Pulling a tooth - you need to know that
Synonyms in the broader sense
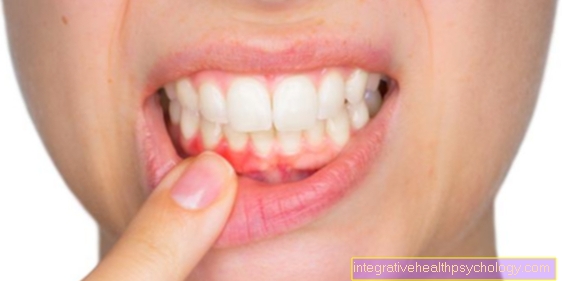
Tooth extraction
introduction
Pulling a tooth the so-called tooth extraction, is a surgical dental service that is fully paid for by health insurance companies.
Read more on the topic: Tooth extraction
A tooth is usually removed under local or central anesthesia so that the patient does not experience any pain.
Read more on the topic: Extraction of a tooth
Reasons - an overview
There can be many different reasons for having to pull a tooth:
- Extensive tooth decay due to tooth decay
- Severe destruction of the tooth due to trauma (e.g. fall)
- Chronic inflammation of the gums that cannot be corrected
- Strong degree of loosening
- Crowded jaws
- Wisdom teeth that have no place in the jaw or are incorrectly created.
Reasons in detail
The main reason for the extraction of a tooth is the complete destruction of a tooth, in which a restoration by conservative or prosthetic measures is no longer possible, for example if a large part of the tooth has broken off, see broken canine.
Even teeth whose tooth supporting structures are chronically inflamed or destroyed can no longer be saved. However, even completely healthy teeth must occasionally be extracted from adolescents, if space has to be created for orthodontic measures when they are crowded. This particularly affects the first small molar, as statistically speaking it is highly susceptible to caries. Another reason are wisdom teeth, which in most cases have to be removed.
Read more on the topic: Operation on the wisdom tooth
Can or must you pull the tooth in the case of a tooth root inflammation?
If there is inflammation in the area of the roots of one or more teeth, tooth extraction is only the very last option.
Read more on the topic: tooth root inflammation
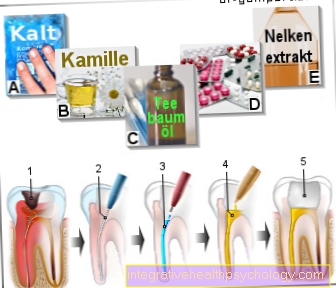
Before doing this, you should seek extensive advice on other treatment attempts. Periodontitis, that is, inflammation of the tooth support system, is very common. If the inflammation continues to penetrate into the pulp in the nerves sell, it can lead to very severe pain. The root canals of this tooth need to be treated in this case. If an inflammation is deep in the area of the root, there is the possibility of removing the inflamed tissue by means of a root syringe resection, i.e. removal of the root tips.
Read more on the topic: Apical resection
The remains of the roots and their root canals are then sealed against bacteria from the oral cavity. Even if inflammation in the area of the teeth can cause great pain, you should always try to preserve your own tooth before deciding on an extraction. As soon as a tooth is extracted, a prosthetic restoration, i.e. a bridge or an implant, has to be considered. And this can also lead to further inflammation.
Read more on the topic: Treatment of root inflammation
Pain during and after tooth extraction
How big is the pain when the tooth is pulled?
Pain that occurs when pulling a tooth (tooth extraction) is felt very individually by the patient. Each time a tooth is extracted, the dentist numbs the affected area. Usually several syringes are used. On the one hand, the entire supply area of the running nerve is numbed (conduction anesthesia) and, on the other hand, the mucous membrane is made locally insensitive to pain in the affected area.
Read more on the topic: Dental pain relief, central anesthesia at the dentist
The dentist pulls the tooth using a tilt, twist and pull technique. Due to the anesthesia, almost no pain is felt during the actual tooth extraction process. You only feel the wobbling and turning, which can be perceived as unusual and uncomfortable in the meantime. If there is great concern or fear of tooth extraction, the patient can be brought into a twilight sleep by means of sedatives, which does not allow the treatment to be perceived and gives the patient a feeling of indifference and lightness.
Another option is general anesthesia, in which the patient is not aware of the treatment. Often more pain is felt when there is severe inflammation and this was the reason for the tooth extraction. If pain occurs during tooth extraction, this can be signaled to the treating dentist, who can expand the anesthesia.
Read more on the topic: General anesthesia at the dentist
How big is the pain afterwards?
After pulling a tooth, so-called wound pain is quite normal as the wound begins to heal. They start as soon as the anesthesia from the dental treatment wears off. They usually last a day or two and are often expressed as a constant throbbing or knocking. This can be very uncomfortable and lead to difficulty swallowing or mouth opening problems. In most cases, pain relievers such as ibuprofen prescribed by the doctor or available over the counter help very well.
