Tailbone inflammation
introduction
In the case of a coccyx sinus, in technical terms too Pilonidal sinus or Pilonidal sinus called, it is an inflammation that occurs in the gluteal fold between the tailbone and the anus (lat: rima ani) is playing.
A coccyx fistula can have different causes. The therapy takes place after the diagnosis by the doctor and can look very different depending on the trigger of the inflammation.
A fistula on the coccyx is often noticeable through discomfort that mainly occurs when sitting. If there is pain, stinging or pulling in the region of the tailbone, it is advisable to consult a doctor to clarify the symptoms.
root cause
There are two main causes of coccyx infection. On the one hand, the inflammation of the periosteum (med: periostitis) of the tailbone or inflammation of the tissue (inflamed hair) above the tailbone due to a coccyx fistula.
Probably the most common cause of this is hair growing into this part of the body. The ingrown hairs can lead to inflammation of the skin and the hair follicle, and it is not uncommon for bacteria to migrate into the inflamed hair roots and intensify the inflammation.
If this inflammation progresses and the secretion of the inflammation, the pus, cannot drain away, a cavity filled with secretion, a so-called cyst, can form under the skin.
If there is an outward outflow, one speaks of a fistula. A cyst can have several of these fistulas and a real system of ducts develops under the skin. Due to the increased hair, very hairy men are particularly affected by a coccyx fistula. Depending on the severity of the inflammation, every intermediate stage can develop, from no complaints to minor complaints to complete inability to sit and walk.

Inflammation of the periosteum can arise after various injuries to the tailbone. As the name suggests, the periosteum is the skin around the bone and supplies it with nutrients via blood vessels and contains numerous nerves, which is why it is very sensitive to pain. The bone itself cannot cause pain.
The inflammation of this periosteum arises from strong or long-lasting irritation of the periosteum such as poorly healing fractures, herniated discs in this region, tumors, accidents or chronic constipation or diseases of the pelvic floor.
The latter reasons lie in the muscle attachments of the pelvic floor to the coccyx and thus also to the periosteum. A strong muscle load is therefore also accompanied by the load on the muscle attachments with a load on the periosteum, which can then become inflamed.
Symptoms
With a tailbone infection you have to between Coccygodynia and Pilonidal sinus distinguish. The former is an inflammation of the periosteum (des Periosteum), which leads to pain in the buttocks area, the latter is a so-called Coccyx fistula, a surrounding tissue inflammation. However, in both cases the symptoms of coccyx infection are very similar. Depending on how advanced the inflammation is, burning or stabbing pain occurs in the buttocks area. Sitting on a hard surface (for example a chair) for a long time is particularly painful, as the coccyx is stressed to the maximum.
Turning over in bed or lying on your back can also worsen tailbone symptoms and lead to pain. The severe pain when defecating are also noticeable (defecation) (s. also Painful bowel movements) or when urinating (micturition). Mainly due to permanent blockages (Constipation) there may be increased symptoms of coccyx inflammation, as the Pelvic floor muscles is heavily used. However, these pelvic floor muscles are attached to the coccyx, among other things, and thus exert a pull on the coccyx that is experienced as very painful in the event of inflammation. The reason for this is the irritation of the periosteum to which the muscles and ligaments attach.
The symptoms of a tailbone inflammation can occur, for example, after a lumbago (lumbago) or after a herniated disc or after falling on the bottom.The periosteum can be injured, especially after fractures, which then leads to the first symptoms.
Diagnosis of tailbone inflammation
Diagnosing a Periosteum inflammation can often be checked by an examination with the finger through the Rectum be asked. If you carefully insert a finger, you can feel the underside of the coccyx through the intestinal wall, which is extremely sensitive to pain when the periosteum of the coccyx is inflamed.
If the cause of the inflammation is unclear, a X-ray, CT or MRI of the pelvis Evidence of the inflammation as well as previous fractures or other causes such as Tumors or Herniated disc of the lumbar spine give.
Diagnosing a Coccyx fistula usually takes place on the basis of the physical examination by touching or the visible external signs of inflammation such as extreme sensitivity to touch and pain sensitivity, as well as swelling and redness, the classic signs of inflammation.
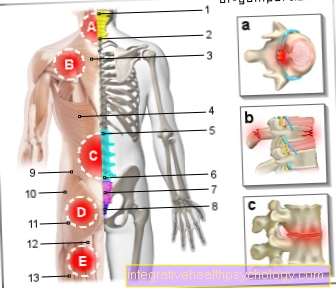
Figure tailbone pain
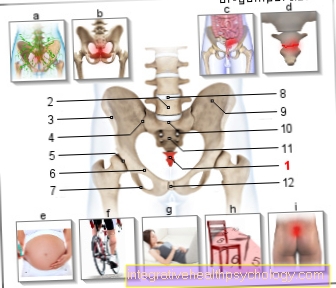
- Tailbone - Os coccyxis
- Fifth lumbar vertebra -
Vertebra lumbalis V - Iliac crest - Iliac crest
- Sacrum-iliac joint
(Sacroiliac joint, abbreviated ISG)
Articulatio sacroiliaca - Hip joint - Articulatio coxae
- Pubic bone - Pubis
- Ischium - Os ischii
- Intervertebral disc -
Intervertebral disc - Iliac bone - Os ilium
- Lumbar cruciate ligament kink -
Promontory - Sacrum - Sacrum
- Pubic symphysis -
Pubic symphysis
Coccyx pain - coccygodynia
a - Nerve Pain - The region of the body
becomes of plexus of nerves
(Plexus coccygeus) supplied
b - inflammation of the tendons,
Muscles or bones -
chronic loads or germs
c - rectum and anus, chronic
inflammatory bowel disease
(Ulcerative colitis, crohn's disease)
d - Coccyx fracture, coccyx contusion -
Swelling, bruising (due to
Fall, kick, etc.)
