Tonsillitis
introduction

The term "tonsillitis" is understood to mean a disease in which inflammatory processes develop in the area of the tonsils (tonsilla palatina). Tonsillitis can be observed in every age group. However, children tend to develop inflammatory processes in the area of the tonsils much more often. In addition, the ambient temperature does not appear to have any influence on the frequency of the development of tonsillitis. Tonsillitis is a highly contagious disease that usually requires antibiotic treatment.
Read more about this under Palatine tonsils
Figure tonsillitis
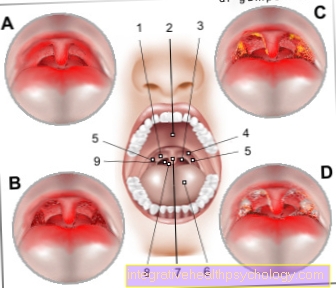
A - tonsillitis - Tonsilitis
B - Simple catharrhal angina -
Angina catarrhalis
C - throat findings in diphtheria
D - ulcers in bacterial
Forms of angina
- Palatine almond bay -
Tonsillar fossa - Hard palate -
Palatum durum - Posterior palatal arch -
Arcus palatopharyngeus - Anterior palatal arch -
Arcus palatoglossus - Palatine almond -
Palatine tonsil - Back of tongue -
Dorsum linguae - Uvula + soft palate
(Soft palate) -
Uvula palatina + palatum molle - Meandering -
Isthmus faucium - Throat (back wall) -
Pharynx
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Based on the course of the disease, tonsillitis can be divided into two different forms. While the inflammatory processes in the so-called acute tonsillitis (Acute tonsillitis) manifest within a very short time, patients suffer with chronic tonsillitis (Chronic tonsillitis) over continuously recurring (recurrent) Complaints. In addition, tonsillitis can be further subdivided based on typical clinical aspects. Patients who participate in a catarrhal anginal tonsillitis suffer from severe redness and swelling of the tonsils. The follicular angina is noticeable through stipple-shaped, purulent coverings on the surface of the tonsils. In the lacunar tonsillitis form on the other hand, in the area of the tonsils, severe reddening and even extensive, confluent (confluent) find purulent coverings.
causes
The main cause of tonsillitis is infection with viral or bacterial pathogens. It is generally believed that most childhood tonsillitis is a viral infection. However, tonsillitis in adulthood seems to be caused by bacteria much more often. The most common bacterial pathogens that lead to the development of tonsillitis are so-called beta-hemolytic streptococci (Strep-A), Pneumococci, Staphylococci and Haemophilus influenza. Due to the fact that a large number of these potential triggers belong to the normal bacterial colonization of the oral cavity, the exact mechanisms of the development of tonsillitis cannot be traced in detail. Above all, a weakening of the general condition of the organism seems to favor the multiplication of the relevant bacteria. For this reason, in addition to tonsillitis, many patients suffer from general cold symptoms (to cough, sniff, fever).
In addition, the psyche seems to have some influence on the likelihood of developing tonsillitis. People who are under severe emotional stress and / or stress suffer from a much higher risk of developing tonsillitis. The reason for this is the fact that stress has an increasing influence on the release of the body's own hormone Cortisol Has. This hormone, in turn, is able to weaken the immune system in the long term and increase the likelihood of an infection. Furthermore there is also for people who attend AIDS or other immunosuppressive diseases have a significantly increased risk of tonsillitis. Since the tonsils are counted as such in the immune system (lymphatic organs), there is a strong bacterial colonization, especially in children. For this reason, many children suffer from purulent inflammation of the tonsils several times a year.
Tonsillitis is a highly contagious disease. The causative germs are per Droplet infection, i.e. transmitted when coughing or sneezing. Transmission through direct contact with contaminated objects is also possible (for example after touching a door handle). For this reason, people who have tonsillitis are advised to keep their hands over their mouth and nose when coughing and sneezing. In addition, greater emphasis should be placed on washing and disinfecting hands in order to protect the immediate environment. It is not clear how long a person suffering from tonsillitis could be a potential carrier of the relevant pathogen. However, it can be assumed that even with antibiotic therapy, those affected are at risk of infection for a period of one to two days.
Forms of tonsillitis caused by viruses are usually highly contagious for a much longer period of time. For this reason, affected patients are advised to pay particular attention to careful hygiene until the symptoms have subsided.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of tonsillitis is usually divided into several steps. In most cases, an initial indication of the presence of tonsillitis can be given during the doctor-patient conversation (anamnese) being found. During the physical examination, the attending physician pays particular attention to painful enlargements of the lymph nodes in the neck area. An inspection of the palate and pharynx should be carried out inside the oral cavity. During the examination, severe reddening in the back of the throat and an increase in the size of the tonsils are noticed. Depending on the type of tonsillitis, there are also purulent specks and / or coatings. Whitish deposits can even appear on the surface of the tongue in a variety of cases. If these findings are typical for the presence of tonsillitis, a blood analysis should also be carried out.
