Symptoms of an umbilical hernia
Synonyms in the broader sense
- Umbilical hernia
- external hernia
- Hernia
English: umbilical hernia
Medical: umbilical hernia

An umbilical hernia causes the following symptoms and complaints
The most noticeable symptom of an umbilical hernia is a lump on the belly button that varies in severity from person to person. In some cases, however, this can be so small that it cannot be seen at all.
It only emerges clearly when a child screams or the adult increases the pressure in the abdomen by pressing. If the existing protrusion disappears spontaneously when lying down, it is said that the umbilical hernia is "repositionable".
This means that the contents of the hernia can be pushed back into the abdominal cavity by applying light pressure from the outside. However, if the protrusion remains in a lying position, it is an irreversible umbilical hernia.
An umbilical hernia does not always have to cause subjective complaints. Sometimes those affected complain of pulling pains in the area around the navel, which is mainly caused by physical exertion, cough or Pressoccur or then intensify.
Most of the time the break can be seen as a bulge, but that doesn't necessarily have to be the case either. If there is an entrapment, the result is usually one Circulatory disorder of the pinched organ, i.e. it is cut off from the oxygen supply, which in the worst case scenario can cause it to die. This causes extreme complaints, ranging from severe pain to the so-called "Acute abdomen“(Acute belly) with a rock hard belly are enough. This can develop into a state of shock, which is to be regarded as a life-threatening emergency.
The symptoms of entrapment are:
- colicky stomach pain
- fever
- nausea
and or - Vomit
If these are available, a surgery be performed.
The umbilical hernia associated with diarrhea
In most cases, an umbilical hernia remains symptom-free in the affected person. Should complaints nevertheless occur, these are usually determined by pain, but also by gastrointestinal complaints.
This is related to the fact that in some cases there is a loop of intestine in the hernial sac of the umbilical hernia.
Usually, in addition to pain, such a jammed bowel loop is more likely to cause constipation than diarrhea. However, so-called stool irregularities can occur, such as constipation and diarrhea alternating.
Since the intestine is irritated by the pinched intestinal loop, many different intestinal complaints can be caused.
Overall, diarrhea should not be viewed as a typical symptom of the presence of an umbilical hernia and does not serve as a key symptom for the determination of an umbilical hernia or the incarceration that results from it.
Nevertheless, if an umbilical hernia is suspected due to a clearly protruding hernial sac on the navel in connection with diarrhea, a doctor should be consulted who can make the correct diagnosis and initiate the necessary treatment.
These symptoms occur in adults

The umbilical hernia, which occurs in adults, is to be regarded as much more problematic. The first symptoms that affect adults include the deformation and bulging of the umbilical region.
In the further course there is a strong increase in volume of the umbilical hernia, which is caused by the passage of organ sections through the hernial ring. The size of the umbilical hernia is variable. It can be the size of a marble or the size of a football.
In addition, the localization of the typical bump in an adult umbilical hernia can also vary. Depending on the location of the weak point in the abdominal wall, it can show the protrusion both above and below the navel. Other symptoms that affect adults with umbilical hernia are more or less random in most cases.
This means that they are only triggered by other factors, such as a strong cough, heavy lifting or pressing. Adults rarely complain of pain in the navel when they have an umbilical hernia. Nevertheless, there are cases in which the affected patients describe drawing and / or burning pain. Symptoms such as:
- Nausea,
- Vomiting and / or
- Stool retention should be perceived as a warning signal in the presence of an umbilical hernia.
It is precisely these symptoms that indicate that sections of the intestine are trapped in the area of the umbilical hernia and thus their blood supply is restricted. In such a case, a specialist must be consulted as soon as possible and an operation initiated.
Furthermore, a distinction must be made whether the symptoms of adults with an umbilical hernia are permanent or whether they can be influenced by certain behavior. An umbilical hernia that can still be repositioned (i.e. an umbilical hernia that can be mechanically returned to the abdominal cavity without surgery) is characterized by the fact that the symptoms disappear when lying down. Pain that occurs when adults suffer from an umbilical hernia can also radiate into the pubic region or the scrotum. In addition, severe reddening of the skin can be observed in severe or long-lasting cases.
Symptoms of an umbilical hernia in women
In general, women are more often affected by umbilical hernias than men. This can have different reasons for the cause.
One of the main reasons for this is probably that an umbilical hernia can occur during pregnancy, among other things, and this contributes to the incidence of umbilical hernias in women compared to men.
Especially after several pregnancies, the risk for women of suffering an umbilical hernia increases.
