Pain in the calf
Different causes of calf pain
The calf (Syn. Lower leg and its musculature / calf twin muscles) can be painful for a number of reasons. The pain can occur under stress, while walking, running or at rest. Since calf pain can not only be a sign of muscular overload, but also an indication of vascular disease, it should be examined by a doctor if the pain persists.

Causes through the muscles
Muscular causes are the most common explanation for calf pain. Injuries such as a torn muscle fiber in the lower leg or a strain can occur as a result of an accident, improper or excessive stress, especially during sporting activities. The muscles can also be overloaded by prolonged stress and sore muscles.
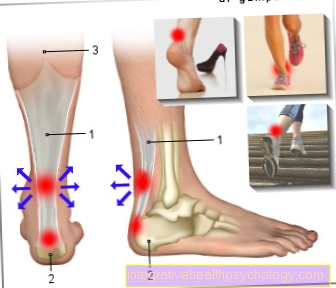
Illustration of the different calf pain

Pain in the calf
- Popliteal artery -
Popliteal artery - Popliteal vein -
Popliteal vein - Large rose vein -
Great saphenous vein - Posterior tibial vein -
Posterior tibial vein - Posterior tibial artery
Posterior tibial artery - Fibula artery -
Fibular artery - Small rose vein -
Vena saphena parva - Sole muscle -
Plantaris muscle - Internal calf muscle -
Gastrocnemius muscle
Caput mediale - External calf muscle -
Gastrocnemius muscle
Caput laterale - Clod muscle -
Soleus muscle - Achilles tendon -
Tendo calcaneus - Long fibula muscle -
Musculus fibularis (peroneus) longus
A. - Atherosclerosis
(Changes in blood vessels)
Arteriosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
B - venous thrombosis, DVT -
Deep vein thrombosis
C - Torn muscle fiber, strain
D - thrombophlebitis -
Inflammation of superficial veins
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.
Causes of circulatory diseases

In particular, pain that occurs when walking and then subsides at rest can be an indication of a circulatory disorder. The reason for this are arteriosclerotic deposits on the vessel walls. Muscular work means that they need more oxygen and, for this reason, increased blood flow.
However, due to the vascular calcifications, the vessels are not capable of increased blood flow, so that pain occurs. Since these calcifications often occur on the coronary arteries in addition to the leg vessels, there is a significantly increased risk of a heart attack. Furthermore, a thrombosis of the deep leg veins can lead to massive pain. The pain is often acute and occurs due to the sudden interruption of the blood supply. In addition, movement can detach the vascular thrombus, which is then transported with the bloodstream into the lungs and leads to a pulmonary embolism there. The result is acute shortness of breath, which can be life-threatening.
More on this: Pain in the calf- What evidence is there that it is a thrombosis?
Causes due to inflammation of the calf
Inflammation of the vessels in the sense of thrombophlebitis can also lead to severe pain in the calf. This is an inflammation of the small superficial skin veins, which is often associated with reddening and swelling of the leg.
Other infections caused by germs penetrating from the outside can also lead to severe pain, redness, swelling and a general feeling of illness.
Causes by the spine
A disc prolapse the lower Lumbar spine can be more appropriate with compression annoycause severe pain in the calf. Also degenerative changes in the spine, fractures with narrowing of the Spinal canal or Bone tumors of the Spine can irritate the nerves and cause pain in the calf.
The leg cramp
Calf cramps are a common cause of calf pain. Many people experience cramps at night and can be so strong that normal running during and after the cramp is not possible because the muscles remain painfully hardened. During the spasm, the Calf muscles cramp-like and can be felt as a hard strand.
The remedy is usually provided by instant stretching of the affected muscle, in the case of the calf, the stretch is performed by a strong angling of the foot reached. The pain then often subsides quickly. Sometimes, however, a feeling remains that resembles a sore muscles.
The cramps usually come on very suddenly, often during exercise or at night. The cause can be Overuse of the muscles, but also one Underload of the muscles be.
At vigorous exercise the body loses fluids and minerals that are important for the normal function of the muscles. This can cause cramps. A sufficient one Hydration and magnesium intake prevents cramps.
