Forearm pain - what is the cause?
introduction
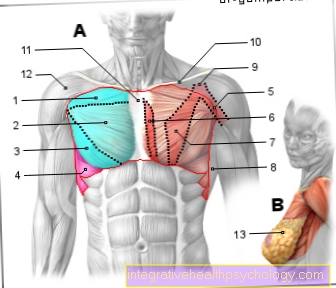
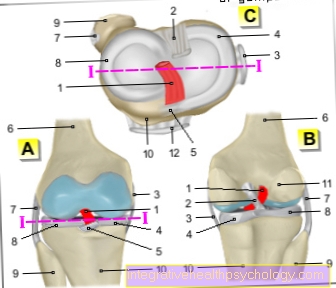
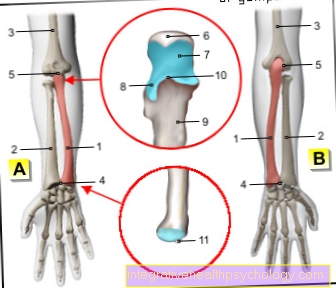
Of the human forearm is from Cubit (Ulna) and spoke (radius) educated. In between there is one coarse layer of connective tissue (Membrana interossea antebrachii) from which the two bone connects with each other.

Together with the humerus, the ulna and radius form this Elbow joint (Articulatio cubiti), by doing diffraction and Elongation takes place. In addition, there are two articulated connections between the forearm bones, namely the proximal (pointing towards the middle of the body) and distal (pointing away from the center of the body) Radioulnar joint. Through these two joints will be Turning movements enables. This closes distally wrist on.
Besides the bony parts, there are numerous stabilizing ligaments, Muscles and tendons in the forearm area. Some structures, such as annoy or bursa, run superficiallyso that they can be damaged relatively easily.
If there is pain in the forearm, stop Time, character and exact location the symptoms often draw conclusions about the diagnosis.
E.g. Gradual onset of pain in the back of the elbow an indication of a Bursitis. Sudden, violent pain in the forearm, on the other hand, can be for you fracture (fracture) speak. In the following text, the most common clinical pictures discussed.
Disorders that cause forearm pain
Tennis elbow
The entire extensor muscles (Extensors) of the forearm arise from a small protrusion of the distal humerus, the Radial epicondyle. This joint tendon attachment of the muscles is irritated by heavy use, so that a painful inflammation can develop. Tennis players, especially beginners with inadequate stroke technique, are often affected. Because the plug muscles are easily overstrained by the typical club movement. The colloquial expression "tennis elbow", compared to the scientific name "Humeri radial epicondylitis"enforced. But unfamiliar, non-sporting demands, such as gardening or carrying boxes, can cause the symptoms.
A tennis elbow is characterized by pain in the lateral elbow, which radiates into the forearm and is aggravated by stretching movements. The affected epicondyle is tender on pressure and partially recognizable from the outside by swelling or reddening.
As a rule, the tennis elbow heals through frequent cooling (e.g. with ice packs) and regular 'stretching' of the forearm muscles (e.g. wrist flexion). In addition, tennis should be reduced to a painless level.
If the muscle origin is in Epicondyle humeri medialis, also a protruding bone of the distal upper arm, and the flexor muscles (Flexors) is affected, one speaks of a golfer's elbow.
You might also be interested in the following topic: Symptoms of tennis elbow
Elbow dislocation
With this violation, colloquially too 'Dislocation' or ,Dislocate' called, leave the articular surfaces of the bones involved external force their usual position. This results in a very painful misalignment of the elbow joint. Often be there annoy or Blood vessels crushed or injured so that the Pain all over the forearm radiate. Due to the high level of pain, the forearm is severely restricted in movement!
Most of the time, the injury is caused by one violent fall on the outstretched arm. After confirming the suspicion by X-rays, the joint must be returned to its original position. This process is also known as Reduction ('Adjusting'). It is not uncommon for the pain to be so severe that the Procedure performed under anesthesia must become. After a successful reduction, a Plaster of paris for about one to two weeks. Otherwise, without immobilization, there is a risk that the elbow will dislocate again.
You might also be interested in this topic: Elbow dislocation
Appointment with a tennis elbow specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
As a former performance-oriented tennis player, I specialized early on in the conservative treatment of chronic tennis elbow.
In the last few years I have successfully treated several thousand tennis arms.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert.
Olecranon bursitis
In the Olecranon bursitis is it a Bursitis of the elbow. Immediately behind the elbow is just below the skin the bursa. By chronic pressuree.g. prolonged desk work and the resulting support can lead to inflammation ("Student elbow "). Mark is a tender swelling on the back of the elbow, which can be the size of a chicken egg. Often there is one Redness and overheating of the affected skin areas observable.