Read more on the topic: Umbilical hernia in pregnancy
The incidence peak for the occurrence of umbilical hernias in women is between 40 and 50 years.
Since congenital connective tissue weakness is more common in women than in men and is a risk factor for the occurrence of an umbilical hernia, this can also be used as an explanation for an increased incidence of umbilical hernias in women.
Statistically, women suffer about 3-5 times more likely to have an umbilical hernia than men.
Other factors that are not specific to women can also be responsible for the occurrence of an umbilical hernia.
Obesity, physical strain, lifting heavy objects and illnesses that cause fluid to accumulate in the abdomen are known risk factors for the development of an umbilical hernia.
The diagnosis of an umbilical hernia in women does not differ from the diagnosis in men or infants. A physical examination can usually clarify the presence of the disease.
In rare cases it may be necessary to do an ultrasound examination.
Such an ultrasound examination can take place during pregnancy to assess the abdominal muscles and their distance.
A doctor should be consulted immediately in order to avoid serious complications and to initiate correct treatment of the umbilical hernia, especially if there is pain and a reddish / bluish color in addition to the protrusion of the navel.
Symptoms in men
Although an umbilical hernia is more common in women and infants, men can also be affected by an umbilical hernia.
Due to the male anatomy, as well as the statistically greater stress in everyday life, men suffer a rupture of abdominal viscera more often overall.
However, these breakthroughs usually occur elsewhere, such as in the groin.
In addition to increased physical strain, there are other risk factors that can contribute to men developing an umbilical hernia.
Above all, being very overweight and diseases that lead to an increased amount of fluid in the abdomen are favorable factors for the appearance of the umbilical hernia in adults.
Other illnesses and activities that lead to increased pressure in the abdomen, such as persistent strong coughing or the "Press“On the toilet can cause an umbilical hernia.
The fact that men are generally less often affected by an umbilical hernia than women can be explained by the fact that pregnancy and a weak connective tissue, which occurs more often in women, also promote the development of the umbilical hernia.
The diagnosis of the umbilical hernia in men does not differ from the diagnosis carried out when an umbilical hernia is suspected in infants or in women.
An umbilical hernia is noticeable through the protruding bulge on the umbilicus, in which, depending on the size, there may be loops of intestine.
Especially if the area is painful and / or red or bluish, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible to examine the person affected.
A physical examination and touching the so-called hernial sac are usually sufficient to diagnose an umbilical hernia.
In contrast to newborns, an umbilical hernia in adults always has to be operated on because there is too great a risk of entrapment of intestinal loops.
There are different methods of surgical repair of an umbilical hernia in adults.
Read more on the topic: Operation of an umbilical hernia
The prophylaxis to prevent an umbilical hernia in adulthood is primarily the prevention of risk factors that can lead to an umbilical hernia.
Classic abdominal muscle training cannot prevent an umbilical hernia or make it less likely to occur. This is due to the fact that the affected area is between two abdominal muscles, in a place that is only surrounded by connective tissue.
Illustration symptoms of an umbilical hernia
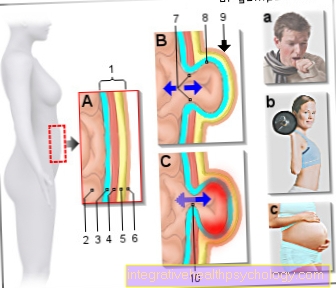
Umbilical hernia, umbilical hernia
Umbilical hernia
- Abdominal wall (3rd to 6th)
- guts
- Peritoneum -
peritoneum - Abdominal muscles -
Rectus abdominis muscle - Adipose tissue
- outer skin -
epidermis - Breach gate
- Hernial sac
(Peritoneum protuberance) - Umbilical hernia
- Entrapment of
Intestinal loops
A - scheme of an abdominal wall
and abdominal cavity from the right
B - umbilical hernia
(Intestine as fraction)
C - entrapment of intestinal loops
(Life-threatening emergency!)
Possible causes:
a - physical stress
(Coughing, straining, strong
Overweight, accumulation of
Liquid)
b - heavy lifting
c - pregnancy
(Pressure in the abdominal cavity)
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Diagnosis of the umbilical hernia
To diagnose an umbilical hernia, palpation of the umbilical region is usually sufficient, since the hernia is usually palpable. With help of a Stethoscope the doctor can listen to the hernial sac.
If he can detect gurgling noises, this indicates that parts of the Small intestine are in it. If there is any uncertainty or if it should be ruled out that parts of the intestine have already moved into the hernial sac, the doctor can use imaging methods such as Ultrasonic, roentgen, MRI or CT help. However, this is rarely necessary.