At Insufficient challenge of the muscles are particularly common at night because the body has not experienced enough movement.
Another cause for Calf cramps are poorly fitting footwear or Misaligned feetthat can overload the calf muscles.
Also with the Taking certain medications an increased incidence of calf cramps is observed. This is especially true for Diuretics (diuretic drugs) or Medicines for high blood pressure (Antihypertensive drugs).
F.If you also suffer from cramps in your feet, read more about this here: Cramps in the foot
How is calf pain diagnosed?
The first step is to take a detailed medical history, especially the Duration of pain in the calf, Localization of pain and the Occur the pain is crucial. This can provide initial clues as to the cause of the pain.
The calf is then carefully examined. The examining doctor pays particular attention to signs of a inflammation, for example Redness, Swelling and a overheat the calf. Tension tenderness in a defined area can indicate a muscular injury.
Furthermore, the blood on inflammation, clotting and Heart disease examined. These can be signs of a thrombosis give. A special investigation, the determination of the D dimers quickly provides information about the presence of a thrombosis. If there is a suspicion of an acute obstruction of the vessels, a Ultrasound examination the course of the vessels can be shown and a possibly existing thrombus becomes visible.
If there is a suspicion of increasing vascular calcification, an invasive visualization of the vessels using a Catheter and contrast agent (Vascular angiography) should be considered. The Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used if there is a suspicion of a spinal disease with radiating pain in the legs.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.
Therapy for pain in the calf
Treatment for calf pain depends on the cause. When chronic pain is triggered by Incorrect or overloading, exist, these should be treated by changing behavior and changing movement patterns. In some cases, exercising may help you stretch the sore muscles to relax the muscles. In the case of acute Muscle injuries, for example one Torn hamstring or one aching, should have the appropriate Muscles be spared and accordingly a break from stress is observed until the pain has passed. Ointment dressings, Bandages or a Tape bandage can help to alleviate the pain and relieve the muscles.
If an acute thrombosis is suspected, the compression as well as a blood thinning medication necessary. The therapy is always inpatient at the beginning until the thrombus is organized and stable. So is the risk of transportation in that lung diminished. In the context of vascular imaging with the administration of contrast agent, the vessels can not only be depicted but also treated.
Bottlenecks can be expanded with a balloon or through the use of a Stents expanded and kept open. In some cases, this therapy is not enough, so a bypass must be laid.
Here another will be long vein taken, which serves as a bypass circuit for the narrowed vessel. So the muscles can be supplied with blood again.
However, this therapy is not sufficient in the long term, as the lifestyle is often decisive for the prognosis arteriosclerosis is. So belong next to a lot Move also one Weight reduction and Nicotine abstinence to the deciding factors. Spinal diseases often have to be treated surgically. By relieving the pressure on the compressed nerves, the pain in the calf is usually reduced. In the case of inflammation of the calf, antibiotic therapy should be initiated, often also in an inpatient setting.
Where can calf pain occur?
Pain on the outside of the calf
Pain on the outside of the calf can have several causes:
- Tension: Pain on the outside of the calf is often caused by tension in the muscles there. Typically the muscles affected are the Peroneal muscles. If there is such tension, a hard muscle strand can usually be found on the outside of the Lower leg Keys. The cause of the tension can for example Misalignments of the feet (Arched feet, Flat foot) or also Misalignments of the legs (Knock knees, If one) be. The misalignments lead to pathological movements that lead to a Overuse and improper use of the muscles to lead. These can then react with cramps and tension, which can be very painful.
- Connective tissue, muscle fascia, nerves: If the complaint is not caused by the muscle itself, the pain can also come from the connective tissue or the muscle fascia on the outside of the calf. Due to heavy loads, for example at extensive physical activity, the structures of the lower leg can become irritated and cause pain. By Compression of nerves can cause particularly unpleasant complaints that can radiate into the foot.
- Other causes: Of course you can too Inflammation explain calf pain through previous injuries in the lower leg area. Then there are usually other signs of inflammation, such as swelling, Redness and overheat the affected region. Furthermore, the differential diagnosis is peripheral, especially in pre-stressed patients Arterial Disease (PAOD) to be excluded. It comes through a Reduced blood flow the muscles lead to severe lower leg pain, which, depending on the severity of the vascular occlusion, occurs either at rest or only during exercise.
