U4 investigation
What is the U4?
The U4 preventive medical check-up is part of the preventive care program for babies and children in order to monitor their physical and mental development and to be able to intervene directly in the event of difficulties. The U4 is particularly about sleeping and eating habits, motor skills and the baby's attention.
Furthermore, the child can be prescribed fluoride and vitamin D again and the screening appointment can also be used as a vaccination appointment for the six-fold vaccination against tetanus, diphtheria, whooping cough, hemophilus, hepatitis B and pneumococci.
You might also be interested in: Vaccinations in the baby
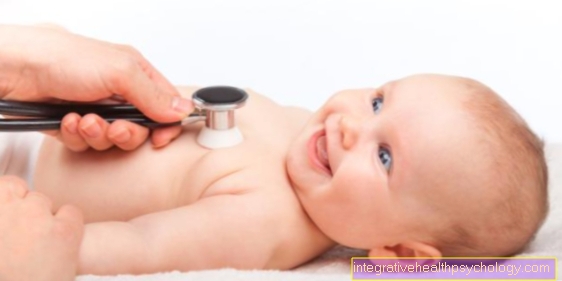
When will the U4 take place?
The fourth check-up is carried out in the third to fourth month of life. The earliest possible time is from the second month of life and the latest possible time is four and a half months. If the examination is to be carried out outside of this time frame, the parents have to pay for it themselves.
The appointment can be adapted to the baby's vaccination calendar so that no additional appointment with the pediatrician is necessary.
Which examinations are carried out?
First, the parents are given a questionnaire in which they fill out what they have observed in their child. The actual examination of the child does not begin until this questionnaire has been evaluated.
The first part of the exam consists of a detailed physical exam that includes measuring and weighing the child.
- The pediatrician will look at the baby's eyes and skin and assess the color and texture. In this way, the doctor can already see possible liver dysfunction or a lack of oxygen from the color of the skin.
- The pediatrician will also examine the baby's stomach and listen to the heart, lungs and stomach. The examiner pays attention to conspicuous heart noises and breathing noises, as well as too strong or too weak digestive noises. Palpation of the abdomen also reveals a possible enlargement of the spleen or liver. If you are unsure, the pediatrician can also perform an ultrasound of the affected areas.
- The pediatrician also feels the baby's fontanelles, i.e. the gaps in the skull, to assess whether the head can grow sufficiently.
- Part of the physical exam also includes testing the mobility of the baby's joints. In the next step, the doctor tests various reflexes and the child's muscle strength. To do this, the examiner pulls the baby up by the hands and checks whether the baby can already hold its head itself.
The physical exam is followed by a vision and hearing test:
- The baby should be able to turn its head towards a sound source. This is tested by having the pediatrician make various sounds with paper or rattles.
- Furthermore, the child should be able to fix people with their eyes and also be able to follow them.
- The baby should also be making babbling sounds, which indicates the beginning of language development.
In addition to the physical examinations, parents are also given advice on nutrition and sleep behavior.
If requested by the parents and at the right time, the second six-fold vaccination will be carried out. This is a vaccination against tetanus, diphtheria, hemophilus influenzae type B, whooping cough, hepatitis B and pneumococci. The pediatrician also recommends the administration of vitamin D and fluoride.
Further appointments for vaccinations and screening can then be arranged.
You might also be interested in: U examinations
Procedure of the U4
The preventive examinations always follow a similar scheme. After a meeting with the parents, a physical exam will be performed first. The child is weighed and measured and the values are compared with peers.
The organs are wiretapped and scanned so that undesirable developments and diseases can be recognized at an early stage. The preventive examinations for babies always include palpation of the fontanelles on the skull. If the parents have noticed something in advance, the pediatrician specifically addresses these observations.
Furthermore, a movement test is always part of the investigation. The age-typical range of movement is checked and the child's reflexes are tested. After this, the pediatrician carries out some special examinations, such as vision and hearing tests.
Following the examination, the baby will receive any pending vaccinations and the parents will be advised on nutrition and sleep. It is advisable to arrange further appointments directly.
Does my child have to go to U4?
The preventive medical check-ups in babies and toddlers should be attended to identify illnesses in good time.
Participation is not compulsory, but paediatricians must report missed appointments to the youth welfare office after repeated reminders from the parents. This is done to protect the children from abuse.
In some federal states, proof of participation must also be provided if the children are to be registered in a daycare center or school.
What happens if I go to U4 with my child?
Since the examinations take some time, an appointment with the pediatrician should be made beforehand. First of all, the parents should report how the baby has developed since the last examination. This is followed by a physical examination and various function tests to clarify the physical and mental development of the baby.
The check-ups are always an opportunity for parents to ask questions. The results of the examinations are entered in the yellow booklet and in the event of abnormalities, a referral to a specialist is issued or physiotherapy is recommended.
Who bears the costs of the U4?
The U4 preventive medical check-up belongs to the spectrum of all health insurance companies. However, in order for the costs of the U4 to be covered by the health insurance company, this must be done within the specified time frame.
The vaccinations that can be carried out for this check-up are also paid for by all health insurance companies and are independent of the exact time frame of the check-up. This also applies to most of the other preventive medical examinations in childhood with the exception of U7a, U10, U11 and J2, which are only partially covered.
How long does the U4 take?
A check-up usually takes between 15 and 20 minutes. However, this time is very variable and depends on the child. Additional examinations may be necessary if there are any abnormalities. In addition, the time frame depends heavily on the advice given by the parents, who have very different questions about the development and care of their baby.