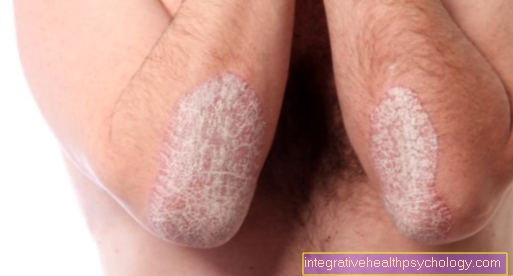
Therapy of psoriasis
introduction
In the treatment of psoriasis, there are three main goals to be achieved:
- Decrease in the speed at which the skin cells migrate
- Anti-inflammatory
- Elimination of triggering factors
In addition to local (topical, e.g. ointments) and systemic (introduced into the organism, e.g. tablets) treatment, UVA radiation is also used to alleviate symptoms.
Local therapy for psoriasis

The local therapy is explained in more detail below:
First, the Dandruff removed with the help of urea ointments and baths. Classical therapy consists of dithranol (in the form of ointments). Dithranol normalizes the excessive proliferation of the epidermis cells.
However, it causes severe skin irritation and stains heavily. Because of the strong skin irritation, it may only be used on the herd, but not on the healthy surrounding area skin, be applied.
The active ingredient concentration is determined individually for each patient. The ointment usually has to be washed off again after a certain exposure time.
Calcitriol, so Vitamin D3 supplements, are also part of local therapy. They inhibit cell reproduction and are usually associated with a UVA / UVB radiation combined. Not only is the increased cell proliferation inhibited, but the maturation of normal skin cells is also stimulated. The effectiveness is about the same as with Cortisone Preparations (Cortisone), in contrast to these, but can be used well for long-term therapy.
Also Retinoids (vitamin A supplements) are used, but must not be used on the face or genitals. Also one pregnancy or breastfeeding (see Breastfeeding) prevents the gift. In addition to inhibiting cell division, retinoids also have an anti-inflammatory effect. They represent an alternative to cortisone therapy.
Glucocorticoids (Cortisone) are also used locally, including on the face and genital area.
They have a strong anti-inflammatory effect and are most frequently administered worldwide for the treatment of psoriasis.
In addition, they suppress the immune reaction and have an inhibiting effect on increased cell division. The undesirable side effects of the locally applied glucocorticoids include, for example, thinning and increased skin vulnerability.
It can also be a so-called steroid acne occur.
Further information is also available under our topic cortisone.
Systemic therapy for psoriasis
Systemic therapy is used when local therapy fails. Systemic therapy is in the form of tablets.
Medications administered include:
- Fumarates
- Methotrexate
- Ciclosporin
- and here too retinoids
- and glucocorticoids.
Methotrexate inhibits the inflammatory processes in the skin and is used for psoriasis with and without joint problems.
It also reduces activated T cells. Since methotrexate damages the liver, this drug may only be used in people with healthy liver. The patient treated with methotrexate should avoid alcohol if possible.
Not only the liver is damaged, but also male germ cells and the embryo in the womb. Therefore, good contraception should be ensured for up to three months after the end of therapy.
You can also find more information under our topic Methothrexate.
The effect of fumarates is based on the inhibition of inflammatory cells and the inhibition of the release of cell messenger substances (cytokines). The therapeutic effect, however, only occurs after about 3-5 weeks. Diarrhea and nausea are some of the undesirable effects.
Ciclosporin is only prescribed for the most severe and therapy-resistant psoriasis. It inhibits the activity of the inflammatory cells and their substances. Because of the possible impairment of kidney function, patients with kidney damage should not receive ciclosporin for therapy.
Retinoids influence the growth and maturation of epidermal cells as well as the inflammatory activity in the psoriasis foci.
Side effects are drying out of the skin and mucous membranes. During pregnancy, there is a high probability that the child will malform. Such a therapy must not be used here.
If possible, glucocorticoids / cortisone should not be used for systemic therapy, as there are considerable side effects, especially in long-term treatment.
Another possible active ingredient for treatment is the immunosuppressant tacrolimus, Enbrel® or adalimumab
Ointments for psoriasis