The strength of the pain depends on the individual pain sensation and can vary greatly. If you do not experience severe pain until three days after treatment, it is recommended that you consult a doctor, as it could be a deep-seated infection.
How long does it take to heal?
With a complication-free tooth extraction, the wound healing takes about 10 days. After this time the edges of the wound have closed and the sutures have usually been pulled. The affected area should be spared from oral hygiene beforehand. If the bone had to be opened for extraction, the healing time will take a slightly longer period of time. Wound healing is not yet complete with the healing of the wound edges. The bone remodeling processes below the superficial wound usually take 6 months to two years before the bone is regenerated.
Different approaches to pulling a tooth
Uncomplicated tooth extraction
In order to understand the process of extraction (pulling a tooth), one has to know that the tooth is not fused directly to the jawbone. There are fibers of connective tissue between the tooth root and the jawbone (Sharpey fibers) with which the tooth is hung in its tooth socket. Tooth extraction is only possible when these fibers are destroyed.
Before the extraction, the pain is eliminated by local anesthesia. In the upper jaw, it is sufficient to directly encapsulate the tooth to be removed. In the lower jaw, conduction anesthesia in the ascending branch of the lower jaw is necessary for the extraction of the molars, since otherwise the nerve cannot be reached.
The anesthetic contains a vascular contracting additive that reduces the tendency to bleed. The tools needed to extract a tooth are levers and forceps. Depending on which tooth is to be removed, the pliers are shaped differently and adapted to the shape of the tooth. The lever is first used to destroy the fibers and thus loosen the tooth, and only then can the tooth be removed from the tooth socket with the forceps (alveolus) to be pulled. It is important that a blood clot forms in the tooth socket that cannot be removed by rinsing. This clot of blood is the best dressing for a wound, and it prevents bone from being exposed, causing pain. This is why you should not rinse after tooth extraction.
Read more on the topic: Local dental anesthesia
Special features when pulling a molar
Pulling a molar is technically equivalent to pulling an anterior tooth. A twisting, tilting and pulling technique is used to pull the tooth out of its socket. When extracting molars, however, there are some special features that should be observed. The molars usually take a little longer to extract than other teeth. On the one hand, they are located deep in the oral cavity and are therefore difficult to reach for the dentist. On the other hand, they have several and often strongly curved roots that make it difficult to pull.
Furthermore, it can happen that the tooth crown breaks off during the extraction and parts of the root remain in the bone compartment. The tooth roots can then be removed.
The molar can easily be swallowed during extraction. Good cooperation between the treating dentist and patient is essential here.
Read more on the topic: Pull molar tooth
Surgical tooth extraction
If a tooth is displaced and lies in the jawbone, these are mainly wisdom teeth, the extraction can only be carried out surgically.
After opening the mucous membrane, the bone covering the tooth is removed and then the displaced tooth is removed with a lever and forceps.
The mucous membrane is sutured again and thus closes the wound. However, it can also happen during normal tooth extraction that a root breaks off and cannot be removed in the normal way.
Then the so-called opening is also necessary, i.e. After the mucous membrane and bone have been removed, the exposed root residue is removed. Here, too, the closure is made by folding back the mucous membrane and suture. The healing normally takes place without complications.
How long does the tooth extraction take?
The duration of a tooth extraction treatment depends on which tooth is extracted. The position of the tooth is also important. Molars that are difficult to reach and that have multiple, often curved roots, take up more time than an anterior tooth, for example. The treatment can therefore last from 10 minutes to half an hour. The duration also depends on the duration of the anesthesia. The local anesthetic usually starts after approx. 10 minutes and usually subsides after a few hours.
General anesthesia for tooth extraction
It is possible to opt for general anesthesia for tooth extraction. This is often very useful for anxious patients. The general anesthetic is only covered by the health insurance if it is necessary for the treatment by the dentist. General anesthesia is indicated, for example, when pulling multiple teeth. There is also an exception in the case of dental phobia. If this has been confirmed by a psychiatric report, general anesthesia is covered by the health insurance company.
Read more on the topic: General anesthesia at the dentist
General anesthesia enables the patient not to notice anything about the treatment. General anesthesia usually lasts for several hours. The person being treated must therefore be picked up by an accompanying person and accompanied home. Furthermore, general anesthesia is associated with increased costs, since an anesthetist (anesthetist) has to be present to monitor the vital functions, i.e. breathing, blood pressure and heartbeat.
Read more on the topic: Wisdom tooth pulling under general anesthesia - when does it make sense?
What complications can arise?
As with any surgical procedure, various complications can arise with tooth extraction, such as edema (swelling), pain or bruises. Furthermore, pain or bleeding can occur in the affected area, especially after the treatment. It is also possible that swallowing or the opening of the jaw and mouth may be impaired. During the actual operation it can happen that the tooth or the root breaks off.