e - pregnancy
(hormonal changes) -
usually in the 1st and 3rd trimester
f - sport - tensioning the ligaments
and muscles (e.g. cycling, rowing)
g - Lying for a long time - (older and
bedridden people)
h - microtraumas - prolonged sitting
on hard chairs
i - coccyx inflammation - redness,
Swelling, fistula (Pilonidal sinus)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
therapy
Treating coccyx infection is not very easy. Therapy is difficult, especially after a fracture, because the tailbone cannot be splinted like the arm bone, for example. If the fracture does not heal properly, it can lead to permanent inflammation, which is associated with chronic pain. In order to keep this inflammation as minimal as possible, it is therefore important to protect the tailbone after a fracture. That means: sit little, don't ride a bike and sleep on your side with pillows if possible.
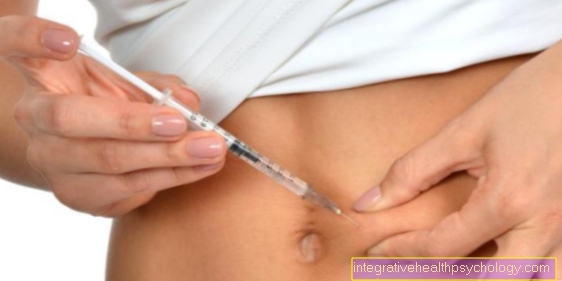
In the case of an already existing coccyx inflammation, an anti-inflammatory ointment is used first as a therapy. If this does not help, you can also give the painkillers orally (by mouth) or inject them into the area where it is particularly painful. Furthermore, a physiotherapy treatment or the patient should take one as a further therapeutic measure Osteopaths seek out. Another option for treating coccyx inflammation is that acupuncture. Here certain nerve endings are stimulated with the insertion of the needle. As a result, there is an increased release of pain-relieving substances (for example Endocannabinoids). These can improve healing and above all painlessness (analgesia) promote.
Also the Reflexology can be considered as therapy. This is particularly helpful when the muscles of the pelvic floor are very cramped. This cramping can be increased by stress or psychologically induced trauma (e.g. sexual assault) arise. Reflex zone massage can help loosen the muscles and thus relieve the periosteum of the coccyx and thus prevent inflammation. If the cramp is of psychological origin, additional therapy by a psychologist is essential.
In addition, a Laser treatment at e.g. the presence of a coccyx fistula.
Another therapy option for coccyx inflammation is the administration of homeopathic remedies. Especially Hypericum and Staphisagria are suitable as suitable means here.
There one Coccyx fistula (Sinus pilonidalis) arises due to an ingrown hair, therapy with painkillers is not sufficient here. In this case, the ingrown hair must first be surgically removed so as not to make the inflammation in the surrounding tissue worse. The hair is perceived by the tissue as a foreign body, and the surrounding tissue reacts accordingly with a painful inflammation. After the surgical removal of the hair, the permanent removal of the hair in the anal area is a suitable therapy, as a relapse rate of over 20% is otherwise quite likely. The removal can be done by laser. Particular personal hygiene is also particularly important after surgery or hair removal.
Surgery for a tailbone infection
A tailbone infection due to a Irritation or injury to the skin of the boneslike after a break (med: fracture) of Tailbone is not to be treated surgically.
At a Coccyx fistula, the so-called Pilonidal sinus or Pilonidal sinus However, surgery is often the only way to permanently remove the fistula.
Several surgical procedures can be used to contain the coccyx fistula. Most will be one conventional total surgery, such as after Karydakis, or the procedures according to Bascom, also Pit picking called, applied.
In conventional surgery after Karydakis the affected person lies in general anesthetic on the abdomen and all parts of the fistula are surgically removed. This type of complete removal by cutting out the affected tissue is also called in medical jargon Excision (Ex = out, caesare = cut) designated.
Only for smaller fistulas can the operation be performed in one local anesthesia be performed. In order not to leave any parts of the duct system and the cyst behind, the dye methylene blue is often used after the cyst has been cut open to stain all parts and display them in the surgical field.
To that Risk of recurrence (= Relapse) to reduce the entire tissue is often removed down to the tailbone and even a "hole“In the gluteal fold.
Due to the removal of the tissue, simple sewing is not possible and there is also a high risk for Wound healing disorders and the recurrence of another coccyx fistula. Therefore, in these cases the wound is left open and not sewn shut.
