Strained calf
introduction
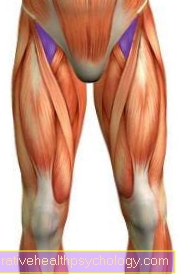
The calf strain is one of the most common injuries in orthopedics and sports medicine. The specialist speaks of one Distension. As with strains of other muscles, the cause of a strained calf is an excessive stretching of the muscle.In itself, a calf strain is a banal injury that occurs in the majority of cases in athletes and does not require any special therapy. Running, soccer or tennis, in particular, are sports with an increased risk of straining the calf. If the symptoms are very severe or persistent, the injury should be clarified to rule out a more serious cause of the pain. There are several muscles on the calf, mostly the Triceps surae muscle is affected.

Symptoms
A strained calf causes a number of typical complaints. Initially, there is unusual or excessive strain on the calf. First, the strained calf makes its way through light pulling on the back of the lower leg noticeable what becomes in the course of a sharp pain developed. This is an important criterion to avoid a strained calf Torn muscle fiber of the lower leg or. Torn calf muscle distinguish in which the pain suddenly kicks in and doesn't gradually get worse. Cramp-like complaints are often described.
Attempting to resume previous activity after a short break is usually not possible due to the pain. After a short time you can feel it Hardening of the calf, through a slight swelling explained in the muscle. Additionally the muscle contracts reflexively. Pain and damage to the muscles result in a strained calf Loss of function the calf, which, depending on the extent of the discomfort, can be pronounced. Climbing stairs is typically difficult, and standing on tiptoe is difficult. There is no bleeding, swelling is not visible from the outside.
Read more about the symptom: pulling in the calf.
root cause

The muscles are made up of many small fiberswhich are closed in bundles and form a muscle in their entirety. They contain a large number of elements connected in series that Sarcomeresthat cause the muscle to contract. Because of the constant alternation between tension and relaxation of a muscle, they are Muscle fibers stretchable. However, excessive stretching does lead to Injury and overstretching of these elements: the muscle is strained.
Typical movements that lead to a strained calf are those in which a sudden heavy load is placed on the muscle. This is especially the case when the knee is extended and the foot is raised at the same time, as e.g. when lunge in tennis occurs. Running uphill leads to calf strains as often as running on difficult and uneven terrain. But also Maximum loads the calf with normal leg position can often cause a strained calf. Typical sequences of movements for this are quick and sudden, repeated starts Accelerations with sudden braking. This explains the increased risk for tennis players and soccer players. A strained calf is not uncommon, especially with amateur athletes who do not have well-trained muscles.
In addition to the causal burden, external circumstances favor the risk of a strain. The main cause in this context is one insufficiently warmed up muscles. Due to the sub-optimal blood flow, the muscle fibers are more susceptible, which is particularly important in combination with cold and wet weather. In addition to this is a tired and overworked muscles predestined to suffer a strained calf. A unbalanced diet Especially those with dehydration and deficiencies in certain nutrients such as calcium or magnesium can promote such a sports injury. Do last Misaligned feet or wrong running shoes with a lack of cushioning or a poorly adapted shape, the development of a calf strain is more likely.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of calf strain is primarily one clinical Diagnosis without a large outlay on equipment, which can be made by an experienced layperson As with almost all illnesses and injuries, it all starts with anamnese. Good indications are the first appearance of the pain during exercise, which begins insidiously at the beginning and gets worse over the course. The following Hardening of the muscle, possibly with Convulsions, confirms the suspicion. In some cases, the person affected can also indicate a certain movement as the trigger. The findings are supplemented by a functional test of the calf. However, this can have a wide range of hardly any restricted function to permanent protective posture exhibit. These findings without further symptoms are usually sufficient to recognize the strained calf as such.
The following diagnosis consists of the fact that the strained calf does not offer any visible evidence and does not cause any typical signs in imaging procedures Exclusion diagnosis of serious injuries. This is only necessary in case of doubt if e.g. the pain does not improve after a few days. A tendon tear can be excluded by certain movement tests. If you suspect one Muscle tear helps one Ultrasonic the calf as well as a classic Palpation with local swelling and bruising. As a last measure, if the cause is still unknown or not clearly differentiated, a Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the lower leg make sense.
therapy
In most cases, the strained calf can be adequately treated with a few simple means. As long as the involved structures of the muscle are not injured, the focus of the therapy is the PECH rulewhich is useful for almost all muscular or bony injuries. These are conservative measures with 4 components:
1st break

