Troponin
definition
The protein troponin is an important component of the contractile apparatus of the heart and skeletal muscles. Together with tropomyosin, its main task is the regulation of muscle contraction on a microscopic level.
The troponin is a complex of the building blocks troponin T, I and C, each of which has its own partial function and can only function together. Both the skeletal muscle and the heart muscle each have their own group of these different troponins, which differ in their structure and function. This is why the so-called troponin value is of great importance in diagnosing various heart diseases. In the so-called smooth muscles, such as the intestinal wall, troponin is completely absent.

Components of the troponin complex
Troponin T
Troponin T is that largest subunit of the troponin complex. Together with troponin I and C, it regulates the conversion of the electrical nerve signal into one Muscle contraction.
Here it works over Tropomyosin in a way, like a brake for the contractile muscle proteins. If a nerve signal reaches the muscle, this brake is released by detaching it from the muscle proteins. These can now contract unhindered.
One finds in the body three types of troponin T, so-called isoforms. One is typical for the heart muscle, while two more are found in the skeletal muscles. The troponin T of the skeletal muscle is further differentiated into a form that is primarily found in slow but persistent muscles and one that is mainly found in muscles of the faster type.
The for the Heart muscle The typical form of troponin T occurs in high concentration only in the heart. Therefore it is of great importance for clinical diagnostics. The so-called hs - troponin T certainly. One speaks of increased troponin levels, is mostly an increase in Troponin T concentration in the blood meant.
Troponin I.
Troponin I is also part of the troponin complex Regulation of muscle strength involved. On the one hand, it serves the Fixation of the entire troponin complex to its position in the muscle cell. According to new findings, however, it also comes together with troponin T and tropomyosin regulatory effect to. It does this by preventing muscle contraction until the signal for contraction has arrived via a nerve.
Exactly as with troponin T one finds with troponin I. three isoforms. While one can only be found in the heart muscle, the other two are distributed between fast and slow muscle fibers in the skeletal muscle. Only about 4% of the troponin I is free in the muscle cell, so it is not bound to proteins of the contractile apparatus or involved in the troponin complex. At a Damage to the muscle cell first becomes this free portion in the blood released and can be detected there by laboratory tests.
Troponin C
Although troponin C is the smallest protein in the troponin complex, it comes in the Regulation of muscle contraction a Key role to. When a nerve activates a muscle, the concentration of free calcium ions increases in its interior due to the electrical activation. A single troponin C binds again four of these Calcium ions and can then do a Change in shape of troponin I and T initiate. Only now can the muscle contract.
One speaks of the so-called electromechanical coupling, as the electrical signal from the nerve is converted into mechanical muscle movement. Unlike with Troponin T and I. no heart muscle specific shape of troponin C. Only so-called fast-twitch skeletal muscles have their own isoform of troponin C, slow-twitch skeletal muscles and the heart muscle, on the other hand, share a second isoform. Since an increase in the concentration of the Troponin C not specific for one of the two muscle groups, it is only determined in a laboratory in exceptional cases.
function
The entire troponin complex consists of Troponin C, I and T. In the skeletal and heart muscles, troponin I and T work together with the muscle protein tropomyosin like a attracted Brake on muscle contraction. This is probably done by a simple cover and with it Blocking of the interaction points of contractile muscle proteins at rest.
Only when a muscle over one Nerve the signal gets to contract, this brake is released and muscle movement occurs through a shortening of the contractile apparatus. At the microscopic level, this signal is one Increase in calcium levels in the plasma of the muscle cell. Calcium ions are through Troponin C bound what a Deformation of the troponin complex triggers a so-called Conformational change. Through this Conformational change the whole complex shifts a little and so gives the Free interaction sites for muscle proteins, there is a contraction.
This process happens in the contracting muscle due to the increased calcium levels in the entire cell plasma in millions of places simultaneously. The decisive factor for the strength of a muscle contraction is Strength of the incoming nerve impulse. A very strong stimulus causes the calcium concentration to rise more, which deforms almost all of the troponin. A great many points of interaction of the contractile apparatus are then exposed. As a result, the muscle contracts stronger and faster than with a weaker stimulus.