In this open procedure, the wound is covered with special bandages or wound sponges and heals over from the depths several months to. The wound is then covered with sponges or other materials, often within the so-called Vacuum therapy (Engl: Negative pressure wound therapy = NPWT) covered airtight and a small suction pump is attached to the drainage system (The tubes that drain wound fluid to the outside are called drainages) connected.
Another method, the so-called Pit picking, the method according to Boscom, is currently engaging with the smallest necessary incisions and can always outpatient under local anesthesia (Local anesthesia) be performed.
With pit-picking, the fistula ducts are cut out with small incisions even in the prone position and an approx. Two cm incision is made on the side, from which the wound secretion should drain. The entire pit picking intervention only takes a few minutes.
Home remedies for a tailbone infection

Few home remedies are effective against coccyx infections. The most important thing is not to put unnecessary strain on the tailbone. This means: Increased walks, during which the pelvic floor muscles can relax more and the tailbone is not exposed to any additional pressure or tension. It is important not to ride a bike as this only promotes inflammation! A seat cushion or a seat ring helps when sitting. This can be made of rubber or foam as required. Heat treatment helps many patients, for example so-called Sitz baths can be found in pharmacies. The warmth relaxes the muscles and gives the tailbone a break.
A cold compress or a so-called quark compress is often used as a home remedy. The latter is a cloth filled with quark that can be placed on the tailbone for a few hours at night or in the evening. This is said to help relieve the pain and help the patient relax. Wraps with Retterspitz® can also provide relief. In addition, you can use a pillow to fall asleep with which you sleep on the side. This also relieves the tailbone. However, the most important home remedy for coccyx infection is rest!
forecast
Both in the case of an inflammation of the coccyx due to the periosteum and also due to the inflammation of the tissue due to the Pilonidal sinus is with a long healing time of several weeks to be expected. The long-term success rates vary, depending on the type of operation, from almost 50% for closed surgery with suturing of the wound to around 20% for surgery Pit pickin or only a few percent after the operation Karydakis.
Compresses, hip baths, contrast baths and, in the case of periosteum inflammation, massages can accelerate the healing process or alleviate the pain during healing. In the case of periosteum inflammation, it is unfortunately not uncommon to expect complete freedom from pain and the inflammation can also be expected to return after surgery on a pilonidal sinus if the cause, the hairiness, is not treated.
Duration
At a Coccyx fistula (Sinud pilonidalis) after the surgical removal of the hair, it takes about 4 weeks for the wound to heal completely. If you spare yourself time, no further inflammation problems should arise afterwards, since the inflammatory stimulus (the hair) is removed.
If the periosteum is inflamed due to incorrect loading of the coccyx, this looks different. If tailbone pain with a slight inflammation occurs after a fall, this pain usually only lasts a few days, provided the patient takes care of himself in between. However, if there is too much strain or if you sit for long periods of time, the pain can last for weeks. In the worst case, chronic pain develops. This occurs especially in patients who ignore the initial signs of inflammation and continue not to change their lifestyle (sitting too long on hard surfaces). In general, one can say that the duration depends primarily on the closed season.
prophylaxis
Prophylactic measures for Prevention of overload make the most sense. Stretching exercises can prevent overloading.
Also the correct posture while sitting, sitting very straight, can relieve the tailbone and thus prevent overloading.
Inflammation after a fracture or contusion of the coccyx can only get through Rest during the healing period Adequate prevention so that too early exposure does not additionally support the inflammation.
Prophylaxis of a coccyx fistula is also only possible to a limited extent. A causal treatment is only through one permanent hair removal possible through laser treatment. Simple shaving is not enough for prevention here. If there is a tendency to the coccyx fistula, one can go through increased personal hygiene and avoiding long periods of sitting can partially prevent hair ingress. In spite of this, ingrowth cannot be prevented in some cases.
Exercise for a tailbone infection
Sport is considered due to the overload of the Musculature around that coccyx as an important trigger of inflammation of the periosteum of the coccyx. It is not uncommon for the complaints to occur only during exercise sudden, severe and stabbing pain in the area of the tailbone.
Similar to the heavy load and overload of the Pelvic floor muscles through chronic constipation Inflammation of the periosteum can also occur when exercising too much. Here, rest is the means of choice for healing. In this context, however, care is not to be equated with renunciation, but means gentle movement of the coccyx.
Gentle sports, such as aqua fitness or the like, that do not put stress on the tailbone are permitted. As a rule of thumb, any sport is allowed that does not cause pain and that does not overstrain the area.
Sports that put a lot of stress on the tailbone, such as cycling or horse riding, are unsuitable for returning to work, but also during the therapy period. In the case of a fistula, sport is only allowed in the pain-free and gentle area.
After an open operation, sitting is not even allowed for a certain period of time, so exercise is completely taboo at the beginning. Only after consulting the doctor will he allow gentle movements at his discretion.
After the pit-picking operation, exercise is allowed to the fullest extent possible on the first day after the operation. Even visits to the swimming pool are no problem due to the smallest wounds.