Swelling of the parotid gland
What is a swelling of the parotid gland?
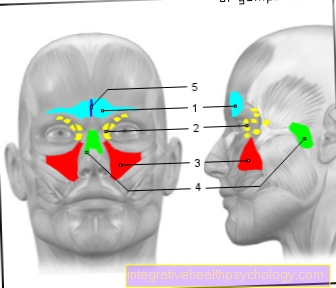
The parotid gland (glandula parotis) lies under the skin on both sides in the area of the cheeks and is one of the largest salivary glands in humans.
If the parotid gland swells, the cheek swells up and a bulging protrusion can be felt under the skin.
The swelling is either unilateral or affects both salivary glands. The swelling is caused by an inflammation with pathogens or has non-inflammatory causes.
Read more on the subject below: Inflammation of the parotid gland

Causes of swelling of the parotid gland
In most cases, swelling of the parotid gland is caused by inflammation. An infection with bacteria causes the parotid gland to become inflamed, swollen and purulent parotitis. A typical bacterial pathogen is Staphylococcus aureus, which migrates up into the gland through the duct of the salivary gland in the mouth.
Often the duct is blocked by a saliva stone, which means that the saliva can no longer drain and the bacteria can easily multiply in it.
The same thing happens when a tumor or scarring obstructs the duct.
Inflammation of the parotid gland (parotitis) can also be caused by various viruses such as neurotropic paramyxoviruses, the Epstein-Barr virus or influenza viruses.
In all cases, the parotid gland swells and hurts. Especially in young children, swelling of the parotid gland is often caused by a viral infection with the mumps virus. In addition to a sore throat and fever, there is swelling of the parotid gland on both sides. Most children these days receive a standard vaccination against mumps.
There are also non-inflammatory causes of a swollen parotid gland. The swelling can occur as a side effect of drugs that reduce the flow of saliva (e.g. beta-blockers for heart problems, diuretics, antidepressants, or antihistamines).
Various metabolic disorders such as metabolic diseases (hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus), malnutrition or alcohol addiction also cause the salivary gland to swell.
Another cause is Sjogren's syndrome. This is an autoimmune disease that causes severe dry mouth.
Diagnosis of a swollen parotid gland
The doctor will feel the swelling and take a blood sample to see if any inflammation caused the swelling.
In some cases, the doctor can also take a smear to determine the exact pathogen.
The diagnosis of a swollen parotid gland is confirmed with the help of an ultrasound examination. It can be used to determine whether the swelling is caused by a salivary stone, constrictions or a tumor.
Swelling of the pancreas is usually caused by inflammation. You can read more about this in the next article: Symptoms of parotid gland inflammation
Concomitant symptoms
Depending on the cause, either only one or both parotid glands may be swollen. The swelling usually occurs quite suddenly and can be clearly felt as a bulge in front of or under the ear.
Accompanying symptoms of the swelling may be pain and a feeling of pressure. The pain can radiate into the teeth and the temporomandibular joint.
If the parotid gland is inflamed, the affected area is reddened in addition to the swelling.
The skin over the salivary gland feels warm and can be tight. Excessive swelling of the parotid gland can make it difficult to open your mouth. The patients are then severely impaired in speaking and especially in eating and chewing and sometimes have severe pain.
Long-term inflammatory swelling of the parotid gland can lead to complications: the inflammation can become encapsulated and form a pus-filled cavity within the parotid gland. One then speaks of an abscess.
Parotid swelling with pain
A swelling of the parotid gland that is associated with pain suggests inflammation as the cause. The cheek on the affected side is usually red, warm, and people may have a fever.
The inflammation is caused by a virus or bacteria and can affect one or both parotid glands.
Are you interested in this topic? You can read more information about this here: Pain in the parotid gland
Painless swelling of the parotid gland
A painless swelling of the parotid gland means there is no inflammation and is known as sialadenosis or sialosis.
As long as the swelling does not affect the function of the masticatory muscles or speaking, the swelling does not necessarily need to be treated.
However, many sufferers perceive the swollen parotid gland to be visually annoying and therefore still consult a doctor.