Pain in the inside of the calf
Pain on the inside of the calf can also have various causes:
- Tension: In principle, the same applies to pain on the inside of the calf as to external calf pain. Pain on the inside of the calf is often the Gastrocnemius muscle or the Toe flexors affected. These can go through heavy load, through extensive physical activity or as part of Bad posture to be overused and with Tension and Convulsions react. This usually manifests itself in pulling or drilling pains, which get worse with movement and strain.
- Connective tissue, muscle fascia, nerves: Also, calf pain on the inside does not necessarily have to originate in the muscles, but can also originate from other structures. By heavy use nerves and connective tissue can be irritated, which can explain the symptoms.
- Other causes: Of course you can too Inflammation explain calf pain through previous injuries in the lower leg area. Then there are usually other signs of inflammation, such as swelling, Redness and overheat the affected region. Here, too, an important differential diagnosis is the peripheral one Arterial Disease (PAOD), which can cause severe lower leg pain.
Achilles tendon pain
Pain in the calf area can result Impairment of the Achilles tendon or the muscles that merge into the Achilles tendon. In most cases, this pain is (Achillodynia) a Tension in the muscles of the calf. Especially tension in the area of the Gastrocnemius muscle and des M.soleus usculus can cause severe discomfort. It comes because of the fact that these muscles go a long way in walking especially when moving to pain in the calf.
In general, one can assume that the Achilles marriage itself does not have to be impaired in order to cause such symptoms. In most cases, the discomfort felt by the affected patient is from that the connective tissue surrounding the Achilles tendon out. Another cause of calf pain is that Achilles tendonitis. This condition is one of the most common causes of the occurrence of Pain over the heel and in the calf area.
Either Overloads, as well as physical changes (for example muscle shortening) can be responsible for the emergence of the inflammatory processes be responsible in the area of the Achilles tendon. Patients with Achilles tendonitis usually experience severe pain over the heel and calf. In addition, it can be due to the inflammatory processes too Redness the skin surface and Swelling come within the tissue surrounding the Achilles tendon. In contrast to simple achillodynia, pain in the presence of Achilles tendonitis occurs both at rest and under stress.
Disorders of the Achilles tendon that can lead to pronounced pain in the calf area either medicinal or non-drug be treated. For acute pain relief it is recommended to use a light pain reliever (analgesic) to take. Mainly drugs that have the active ingredient Paracetamol or Ibuprofen are particularly suitable for the treatment of pain in the heel and in the calf area. Patients suffering from Achilles tendonitis should, however, prefer pain relievers containing ibuprofen. This is because of the fact that ibuprofen is about both pain reliever, as well as over anti-inflammatory properties disposes. In addition, slight impairment of the Achilles tendon can cause calf pain from the application of Kinesio tapes be treated.
Pain down to the hollow of the knee
In the case of pain in the calf that radiates to the hollow of the knee, the gastrocnemius muscle is often the origin of the complaint. Its starting point is at the lower end of the thigh bone. If this muscle is tense or cramped due to vigorous sporting activity, for example, this can cause the pain. Depending on the degree of tension, the knee can sometimes no longer be fully extended. The cause of the tension can also lie in a poor posture, a hollow back is the cause particularly often. This leads to an unfavorable shift in body weight, which leads to an overload of the gastrocnemius muscle.
Read more on this topic: Pain in the calf and the hollow of the knee
When can calf pain occur?
Pain at rest
Many patients experience pain in the calf area, especially during exercise. However, there are also diseases that typically lead to pain at rest.
One possible cause for the development of pain in the calf, which can occur both at rest and when moving, is so-called "phlebothrombosis" (deep vein thrombosis in the leg, Thrombosis in the leg). This term refers to a disease that occurs when deep leg veins are blocked by a blood clot. In patients with deep vein thrombosis, there is a risk that the blood clot will suddenly break loose and enter the lungs or other organs with the bloodstream. This can lead to life-threatening pulmonary embolism, for example.
