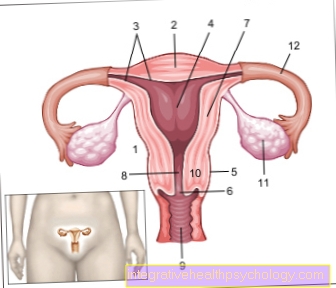
What is a contraction drip?
Definition - what is a contractions drop?
A contraceptive drop is an infusion that contains the active substance oxytocin. This infusion is used in obstetrics to induce childbirth with drugs. This means that this oxytocin is used to induce labor. This should enable a spontaneous delivery if the deadline is missed.
Oxytocin is a hormone that is naturally produced in the human body. During and after childbirth, it causes the muscles of the uterus to contract and thus promotes labor. Oxytocin also strengthens the mother-child bond and promotes milk secretion from the breast. The name oxytocin comes from ancient Greek and means "easily giving birth".
Find out everything about the topic Induce labor

Who needs a contraction drip?
The so-called contractions drop is used to induce childbirth with medication.
Pregnant women who have missed their due date are given a contraceptive drip to help them give birth. The calculated due date is often exceeded and this does not pose a problem in itself. In obstetrics, transmission is spoken of after the 42nd week of pregnancy.
However, if the limit is exceeded, the birth must be initiated with medication. The oxytocin infusion, or the contraction drip, has established itself as the standard method of inducing labor in a mature cervix.
What are the risks of a contraction drip?
The contraction drop is only used under medical supervision so that any complications or side effects can be competently countered. With the correct dosage and good monitoring, a contraceptive drop is very well tolerated.
However, side effects can occur in rare cases.
Side effects of an overdose of the contraceptive drop
Overdosing can lead to uterine overstimulation. This can result in excessive contractions, impaired breathing in the newborn or even a rupture of the uterus.
If the drug is administered too quickly, it can also lead to a sudden drop in blood pressure (hypotension) and reduced blood flow to the heart muscles (myocardial ischemia), especially if the patient has previous heart diseases.
More common side effects of the contraction drip
Some of the more common side effects of a contraction drip include
- a headache
- Tachycardia (too fast heartbeat)
- nausea
- Vomit
Rare side effects of the contraction drip
The following reactions to the contraceptive drop have been reported very rarely:
- Coagulation disorder resulting in thrombosis and embolism
- Allergic reactions
- Reduced excretion of water by the kidneys and associated water poisoning (can lead to cerebral edema)
How does a contraction drop work?
The active ingredient of the contraceptive drop is a hormone that is naturally produced in a special part of the brain, namely in the hypothalamus. This hormone is oxytocin.
Oxytocin takes on various functions in the human organism.
Among other things, it promotes interpersonal bonds, which is why it is often referred to as the "cuddle hormone".
Oxytocin takes on important tasks during and after birth.
It encourages the uterus to contract, causing labor. In the case of a weak contraction, the contractions can be intensified and the birth can be advanced.
Furthermore, oxytocin causes the placenta to be excreted after the birth and the postpartum, i.e. postnatal, bleeding is stopped.
After using a contraction drop, contractions usually occur within a few hours.
What are the alternatives to a contraction drip?
The contraceptive drip has established itself as the medical standard in the drug induction of childbirth. The contraceptive drop can only be used if the cervix is already mature.
If the cervix is still closed, so-called prostaglandins can be used to induce labor. These are messenger substances that act on various receptors - i.e. binding sites - in the body. Prostaglandins also have an effect on the cervix, among other things.
There they can be applied directly in the form of a gel. Application in the form of vaginal tablets or pessaries is also possible. Prostaglandins cause the cervix to open. Prostaglandins can also induce labor.
Another possible side effect of using prostaglandins is overstimulation of the uterus, which can be associated with an increased heart rate of the fetus and so-called fetal stress. However, with the correct dosage and medical supervision, the risk of such complications can be reduced.
Studies have also shown that the rate of spontaneous births within 24 hours of using the prostaglandins could be increased significantly, whereas the rate of caesarean sections was reduced.
Find out about contraceptives and Home remedies
How long does it take from the start of the contraction drip to the birth?
The contraceptive drop must be administered continuously. This means that a stable concentration of the active ingredient oxytocin must be achieved in the body.
Therefore, the infusion runs at a relatively slow rate over several hours. However, the speed and duration of administration also differs depending on the dose of the drip. This is adapted to the existing labor activity, which is always monitored with the CTG.
So it may well be that after 2 hours there are enough contractions and the birth begins.
However, a speed of around 2 ml per minute should not be exceeded. For a total of approximately 500 ml of the infusion, this results in an approximate duration of 250 minutes or 4 hours and 10 minutes.
If the running-in speed is too fast, there can be considerable side effects, which is why sufficient time is very important for the administration of the contraceptive drop.
After the administration of the contraction drop, contractions usually occur within a few hours. However, this can differ from woman to woman. However, many women can expect to go into labor within 3 to 4 hours.
The birth itself then usually takes another hour or so. In some cases, however, there may still be insufficient labor in the CTG after a full infusion. In such a case, the attempt to induce labor is terminated. It can be repeated the next day.
Can I expect pain when using a contraction drip?
Childbirth pain differs from woman to woman. There are various factors that can make childbirth worse.
For example, according to research, being very overweight appears to increase pain during childbirth.
Psychological factors, such as anxious or stressed expectations, can further aggravate the pain at birth.
It is important to understand that the pain experienced during childbirth is very individual. It is therefore not possible to make a general prediction of how severe or weak the pain to be expected will be.
This is also not possible with the use of a contraceptive drop. The contractions can lead to intense and therefore painful labor, but this does not have to be the case.
Furthermore, one cannot say how strong the pain is felt by the pregnant woman in the end, as this depends heavily on their own pain tolerance.
The pain associated with using a contraction drip does not have to be stronger than the contraction pain without a drip.
Read our articles about this:
- Pain in childbirth
- How can you relieve birth pains?
Contractions after caesarean section
A contraceptive drop can also be used after a caesarean section. This may sound ambiguous at first, but it is easy to explain.
The contraction drip promotes contraction, i.e. movement, of the uterus. After the child is removed from the uterus in a caesarean section and the placenta has been removed, the uterus must contract and move in order to stop the bleeding.
This can be supported with the help of a contraction drop. In the right dosage, oxytocin helps stop postnatal bleeding.
This procedure is particularly useful for women with a known weakness in labor who have already had several caesarean sections or after the birth of a very large child (macrosomia).
Get more information about the Caesarean section