Troponin test
The troponin test determines the concentration of troponin in the blood. Often only troponin T and I are tested, since these two proteins are heart muscle-specific, so they usually only occur there.
To test the troponin concentration, a small amount of blood is drawn, usually from a vein. Normally, one tests the concentration in the blood serum, i.e. the watery part of the blood. The actual test is carried out with the help of a so-called immunoassay. With this precise method, the troponin concentration can be precisely determined.
Alternatively, there is a rapid test, the functionality and evaluation of which is similar to a commercial pregnancy test, but is carried out with blood. However, the rapid test does not allow a precise determination of the concentration, but only detects an increase in troponin above normal. The measurement of the troponin concentration is repeated after a period of several hours. In an acute process, such as a heart attack, one would notice a change in the values. If, on the other hand, both values are similar, the cause of the troponin increase has probably already existed over a longer period of time.
Read more on this topic at: Troponin test
Standard values
Cardiac troponin occurs in a healthy adult almost not in the blood in front. There is therefore no value that is too low.
In the case of troponin T, the limit value for a potentially dangerous increase in troponin is at a concentration of over 0.1 ng / ml (0.1 µg / l). If there is a severe heart attack, this value can rise to 90 ng / ml and more. The situation is similar with the normal value of troponin I. Here, too, the concentration should be below 0.1-0.2 ng / ml amount, with healthy it is in hardly detectable amounts available.
What does a troponin increase mean?
A Increase in troponin levels can have many reasons. Very often they rely on one Damage to the heart muscle lead back. This is the only tissue of man in which one is large amounts of cardiac troponin Can be found. Even with minor damage to the heart muscle, the troponin value increases measurably.
However, must not always a heart attack be the cause of an increase in troponin levels. Already at minor circulatory disorders of the heart muscle, the values can change due to cell damage. Also one Inflammation of the heart muscle, the so-called Myocarditis or dysfunction of the heart, the so-called Cardiomyopathies can cause elevated troponin levels.
At poor kidney function there is no filtering of the blood and troponin T can accumulate in the body. Come several of these factors together, the troponin value can be significantly changed, without causing acute damage to the heart muscle caused by, for example, a heart attack. A clean Increase in troponin concentration in the blood is thus relatively unspecific, should not happen in completely healthy people.
Signs of a heart attack
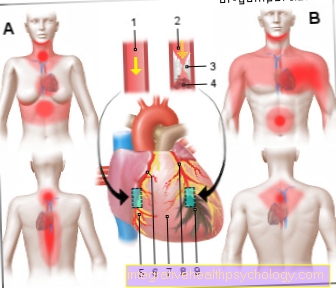
Troponin in a heart attack
Troponin T is the one these days most important laboratory parameters for safe Heart attack diagnosis. The root cause a heart attack is that Occlusion of an artery, which is normally responsible for the supply of the heart muscle. This can be done, for example, by a Blood clots happen. As a result, the muscle cells that are not supplied perish. If this happens, the Permeable cell membrane for larger proteins like troponin. Therefore occurs Troponin into the blood during a heart attack from where it can be detected.
Since a large part of the troponin is bound to other proteins intracellularly, this happens not immediately after closure a coronary artery and the associated symptoms.
An initial increase occurs depending on how much heart muscle is affected only three to eight hours after the onset of the infarction. Maximum values are often only reached up to four days later. Several weeks after a heart attack should be the Values normalized to have.
Diagnosis of myocardial infarction
Troponin in renal insufficiency
In healthy people the kidney filters the blood. This is no longer the case with kidney patients. This insufficient kidney function is called Renal failure. What becomes available Troponin accumulates therefore in the blood and it comes an increase in the long term the troponin value without direct cardiac muscle damage. Often, however, patients with severe kidney damage are also heart damaged or at risk.
The causes for this are varied and often range from anyway old age the patient, the role of the Kidney in blood pressure regulation up to the hormonal interplay between heart and kidney. Clinical studies have shown that high troponin levels in patients with kidney failure also suggest that the heart is at risk. That's why they can of great importance in terms of prognosis be.
Read more about this at:
Renal failure