The thrombosis in deep leg veins, which can lead to pain in the calf, is provoked by the interaction of various factors (so-called Virchow triad). A pronounced slowdown in blood flow plays a crucial role in this context. Especially long bending of the knee joints (for example on long-haul flights) can significantly restrict blood flow. In addition, a lack of blood circulation after surgery can significantly increase the risk of developing a leg vein thrombosis with pain at rest that occurs in the calf area.
Further risk factors are changes in the composition of the blood and changes or damage to the vessel walls. In addition to the pain in the calf, which can also occur at rest, there are increased vein markings, overheating of the affected leg, tense, shiny skin, calf pressure pain (Lowenberg sign), Pain in the calf when stretching the foot (Hohmann sign) and sole pain when pressure is applied to the inner sole of the foot (Payr sign) to the typical symptoms of leg vein thrombosis.
In addition, the affected patients may develop a fever and have increased levels of inflammation in the blood.
The treatment of deep vein thrombosis, which can lead to pain in the calf even at rest, usually has three important goals. Both the spread of the blood clot and its spread, as well as the restoration of the original blood flow are among the most important treatment goals. Another cause of the development of pain in the calf, which can also be seen at rest, is calf cramp. In the case of a leg cramp, there is involuntary tension (contraction) individual muscles or entire muscle groups in the lower leg. In most cases, stressful situations lead to the development of a calf cramp. Often, however, people also report being woken up at night by a calf cramp that occurs at rest. Typically, the pain caused by a leg cramp is so severe that the sleeper can no longer rest for the time being.
In addition, the acute hardening of the affected muscles is one of the typical symptoms of calf cramps. Most of the time, the leg cramp, which can lead to pain in the calf even at rest, is often caused by a harmless disturbance in the electrolyte balance. These electrolyte shifts are based, for example, on underlying diseases that lead to increased electrolyte loss. Classic examples of such diseases are acute diarrhea, vomiting, diabetes insipidus and chronic inflammatory bowel disease. In addition, various drugs (e.g. diuretics) can lead to a pronounced electrolyte deficiency. A lack of magnesium in particular can provoke muscle spasms, which lead to pain in the calf even at rest.
Read more on the topic: Muscle twitching in the calf
In addition to the occurrence of muscle cramps, severe headache, general weakness, fatigue and cold feet indicate a magnesium deficiency. Furthermore, overloading during the day can lead to cramps at rest.
Older people are much more likely to develop calf cramps. The reason for this is the fact that the muscles become increasingly short as we age. Regulatory disorders of the cardiovascular system, on the other hand, typically lead to pain in the calf, which increases with exertion and decreases significantly when at rest.
Pain after jogging
Pain in the calf, especially after to jog occur are usually through a Overuse the calf muscles. This is exposed to a lot of stress while running and can be painful Tension or Signs of fatigue react. Sometimes it is Footwear The cause of the pain if it is not suitable for jogging or is not optimally adapted to the runner. Also bad running techniques with the resulting incorrect load, the symptoms can trigger. Also Misaligned feetthat have not been properly corrected with orthopedic insoles can put a lot of strain on the calf muscles when running. Optimal footwear is therefore essential for every runner and should definitely be purchased in addition Signs of wear and tear in the joints to prevent. The cartilage in the knee joint is permanently damaged by incorrect loading.
Pain when walking or running

Many of the affected patients experience pain in the calf area primarily when walking or running. In some cases, these complaints persist even at rest, but they become significantly more intense when walking or running.
The most common causes of calf pain when walking or running include muscle injuries (such as pulled muscles or torn muscles).
Under the term "strain“ (Technical term: distension) one understands in the medical jargon the process of a muscle stretching which exceeds the usual measure. Simple muscle strains have to be differentiated from a muscle fiber tear, as the extent of injury is much more pronounced in a muscle fiber tear. In contrast to uncomplicated muscle strain, clear structural changes can be detected in the presence of a muscle fiber tear, which lead to both the destruction of some muscle cells and local bleeding into the muscle tissue.
A ruptured muscle fiber is one of the most common sports injuries. In terms of symptoms, however, both clinical pictures are very similar. With both muscle strain and muscle fiber rupture, a sudden shooting, severe pain in the calf area that increases in intensity when walking or running is one of the typical symptoms. In addition, the mobility of the affected part of the body is significantly restricted immediately after the muscle injury has occurred.
