the cardiomyopathy, also have a significantly reduced life expectancy. The most important thing is to prevent cardiomyopathy in any case, as there is no treatment for this serious disease.

.jpg)