An important differential diagnosis of the umbilical hernia is the so-called Diastasis rectus (from rectus abdominis = muscle straight abdominal muscle).
This is a thinning of the fascia of the abdominal muscles without a defect in the abdominal wall. There is therefore no risk of entrapment, which is why there is consequently no indication for an operation.
In the case of a wide gap in the rectus fascia in the midline, one speaks of a "Space belly". This is a serious finding in which the small intestine is only covered by skin. With an ultrasound, however, these similar clinical pictures can be clearly differentiated from one another. The ultrasound should be carried out by a specialist, as many factors are decisive for a usable result, for example in which position the examination takes place or what kind of transducer is used.
Umbilical hernia in pregnancy

An umbilical hernia can occur in women during pregnancy. It is one of the reasons why women are more likely to have an umbilical hernia than men overall.
This can be explained by the fact that the Pressure in the abdominal cavity increases during pregnancy and thus press the internal organs more strongly against the abdominal wall.
Due to the increase in pressure and the stretching of the abdominal wall by the growing child, the distance between the Abdominal muscles also increased.
Between the abdominal muscles, only connective tissue separates the abdominal cavity with the skin. As a result of pregnancy and the associated divergence of the abdominal muscles, both the surface area and the pressure on them increase and thus the risk of suffering an umbilical hernia during pregnancy.
An umbilical hernia during pregnancy should not be associated with the normal "Elapse“Of the navel can be confused.
The spread of the navel against the skin on the stomach of the pregnant woman occurs in many cases and is medically normal and harmless.
However, instead of stroking the navel, should a significant bulging visible occur in the umbilical region, an umbilical hernia can be assumed in most cases.
In general, an umbilical hernia is usually harmless and harmless for both the pregnant woman and the child.
The protrusion that has occurred should be viewed by a doctor, who may confirm the harmlessness of the occurrence, but in most cases it is not a cause for concern.
An umbilical hernia becomes critical during pregnancy if one Loop of intestine in the hernial sac that has occurred, i.e. the protrusion, and causes problems there.
In the worst case, it comes to a so-called acute abdomen, a situation that can be potentially dangerous for both the mother and the child.
An acute abdomen can occur if a Incarceration present. If a loop of intestine lies in the protrusion of the umbilical hernia, it can get stuck and through a insufficient blood supply this part of the intestine, cause problems.
The symptoms of an umbilical hernia during pregnancy do not appear in most cases, in addition to the visible bulging of the umbilicus. But should Pain in the affected region around the navel, as well reddish or bluish changes occur on the protrusion, a doctor must be consulted as soon as possible.
When these symptoms occur, an incarceration and thus the Indication for an operation probably.
The diagnosis of an umbilical hernia is relatively simple for the doctor, especially during pregnancy physical examination and the Buttons of protrusion correct diagnosis by a doctor.
Under certain circumstances, an examination with a. To establish a reliable diagnosis and to determine whether there is an incarceration Ultrasonic respectively.
The therapy of an umbilical hernia during pregnancy can be done in different ways and is designed according to the individual severity of the disease.
For example, therapy can be dispensed with in women who are symptom-free despite having an umbilical hernia and who do not experience any pain.
After the birth of the child and the associated drop in pressure in the abdomen, the Umbilical hernia regress by itself.
If there is pain and possibly even an incarceration, it should definitely be surgery to protect both mother and child from the complications of the disease.
Today's surgical techniques can allow minimal risk for both mother and child.
If an umbilical hernia occurs after birth or does not go away on its own, surgery on the hernia is recommended.
The recurrence an umbilical hernia after a successful operation is almost impossible.
Symptoms of an umbilical hernia in the baby
An umbilical hernia in babies is in most cases absolutely harmless and often resolves completely by the age of three without medical intervention. In addition, if a baby has an umbilical hernia, there are usually no symptoms.
There is no pain, nausea or vomiting. If the umbilical hernia in the baby is painful, there is a risk of entrapment (Incarceration) of the organ sections located in the hernial sac. There is a risk of these intestinal sections dying off, as the blood supply is severely restricted. For this reason, a pediatrician should be consulted immediately in such a case.
If, however, there is reddening and swelling of the belly button, possibly also a purulent navel, this more likely indicates a navel infection in the baby. However, it can lead to inflammation of the navel in the child, usually triggered by the same pathogens as in the baby. In both cases, the pediatrician should be seen as soon as possible so that no complications develop.
Read more on the topic: Umbilical hernia in babies and navel inflammation in babies