Therapy for a patient with psoriasis should always be in specified levels respectively. This means that before resorting to more aggressive treatment measures, start with them first Gentle therapy methods possible apply. Ointments and creams are particularly suitable for mild psoriasis. Even with the regular use of these local therapeutic measures, satisfactory treatment results can often be achieved.
Preparation of the skin surface
In order to positively influence the treatment result, the affected patients should a few steps before applying the ointment note. Before the psoriasis ointment is applied to the affected areas of the skin, their must Surface careful of skin flakes be freed. For this purpose are suitable fatty creams or ointments the above Urea or salicylic acid feature. In this context, however, it must be noted that a Salicylic acid-containing ointments should never be applied over large areas may be used on extensive skin areas. Ideally, the ointment is first applied to a small area of the body. If there are no skin reactions even after an exposure time of around ten minutes, the actual treatment can begin. Patients who may be allergic to the application of common ointments and creams alternatively oil baths to peel off the skin surface use. In the case of less pronounced illnesses, special shampoos can already be sufficient to achieve successful psoriasis therapy.
Tar ointment / dithranol ointment
After the skin surface of the affected patient has been scaled and prepared for the use of further substances, the actual psoriasis therapy can be started by applying an ointment. Especially through the regular use one Ointment containing coal tar could so far satisfactory treatment results be achieved. The active ingredients contained in the ointment inhibit the excessive cell division typical of psoriasis, throttle inflammatory reactions and prevent the keratinization of the top layer of skin.
In addition, creams and ointments have been used over the years Active ingredient "Dithranol", a synthetic tar preparation, have proven themselves in the therapy of psoriasis. With regular topical application of this ointment, the typical inflammatory processes and excessive horn production are demonstrably reduced.
The therapy of psoriasis with the help of a dithranol ointment should, however, be viewed critically. Body parts where the ointment overly applied will tend to be a brownish discoloration to accept. For this reason, the therapy of psoriasis with an ointment containing dithranol should be carried out very carefully and sparingly.
In the event of any abnormalities after use (redness, burning, itching), a specialist in dermatology (dermatologist) must be consulted immediately.
Cortisone ointment
Moderate and severe forms of illness usually hardly respond to ointments containing tar. For this reason, the affected patients usually have to go to a Cortisone ointment To fall back on. This ingredient is a hormone, which is also in the Adrenal cortex is formed. When treating psoriasis with an ointment containing cortisone, however, care must be taken to ensure that the surface of the skin very economical is covered. In addition, this ointment is allowed never on children, on the face, neck or genital area be applied.
The reason for this is the fact that the active ingredient is cortisone Skin surface thins and the areas of skin just mentioned are already quite thin. The main side effects of cortisone ointment include redness, burning, and itching. If such a side effect occurs, the therapy must be interrupted and a specialist consulted.
Vitamin D derivatives
In everyday clinical practice, ointments are also used Vitamin D derivatives have proven to be particularly suitable for the therapy of psoriasis. Especially Vitamin D3 ensures with regular application that the It has a positive influence on the growth and maturation of epidermal cells and those typical of psoriasis Dandruff inhibited becomes. According to extensive studies, the effectiveness of the vitamin D-containing ointment can be equated with that of a medium-strength cortisone ointment. In terms of possible side effects, however, vitamin D derivatives are much gentler and better tolerated. The best-known ointments based on vitamin D include: Curatoderm® (tacalcitol), Silkis® (calcitriol), Daivonex® (calcipotriol).
Vitamin A derivatives
The classic ointments over Vitamin A- Offspring are particularly suitable in therapy mild to moderate psoriasis- Characteristics. On average, about 70-80 percent of the herd can be expected to heal after regular use of a vitamin A ointment. If the disease is severe, an ointment containing vitamin A can be combined with an ordinary cortisone cream.
Treatment of psoriasis in pregnancy

Therapy for psoriasis can be problematic during pregnancy. This is especially the case if an expectant mother has a particularly severe form of psoriasis.
The reason for this is the fact that the local application of ointments and creams alone is usually not enough to effectively alleviate the symptoms.
Since most drugs that are suitable for the systemic therapy of psoriasis cannot be administered during pregnancy, treatment often has to be paused.
This is particularly problematic because the classic symptoms of psoriasis increase in many women during pregnancy anyway.
For this reason, women who suffer from psoriasis and are planning a pregnancy should inform their dermatologist at an early stage.
Only then can it be decided at an early stage whether the respective therapy can be continued during pregnancy or whether the patient may have to be switched to another drug.
However, it must be noted that there are not many psoriasis drugs that are approved during pregnancy.
With most active ingredients, it is assumed that damage to the fetus cannot be completely ruled out.
The use of systemic medications can lead to serious malformations, especially during the first trimester of pregnancy.
For this reason, all oral medicines used to treat psoriasis should be discontinued during pregnancy.
This applies in particular to drugs that contain the active ingredients "acitretin" (or other vitamin A derivatives) or "methotrexate".
Both active ingredients can lead to both serious malformations and miscarriages during pregnancy. For women who take one of these preparations, it is important to ensure effective contraception throughout the therapy.
In addition, affected women should not become pregnant after the actual intake (two years in the case of acitretin; four months in the case of methotrexate).
In general, topical drugs for psoriasis therapy can also be used during pregnancy. Creams and ointments containing vitamin A are an exception. These must not be applied during pregnancy.
Read more on the topic:
- Psoriasis in Pregnancy
- Skin changes during pregnancy











.jpg)