How can you recognize a thrombosis?
introduction
A thrombosis can occur on average in every second German in the course of their life. One differentiates thromboses Arteries and Veins, whereby the venous thromboses are more common.
A Blood clots the deep leg vein goes with one swelling and Pain on the affected leg.
If left untreated, the thrombosis poses a high risk for one Pulmonary embolism which is life threatening. The timely detection of a thrombosis can save valuable time.
While the symptoms are not always clear, there are signs that shouldn't be ignored. Depending on your own risk of thrombosis preventive action to prevent thrombosis.
definition
A thrombosis is a blood clot that blocks a vessel.
The clot consists of Platelets (Platelets), which usually close a bleeding wound.
The clumping mechanism of the blood protects the body from bleeding to death. If, on the other hand, the Clotting ability of the blood, thrombi can also form within the vascular system.
As a result, not only does the risk of a life-threatening pulmonary embolism increase, but also of an insufficient oxygen supply to the downstream organs.
root cause
Hereditary and external factors can influence blood coagulation and impair its function.
There are basically three main causes that contribute to the formation of a thrombosis. They are known as Virchow's triad: A disturbed balance of anticoagulant and coagulant factors in the blood, an internal injury to the vessel walls or insufficient blood circulation after long periods of immobilization (phases with little movement, such as being bedridden).
The composition of the blood is based on a sensitive balance of substances that promote and inhibit coagulation. Hereditary factors such as an increased tendency to clot, an APC resistance or a protein S deficiency disturb the balance.
Pregnancy, certain medications such as the contraceptive pill and severe dehydration also promote coagulation (see: Thrombosis risk of the pill).
The less the blood can circulate in the vessels, the higher the risk of developing a thrombosis.
Sitting for long periods of time, for example when flying, being bedridden due to an illness and pathologically dilated veins (varices, varicose veins) all contribute to a restriction in blood flow.
Blood platelets accumulate not only in the event of external injuries, but also in the event of internal damage to the vessel walls. These can occur after operations and accidents, as well as in the course of the natural aging process, diabetes mellitus ("diabetes") and cigarette consumption.
Thrombosis of the arteries can cause a heart attack or stroke.
Blood clots in the veins affect either superficial or deeper vessels. Thrombophlebitis is the inflammatory thrombosis of superficial veins. If the clot moves deeper, it can lead to deep vein thrombosis.
Read more on the topic Thrombosis causes
These causes can also lead to a pelvic vein thrombosis. This is problematic because of its symptom-free course, which is why it can be discovered too late. Also read the following article in this context: Pelvic vein thrombosis
The Pregnancy-associated thrombosis is a deep vein thrombosis that is primarily localized in the left leg. Their occurrence is one of the most common complications in pregnancy.
It usually occurs before the 20th week of pregnancy. The risk remains until twelve weeks after delivery. Obesity, regular vomiting and little movement increase the chance of a blood clot.
diagnosis
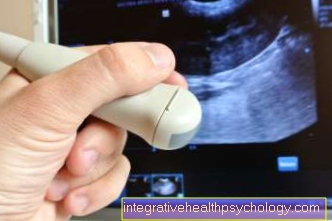
If symptoms suggest a thrombosis, should urgently consulted a doctor become. Especially after long journeys, is increased vigilance required.
In addition to questions about the medical history and possible risk factors (anamnesis), the attending physician conducts a physical examination to identify a possible thrombosis.
After a blood draw, the value of the so-called D dimers certainly. It refers to Degradation products of thrombi. If the D-dimer test is negative and the overall clinical picture is normal, a thrombosis can be ruled out with a high degree of certainty.
If the test is positive, an Doppler- or. Duplex-Ultrasonic performed to detect thrombosis.
By squeezing the vessel, the examiner can determine whether the blood flow is restricted. A Venography (X-ray examination of the vein with contrast agent) is used to clarify uncertain findings.
Frequency distribution
The risk of venous thrombosis increases with age. Every year around 1,000 out of a million people in Germany are affected. In most cases, thrombosis occurs in the deep veins in the legs and in the pelvic veins.
Symptoms
Even if the symptoms of a thrombosis are often ambiguous, they should be taken seriously.
Some thromboses lead to symptoms only in the course of the disease and can cause life-threatening pulmonary embolism despite harmless signs. Typically, venous thrombosis is accompanied by swelling and a feeling of tightness.
The skin is overheated, reddened and feels plump and tense. In addition, tenderness and pain can occur.
If the location of the thrombosis is in the leg, the symptoms are significantly alleviated after elevation.
Read more on the topic: Burning in the legs
Fever and an increased heart rate can also be observed in some cases and can help to identify a thrombosis.
The symptoms are similar regardless of whether the thrombosis is in the leg, pelvis, or arm.
A leg vein thrombosis can be recognized by typical signs such as pain when pulling the foot and when pressure is applied to the sole of the foot.
Complaints in the calf are similar to sore muscles and can also be triggered by applying pressure with both hands.
A thrombosis in the arm can be recognized by a swelling and the clear protrusion of the veins.
therapy
If a thrombosis has been detected, its resolution has top priority. The so-called Thrombolysis should be done as soon as possible after the blood clot has formed.
Come at the breakup anticoagulant drugs how Heparin and Factor Xa inhibitors for use. The risk of complications is particularly high in the first three to six months after the onset of the thrombosis.
To prophylaxis serves the Vitamin K antagonist Marcumar® and wearing Compression stockings. Regular medical checks should be carried out.
The surgical therapy is only appropriate in rare cases.
forecast
The forecast a timely recognized and treated thrombosis is with appropriate therapy and prophylaxis Well.
The risk of varicose veins, post-thrombotic syndrome and life-threatening pulmonary embolism increases the later the thrombosis is detected. After a thrombotic event, there is a risk that a blood clot will recur elevated. This is especially true for men.
prophylaxis
Thrombosis can develop in different ways prevented become. Have a positive impact lots of movement, one sufficient amount of water to drink of 1.5-2 liters per day and wearing Thrombosis stockings after surgery and childbirth.
One should avoid long immobilization, the combination of smoking and the use of contraceptives ("pill") and being overweight.
For short-term thrombosis prophylaxis, for example after surgery, heparin and are used Acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin®).
Long term become anticoagulants like the oral one Anticoagulant (Anticoagulant) Marcumar® prescribed.
For more information, see: Thrombosis prophylaxis and thrombosis prophylaxis measures