Common causes of sialadenosis are various metabolic disorders, such as Diabetes mellitus or an overactive thyroid, or a protein or vitamin deficiency.
Often a non-inflammatory swelling of the salivary glands occurs as a side effect of various drugs.
You can read more information on this topic in the next article: Diabetes Mellitus
Swollen lymph nodes
Lymph node swelling is a sign of infection and an immune response in the body. An inflamed parotid gland causes the surrounding lymph nodes to swell.
The swollen lymph nodes are clearly palpable in front of and behind the ears, under the jaw and along the neck muscle.
Read more information on the subject under: Lymph node swelling - How dangerous is it?
Which doctor treats this?
Patients with swelling of the parotid gland are best advised to consult an ear, nose and throat specialist (ENT).
ENT doctors have the diagnostic and therapeutic options to diagnose a disease and to prescribe the appropriate therapy. Larger cities have their own salivary gland centers that specialize in diseases of the salivary gland.
Treatment and therapy
Treatment for a swollen parotid gland depends on the cause. Inflammatory swelling is often caused by salivary stones.
The salivary stone obstructs the duct of the gland and can be removed either surgically or by mini-endoscopy of the salivary ducts.
- Very large stones must first be crushed by ultrasonic waves, this process is called extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL).
- Smaller stones can also be removed by massaging the gland.
- If the swelling of the parotid gland is caused by an infection, the inflammation must be treated as quickly as possible. If left untreated, the body can encapsulate the inflamed tissue and the pathogens, and a purulent abscess forms in the parotid gland, which must be surgically removed.
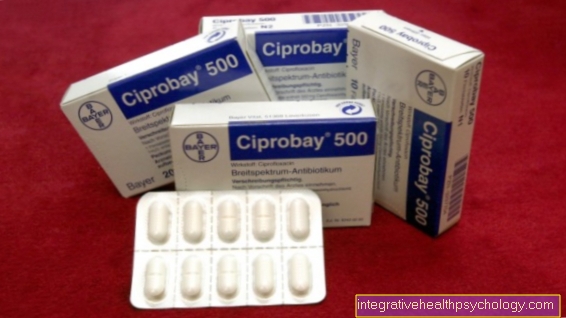
- A bacterial infection is treated with antibiotics. In addition, the doctor prescribes pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or paracetamol.
- In the case of a viral infection (e.g. mumps, influenza viruses), only the symptoms can be treated, i.e. antipyretic and analgesic drugs are prescribed.
- In the case of chronic and frequently recurring inflammations of the parotid gland or if a malignant tumor disease is suspected, the parotid gland can also be surgically removed (parotidectomy).
Read more on the subject below: Shock wave therapy
Which home remedies can help?
In general, a doctor should be consulted if the swelling of the parotid glands persists or if there is pain. The doctor can make the exact diagnosis and find the cause of the swelling.
In addition to the prescribed medication and antibiotics, there are also some home remedies that also help the parotid gland to swell again as quickly as possible.
Patients are advised to drink plenty of fluids to prevent the mouth from drying out and making it harder for bacteria to multiply. Chewing gum and sugar-free candies stimulate the flow of saliva and thereby accelerate healing.
The most common cause of parotid swelling is bacterial infection.
A targeted strengthening of the immune system through adequate sleep, a balanced diet and regular exercise can contribute to accelerated healing.
In addition, regular and careful oral hygiene helps prevent the bacteria from spreading further.
See the next article for helpful tips on good oral hygiene: Oral hygiene
homeopathy
Swelling of the parotid gland caused by a bacterial infection must be treated with antibiotics in most cases, as otherwise serious complications (abscess formation) can occur.
In addition, patients can take homeopathic remedies to eventually speed healing.
The homeopathic treatment options for a swollen parotid gland include therapy with Arsenicum album and Chamomilla.
However, the treatment should be individually adapted by a homeopath or naturopath.
Duration of parotid gland swelling
The duration of parotid gland swelling depends primarily on the cause.
A bacterial inflammation is treated with antibiotics and the swelling goes down after a few days and usually heals without any problems.
The removal of the salivary stones is a routine procedure and after a few days the patients no longer have any symptoms.