In addition, local bruises and bruises can cause calf pain that increases in intensity when you walk or run. Such lesions are often sports injuries, which are popularly known as a horse kiss.
In some cases, patients who suffer from pain in the calf have a significantly higher risk of developing a heart attack due to the cause. In this context, pain in the calf, which occurs when walking or running and which subsides again when the person is resting, is an indication of a circulatory disorder (arteriosclerosis). Furthermore, inflammation of the superficial leg veins can lead to chronic pain in the calf area, which particularly restricts those affected when walking or running.
Pain at night

There can be various causes for the development of pain in the calf, which mainly occurs at night.
Many patients who feel pain in their calves at night suffer from the so-called "Restless Legs Syndrome" (Synonym: restless legs, Wittmaack-Ekbom syndrome). This clinical picture is a neurological disease that is mainly noticeable through sensory disorders and a pronounced need to move in the calves and feet. In addition, many of the affected patients suffer from pain in the calf and involuntary movements (Twitches). Occasionally, a similar clinical picture can also be observed in the area of the arms.
Restless legs syndrome causes strong pulling in the calves and feet, especially in states of rest, for example at night. In addition, the majority of affected patients report a pronounced feeling of tension, tingling and pain.
The symptoms caused by the neurological disorder trigger an irresistible urge to move in those affected, as tensing and stretching the muscles of the calf at least temporarily alleviates the symptoms. Although the symptoms typical of Restless Legs Syndrome can occur at any time of the day, most patients report that the symptoms are worse in the evening or at night than during the day. A typical characteristic of Restless Legs Syndrome is the immediate relief of symptoms by moving the affected limb. In particular, slow walking, squats, and periodic tensing of the calf muscles can help alleviate the symptoms. The pain in the calf caused by this condition can negatively affect sleep at night. In the affected patients, the sleep rhythm can be disturbed to such an extent that they suffer from increasing tiredness, exhaustion and exhaustion during the day. In this way, the restless legs syndrome and the associated complaints at night can also have a lasting effect on the psyche of those affected. The cause of the development of this disease could not be clarified until today. However, it is assumed that the neurotransmitter dopamine plays a decisive role in the development of the disease.
The treatment of restless legs syndrome is primarily based on the subjective level of suffering of those affected. Since the symptoms that mainly occur at night cause a pronounced lack of sleep and in this way can cause psychological ailments (e.g. depression), restless legs syndrome should be treated early. Possible forms of treatment range from the oral substitution of iron preparations, through the administration of highly potent painkillers, to the ingestion of synthetic messenger substances. Levodopa, a precursor to dopamine, is particularly suitable for treating restless legs syndrome.
Prophylaxis of calf pain
Unfortunately, not all calf pain can be prevented. A healthy lifestyle, a lot Move, avoiding Obesity, as well as renouncing alcohol and nicotine can help to avoid pain caused by vascular diseases in particular.
Around aching Avoiding in the context of sporting activity can be a regular Muscle stretching prevent pain after exercise.
Summary
Calf pain can have many causes. These can occur harmlessly in the context of muscular overload, or they can be signs of an injury.
This pain is usually directly related to vigorous physical activity or an accident. If the pain is recurring, especially after a short distance, which subside when you are at rest, it is suspected Vascular calcification. This can also indicate additional calcifications, especially of the coronary arteries.
These are associated with a significantly increased risk of heart attack. Inflammation, which is part of overheat, swelling and Redness should be treated with antibiotics. Is there any suspicion Spinal disease, the diagnosis can be made with imaging tests.
In most cases there is one surgery necessary. As part of the diagnosis, the anamnesis is first taken and a precise clinical examination is carried out. Laboratory parameters are also determined. Further examinations, such as imaging procedures, follow. Therapy generally consists of a healthy lifestyle and plenty of exercise. Depending on the diagnosis, surgical or angiographic interventions may be necessary. Since the vascular calcifications in particular can indicate an increased risk of heart attack, persistent pain in the calf should be examined by a doctor.