Therapy consists of cooling the elbow and using anti-inflammatory ointment (Anti-inflammatory drugs).
Please also read our topic: Bursitis on the elbow
Forearm fractures
One differentiates between Forearm fractures between broken bones in the proximal ("Towards the upper arm") and distal ("Towards the wrist") forearm and fractures of the forearm shaft.
The fracture of the Radial head, i.e. the part of the spoke that is involved in the formation of the elbow joint. Typically, the fracture is caused by one Fall on the hand with extended elbows. It is caused by pain Limited mobility after the accident and kick it massive swelling and Hematomas ("bruises") on the elbow.
First of all, the X-rayed forearm. When the fragments shifted against each other (dislocated) they have to undergo an operation brought to their original position and then by e.g. Stabilized screw systems become. In the case of a broken bone without dislocation, it is sufficient to immobilize the forearm.
The distal radius fracture is the most common bone fracture in humans. By falling on the outstretched hand breaks the spoke above the wrist. In this case one speaks of one 'Colles fracture'. If the fall occurs on the back of the hand in a bent position, the resulting break is called 'Smith Fraktur'.
A Colles' fracture is easy on the characteristic "bayonet position" of the wrist To recognize: The fragments of the spoke move towards the thumb so that the hand is bayonet-like to the forearm. In cases of a non-displaced fracture, you can only tendernessas well as swelling. Mostly, however severe pain and swelling the rule immediately after the accident.
The therapy depends on the exact type or fracture line of the injury. If the injury is that Does not include wrist, the forearm is in a so-called "Girl catcher association " immobilized. If there is a comminuted fracture or a fracture of the articular surfaces of the wrist, a Recovery through surgery be displayed. Due to the complicated course of nerves and vessels on the distal radius, are Complications in the healing process are not uncommon.
Fractures of the forearm shaft are common Result of traffic accidents or falls, they are caused by direct violence. Often both ulna and radius are affected. The so-called Paper fracture dar: Through direct violence (e.g. baseball bat attack), it comes to a isolated fracture of ulna.
The pain affects the entire forearm. In addition, movements in the two joints between the ulna and the radius are painful and there are extensive bruises and swellings to observe.
Usually one occurs in adults affected surgical intervention, with non-displaced hernias in children can in many cases be a plaster cast sufficient. Dreaded complication is an ossification of the connective tissue Membrana interossea antebrachii between ulna and radius. In the worst case, it can Rotation movement canceled by the forearm become.
Pain on the outside of the forearm
Forearm pain often occurs on the outside of the arm. Cause for it can different clinical pictures be partially on upper forearm or. Elbow or in the Tendons and Muscles have their origin below. The cause of pain on the outside of the forearm can also be further away. In most cases there is one Tense muscles or one permanent irritation and overloading of tendons and tissues Triggers the pain.
A common cause of forearm pain, which mainly occurs outside, is the so-called Tennis elbow. This is an irritation and inflammation of the attachment tendons of the muscles caused by overload, which are responsible for the Extension of the hand and fingers responsible is. These start at the elbow, so that the pain arises on the outside of the elbow and continues into the forearm, sometimes up to the hand.
Access and the Clench a fist cause the pain. The tennis elbow is through a Sports break usually adequately treated, the pain in the forearm disappears on its own.
Tension in regions further downwards also causes pain on the outside of the forearm. So can a Flexor and turning muscles in the elbow joint, the Brachioradialis muscle, Be the origin of the complaints. It runs from the outer elbow on the outside of the arm towards the thumb and is mainly at Hold work burdened with bent arm. Waiters are often affected here. If this muscle is tense, it sometimes happens sharp pain in the forearm outside.
The muscles that pull from the forearm to the hand and move the wrist can also work their way through chronic strain tense and pain. Often people suffer from this often work on the PC and keep your wrists in an inconvenient, bent position while writing. In this case, the pain will drag further down the forearm starting high outward and forcing you to give up the activity.
Muscular tension is treated by a Exercise break and maybe light massages of the muscles. In the case of permanent bad posture, this should of course corrected become. Soft wrist pads can improve posture for the workplace at the PC.
Some medical professionals assume that pain in the forearm is also caused by tension and processes in more distant muscles like the outside chest or on move be evoked. Through so-called Trigger points and transmitted pain there are also symptoms in the forearm. Massages can help here.
Right forearm pain
There are the typical causes such as muscle tension or tendon irritation that lead to pain in the forearm on the right and left. Especially with Right handed If you have a tennis or golfer's elbow or tension from writing too long on the right. People who do physical work and, above all, who lift loads on the right, complain more often of symptoms on the right.