Immediately after a calf strain is noticed, running training, playing football, playing tennis, etc. should be stopped. A complete relief of the calf for at least 3 days With subsequent advanced training has shown better results than the earlier recommendation of a longer break. Then, depending on the pain, you can start with light exercises to bring the muscle to bear. 4-6 weeks long, however, the person concerned should have a avoid maximum stress. How long the break must be depends on the severity of the calf strain.
2. Ice
Pain-relieving and decongestant effects have in all cases cooling measures. Reusable ones are particularly suitable Gel cooling packsthat adapt well to the shape of the calf. These must be wrapped with a cloth before being applied to prevent cold damage to the skin. The earlier it is started, the greater the effect of cooling.
3. Compression
In addition to the measures described, a light compression bandage good results around the calf too. With a elastic bandage wrap the calf between the knee and ankle with a gentle pull. This gives the hardened muscle an additional stimulus and the signal that it is too tense. As a result, a slight relaxation is observed. The intramuscular swelling is also positively influenced. It should be noted that a certain pressure should be exerted on the calf, but without restricting blood flow.
4. Elevate
The last point of the PECH rule involves elevating the leg affected by the strained calf. Following gravity the muscle swells better. Elevation also protects the calf and there is no strain.
In addition to the PECH rule, there are other useful measures. For acute pain relief, the common remedies such as Diclofenac or Ibuprofen. In addition to relieving pain, they reduce the inflammation that may result from straining the calf. Under no circumstances should you take painkillers in order to participate in the next competition. After the days when no exercise should be done, locks in easy training on. This can come from light stretching and gymnastics and increase the load step by step, whereby you should not train "into the pain". swim and To go biking are good alternatives for continuing to exercise while straining your calves. As a rule, a calf strain can be cured without any problems. However, if the pain persists for a long time, further clarification must be carried out with a specialist.
forecast
The forecast a calf strain extremely positive. It is a common injury that in almost all cases heals after a reasonable amount of time. In the majority of cases, that is Consultation of a doctor not necessary. Complications that can occur are caused by too early and, above all, too much stress after the strained calf. One should listen to one's body and take pain seriously as a warning signal. An unhealed calf strain can, in the worst case, lead to premature stress Torn hamstring possibly with violation of Tendons to lead. Treating this injury then takes significantly longer than taking a few days off and giving the calf strain the time it needs. Careful stretching and gymnastics exercises after 3-4 days have one accelerating effect on healingas long as it is not overloaded.
prophylaxis
The calf strain is an injury that can be dealt with using simple methods targeted prevention or at least that Significantly reduce risk can. As a mandatory task of every athlete should be a careful Warm-up program with subsequent Stretching exercises must be completed before the load is increased. This can prevent a strained calf. In addition, must be on suitable footwear be taken care of with sufficient suspension. Some sports shops offer one for this free running analysis on.
When choosing the running route can be on one level ground without many roots are respected, as the risk of incorrect loading is higher here. Finally, the extent of the training should be chosen so that you do not stand too often and too long under maximum stress, as well as your body at regular intervals for regeneration.
Illustrations on the subject
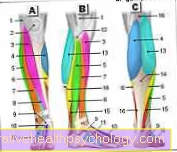
Illustration
Muscles - lower legs
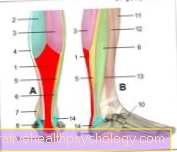
Illustration
Achilles tendon
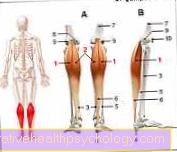
Figure calf muscle
Gastrocnemius













.jpg)