gonorrhea
Synonyms in a broader sense
Gonorrhea
Introduction / definition
Tripper is a globally widespread, highly contagious, sexually transmitted disease that occurs only in humans (STD = sexually transmitted diseases) caused by infection with so-called gonococci (Neisseria gonorrhea) is triggered. These gram-negative, oxygen-dependent (aerobic) After transmission, bacteria can infect the mucous membranes of the sexual organs, urinary tract, intestines, throat and conjunctiva of the eyes.
causes

The reasons for infection with the Gonococci usually suffer from infection unprotected sex (without a condom) with an infected person. Other sexual practices such as anal or oral sex can also lead to the transmission of the bacteria. People with experience a particular risk of infection with gonococci frequently changing sexual partnerswho have unprotected sexual intercourse.
Since the symptoms of the disease are initially absent, the infection remains long undiscovered and can be spread like that.
Furthermore, infection can also be from someone with gonorrhea infected mother happened to the child during birth and should therefore be diagnosed in the mother before birth.
Frequency distribution
The World health organization (WHO) estimates the number of new cases (incidence) per year at approx. 60 million (1% of the world population). In Germany there are around 11-25 sick people per 100,000 inhabitants. Usually the younger population (around 30 years of age) is affected by gonorrhea.
Since 2000, gonorrhea is no longer one of the notifiable diseases in Germany.
diagnosis
The typical symptoms described by people infected with gonorrhea are a first indication of an infection with the bacteria (Neisseria gonorrhea) given. As a next step, the doctor should carefully inspect the affected parts of the body. For a closer examination it is necessary to rehearse of the possibly infectious fluid secretions (e.g. from the cervix or urethra) remove. This can then be done with a so-called Gram stain examined under the microscope. However, microscopic examination is not always sufficient. To confirm the diagnosis, the fluid sample should be sent to a laboratory in which a culture is set up on a nutrient medium. It is now being investigated whether the gonorrhea causing gonococci to settle. At the same time a so-called Antibiogram designed to test whether there is any resistance to certain Antibiotics are available for the treatment of gonorrhea, and so another form of therapy is necessary.
Another way of securing the diagnosis of gonorrhea can be through an examination of the pathogen genome with the help of a so-called PCR = Polymerase chain reaction take place.
Symptoms
It usually takes a few days for the first signs of a gonorrhea infection to show up. Women in particular often have very few or no symptoms at the beginning, which makes further infections and disease complications possible when starting therapy later.
In women, infection with the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhea can manifest itself as a slight discharge from the vagina. However, this is often viewed as not unusual. If the glands at the vaginal entrance are inflamed (Bartholini-Glands), which can be caused by the bacteria, those affected complain of pain in the vaginal area, which mainly occurs when sitting. Inflammation of the cervix (Cervicitis) or the urethra, which are expressed as pain, discharge or other complaints, are possible. Severe pelvic pain and fever indicate an ascending infection with inflammation of the fallopian tubes or ovaries, which must be treated as soon as possible. In addition to the uterine inflammation and inflammation of the ovaries or fallopian tubes, inflammation of the peritoneum (Peritonitis) and infertility due to adhesions and adhesions of the fallopian tubes are possible complications of gonorrhea in women.
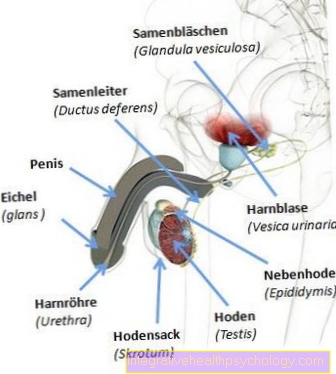
Men usually have a so-called purulent "Bonjour drop" in the morning, which is caused by an inflammation of the urethra by the gonococci. This secretion usually emerges from the urethra before the first morning urination. In addition, pain when urinating and redness and swelling of the urethral opening can occur. An increase in the infection, which is a complication of gonorrhea, can lead to pelvic and testicular pain. Other notable complications are epididymitis (Epididymitis), Prostate inflammation (Prostatitis) or the impending infertility (sterility).
When infected with gonococci as a result of anal or oral intercourse with someone infected with gonorrhea, inflammation in the throat (Sore throat) or the intestinal lining (Pain when defecating / mucus) occur. Conjunctivitis from contaminated hands is also possible.
In both men and women, the spread of bacteria via the bloodstream is a serious complication of gonorrhea. Joint pain and inflammation of the joints, as well as fever and skin changes (Blistering). Blood poisoning (Gonococcal Sepsis), meningitis (Gonococcal meningitis) or inflammation of the heart (Gonococcal endocarditis) represent dangerous complications.
Please also read our article on this Burning sensation in the urethra.
therapy
To treat gonorrhea you need one Antibiotics-Therapy. These are supposed to kill the causative bacteria in a targeted manner. Nowadays it is usually called a Cephalosporin antibiotic of the 3rd generation used because many resistances have already developed against older antibiotics. During treatment and until healing should be refrains from sexual intercourse become. In addition, the simultaneous treatment of sexual partners of great importance, as these too may have been infected with the bacterium.
prophylaxis
The use of Condoms provides good protection against gonorrhea infection, but infections cannot be ruled out even when using condoms.
forecast
If gonorrhea is detected early, the infectious disease usually heals without consequences.