In addition, there are other diseases that do not originate in the forearm but can still lead to pain on the right. So can a inflamed gallbladder Radiate into the right shoulder and right arm. Even if mostly the upper arm is affected, the pain can extend into the forearm. The fact that problems with the gallbladder Pain in the right forearm can cause is due to the interconnection of the various nerve fibers in the spinal cord.
If the nerves that send gallbladder pain to the brain are active, switching to nerves coming from the forearm is possible. Then the patient also feels pain in the right forearm.
Likewise, if the right one is called Brachial plexuswho is at armpit level is damaged, pain in the right forearm can occur. The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that sends pain impulses to the brain, among other things. Pressure-related damage or injuries to the plexus therefore lead to pain in the arm and forearm.
You can find more information on our website: Right forearm pain
Pain in the left forearm
In addition to the typical causes such as tension and tendon irritation due to overload, which in Left handed logically occur preferentially on the left, other causes can cause pain in the left forearm. Like the gallbladder on the right, there are also diseases of internal organs that radiate to the left into the forearm.
It is known that a Heart attack often radiates into the left arm in addition to the existing, severe chest pain, which can spread to the forearm. This pain occurs suddenly up and are with strong fear connected. Pain that only occurs in the left forearm is highly unlikely to be caused by a heart attack.
In addition to the heart, the pancreas radiate into the left forearm. The reason for the pain radiating from internal organs is the interconnection at the spinal cord level. Here different nerve endings are close together, so that other, actually uninvolved, nerves can be stimulated at the same time. The person concerned then feels e.g. Pain in the left forearm.
Furthermore come Nerve damage on the left side as a cause of forearm pain. The so-called brachial plexus can e.g. by degenerative changes in the spine impaired, which also causes pain in the further course of the nerves.
Please also read our topic: Pain in the left forearm
Pain in tendons or muscles
In most cases, forearm pain is caused by a tense muscle or through Processes in a tendon evoked. The tense muscle is often a muscle on the forearm that moves the fingers or wrist. Muscles of this type exist on the outside as well as on the inside of the forearm and are made by them chronic strain or Overstimulation tense. The forearm pain worsens with exercise.
Typically both people are who working on the PC are or often carry loads need to be affected as well as athletes. In addition to the tennis elbow, which causes pain on the outside, there also exists Golfer arm. This is caused by pain in the Inside of the forearm and elbow noticeable.
In addition to a muscle, a tendon can also cause pain in the forearm. If a tendon is stressed too much, it can lead to abacterial (so bacteria-free) inflammation come that too strong exercise-dependent pain can lead. Usually the tendon sheath is also affected, the doctor speaks of one Tendovaginitis.
Typically suffer guitar player often with pain in the forearm caused by a tendon, but also after too hard Dumbbell training or symptoms can arise from permanent incorrect stress. The pain occurs on the forearm on the flexor side and can be provoked by moving the fingers. A Break from any stress on these tendons, possibly for weeks, cold and Painkiller improve things.
Pain after falling
Often times, forearm pain is associated with a fall. Pain occurring after a fall should always be accurate observed as the injury can have various dimensions. In the simplest case it comes to bruise. The bone remains completely intact and no special therapy is required, cold and Painkiller alleviate the symptoms.
However, the pain can be relatively severe and may accompany the fall bruise on.
After falling on the forearm, the pain is unbearable or occurs additionally Restrictions on movement in the arm or wrist, a doctor should be consulted. This could be a fracture that can be diagnosed with an x-ray. Sometimes you can see one after the fall Misalignment, a hospital is to be visited here immediately. But even if the pain in the forearm does not get better after a fall or is very severe, a fracture can be behind it, usually with significant swelling goes hand in hand. Even then, a doctor's visit is advisable. People under osteoporosis should definitely be examined if there is pain in the forearm after a fall.
Pain in the forearm during a heart attack
In the vast majority of cases, forearm pain is harmless in nature and does not require any special therapy. In some cases, however, forearm pain can also occur Heart attack occur. Typically, the pain radiates into the left arm out. Even if the pain is usually limited to the upper arm, in the case of a heart attack it can also reach the forearm.
If the pain is caused by a heart attack, however, other symptoms that occur in parallel are usually in the foreground. A typical heart attack is a severe chest pain, the one with Fear of death and in many cases nausea goes hand in hand. In addition, there are often signs like Shortness of breath, Loss of consciousness or dizziness on.
Pain in the forearm that occurs without any further symptoms is therefore unlikely to be the only sign of a heart attack. Nevertheless, if in doubt, you should seek medical advice if you are not sure. If the above-mentioned other symptoms occur, the ambulance and the emergency doctor must be alerted immediately in order not to waste the time, which is so important in a heart attack.
Read more about the: Signs of a heart attack


.jpg)



.jpg)