For the further course of the disease and the choice of the appropriate therapy, it is essential to clarify whether it is bacterial or viral tonsillitis. The presence of purulent coatings in the area of the throat speaks in principle more for a bacterially induced form of the disease, but under no circumstances should a blood test be dispensed with. Especially with a sharp increase in white blood cells a bacterial infection can be assumed. By Streptococci of group A (beta-hemolytic streptococci) triggered tonsillitis can be detected within a few minutes by a throat swab. Because some symptoms of acute tonsillitis are similar to those of a more serious condition (Pfeiffer's glandular fever), the liver and spleen should be palpated during the physical exam.
Symptoms
The symptoms of tonsillitis depend on the causative agent. In most cases, patients who develop tonsillitis feel the onset very early Sore throat. Due to the sometimes severe swelling of the tonsils, tonsillitis causes severe swallowing difficulties for those affected. Many patients describe the pain they feel as stabbing. Pronounced clinical pictures cause pain that radiates into the ears. The reason for this phenomenon is the fact that there is access to the ears in the area of the throat. Due to the sometimes severe swelling of the tonsils, this access can be blocked and the ventilation of the ears restricted.
Characteristically, the discomfort in the area of the ears worsens, especially during the swallowing process. In addition, the acute forms of the disease in particular can lead to pain-related restriction of the mouth opening. Due to additional swelling of the Lymph nodes even the slightest movement of the neck can be perceived as painful. Since tonsillitis is a disease caused by bacterial and / or viral pathogens, general symptoms can occur parallel to the inflammation of the tonsils. Inflammatory processes in the area of the middle ear can often be observed, especially in children. In addition, the affected patients often suffer from severe coughs and runny nose. If tonsillitis is caused by a viral pathogen, the simultaneous occurrence of fever is not uncommon.
therapy
Self therapy:
In the presence of tonsillitis, the affected patient can initiate some treatment steps from home. In most cases, the accompanying symptoms in particular can be treated quickly and easily. If the person concerned suffers from pain and / or fever, then light painkillers are suitable. Especially the active ingredients Paracetamol and Ibuprofen are able to effectively alleviate pain and at the same time have an antipyretic influence. Furthermore, cold compresses that are wrapped around the calves (so-called Calf wrap) contribute to a rapid decrease in body temperature. Even if the throat should always be kept warm in the presence of tonsillitis, it is important to ensure that the body does not overheat, especially with children.
If you have pronounced swallowing difficulties, hot tea with a serving of honey can help to relieve. As a general rule, people should drink as much fluids as possible while they have tonsillitis. In addition, the food can be pureed to facilitate food intake. People who suffer from acute tonsillitis should refrain from eating acidic foods within the first few days of illness. Drinking juice can also increase the symptoms noticeably. Cold drinks and ice cream, on the other hand, have a soothing effect on the patient's sore throat and difficulty swallowing. If the symptoms are severe, special lozenges can help relieve both sore throats and swallowing difficulties. In addition, those affected should refrain from consuming nicotine and alcohol, as both substances negatively influence the course of tonsillitis and can exacerbate the symptoms.
Medical therapy:
Before appropriate treatment can be initiated, the cause of the tonsillitis must be determined. In the case of viral forms of illness, the symptoms felt by the patient must be alleviated. The viral infection itself is not treated in the case of tonsillitis. If there is tonsillitis caused by group A streptococci (Strep A), antibiotic treatment must be given. The drug of first choice in these cases is oral penicillin (especially Amoxicillin). Alternatively, antibiotics from the group of Macrolides can be used.
complication
With an early diagnosis and prompt initiation of a suitable therapy, the development of complications in uncomplicated tonsillitis is usually not to be expected. If targeted treatment is neglected and the disease progresses, however, secondary diseases can occur. Possible complications of tonsillitis are:
- Abscesses
The bacterial colonization of the pharynx (in particular the tonsils) can occur with pronounced weakening of the Immune system lead to the formation of abscesses. It is a collection of pus, newly formed tissue cavities. Starting from a tonsillitis abscesses can occur in the so-called Retropharyngeal space (Retropharyngeal abscess) and the tonsils themselves (Peritonsillar abscess, paratonsillar abscess) to be watched. The affected patients usually suffer from severe swallowing difficulties and a visibly restricted mouth opening. Typically, the symptoms in these cases are limited to one half of the body.
- Rheumatic fever
Severe, treatment-resistant forms of tonsillitis can cause the infection to spread to other organ systems. In this context, the heart, kidneys and joints are particularly at risk.
prophylaxis
Since tonsillitis is a disease caused by bacterial or viral pathogens, its development can be prevented in many cases. First and foremost, particular emphasis should be placed on washing hands. The germs that lead to the development of tonsillitis are mainly found on door handles and door openers. People who suffer from a temporary or general immune deficiency should also disinfect their hands several times a day. In addition, the vaccination It is now recommended against a number of the causative bacterial pathogens and has even been fully covered by health insurance companies. Children and people who have reached the age of 60 in particular should be protected against pneumococci and Haemophilus influenza by vaccination.
forecast
With prompt diagnosis and prompt treatment, the prognosis for tonsillitis is extremely good.As a rule, viral forms of the disease heal completely within one to two weeks. In most cases, bacterial tonsillitis disappears completely within a week with antibiotic treatment.











.jpg)