After a tooth is removed, the bone compartment in which the tooth was previously located is exposed. The bone is exposed to the bacteria in the mouth. Inadequate oral hygiene can therefore lead to infections of the jawbone (alveolitis sicca). For this reason, the patient's cooperation after the operation is very important in order to avoid possible complications that could arise postoperatively. This includes adequate oral hygiene, cooling the affected areas, avoiding products containing milk during the first few days and avoiding throat, alcohol, coffee or exercise.
Read more on the topic: Wound healing disorders on the tooth
Accompanying symptoms after the operation
As with any operation, various symptoms, i.e. complaints, can occur. These primarily include pain in the affected area in the mouth. Usually it is healing pain that manifests itself in a knocking or throbbing. As with any type of pain, one feels physically tired and impaired. Swelling or bruises (bruises) can also occur. The swellings can spread to the face area. For example, when extracting wisdom teeth, one often has very swollen cheeks.
Read more on the topic: thick jaw
In the most uncomfortable case, the swelling can be so severe that it restricts the opening of the jaw or mouth. These accompanying symptoms are completely normal in and of themselves and usually subside after two to three days. If they persist, it is recommended to see a dentist, as it may be a deeper inflammation.To relieve the discomfort, the affected areas should be cooled. Painkillers can also be taken. However, aspirin should not be used here, as otherwise bleeding could occur. The following applies to cooling: After a cooling phase of 10-15 minutes, an equally long cooling break should be taken.
Pus formation after tooth extraction
The formation of pus always indicates inflammation as the cause. If the wound caused by tooth extraction does not heal properly or if pus appears, a dentist should be seen immediately. In many cases, so-called granulation tissue has then formed on the wound, as a result of which the wound cannot heal. Granulated tissue (granuloma, wild meat) is new knot-like tissue that spreads in the area of the wound
Bad odor after pulling a tooth
A bad smell from the oral cavity is often accompanied by a very unpleasant taste. If this occurs several days after the operation or has persisted since then, these signs are an indication of an infection of the extraction wound. The cause is usually a colonization of the wound by germs that are in the oral cavity. Poor oral hygiene can promote this. However, premature dissolution of a blood clot that has formed in the bone compartment can also be the cause of the germ colonization.
Read more on the topic: Causes of Bad Breath
The swelling afterwards
Swelling after tooth extraction is common and not uncommon. To prevent swelling, it is very important to cool the affected area immediately after the operation. This can be done from the outside using cold compresses or by sucking ice cubes from the inside.
It can be cooled again and again. It is important that there is no fever (over 38.5 degrees) or any difficulty swallowing accompanying the swelling. If the swelling appears several days after the operation and is accompanied by pain, a dentist should be seen. It is then not a normal postoperative swelling but a deeper inflammation. It should only be cooled continuously for 10-15 minutes. After that, you should take an equally long cooling break.
Treatment after surgery
What can you do about the pain?
Every tooth extraction means an operation and thus a wound that has to heal afterwards. In order to alleviate the symptoms of wound healing, painkillers prescribed by a doctor, such as ibuprofen, can be taken. It is important that no preparations such as ASA (aspirin) are taken, as these have an anticoagulant effect and increase the risk of bleeding.
Furthermore, the affected area can be cooled from the inside with cold compresses or by sucking ice cubes in the mouth. Cooling can lower the mouth temperature and prevent severe swelling of the affected area. Heat should be avoided in any case. After pulling a tooth, vigorous chewing of hard foods should be avoided for at least a week.
This results in faster wound healing and protects the masticatory muscles. Arnica preparations or chamomile, which have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects, can still be used to reduce swelling. After eating, chamomile can be used as a preventive rinse to prevent infection of the wound. (Let the tea cool down!)
When can an implant be placed?
After losing a tooth, many patients decide to place an implant in the gap created by tooth extraction.
The time span between tooth extraction and insertion of the implant always depends on the quality of the bone.
This includes, on the one hand, the bone volume and, on the other hand, the jaw bone density, because it must be possible to assess whether the bone is stable enough to support an implant.
So-called direct implants made of titanium can very often be placed during tooth extractions. They are used in the same session immediately after the extraction and can then grow together optimally with the bone.
Read more about this at: Dental implant
Homeopathy after tooth extraction
Homeopathic medicines are a popular measure to support healing after tooth extractions. In general, homeopathic medicines cannot fix the cause of bacterial inflammation. However, after a dental treatment you can alleviate the symptoms and accelerate healing. These include, for example, Phosphorus, Hepar Sulfurs, Hypericum, Staphisagria, Arnica or Belladonna. This should be discussed with the attending physician before taking.
When are antibiotics necessary?
Antibiotics are not routinely prescribed by the dentist. Fever, toothache or swelling are not direct indications for the administration of an antibiotic. Rather, it is prescribed when it comes to combating bacterial inflammation. Root canal treatments, root tip resections, for example, are among the treatments in which antibiotics are prescribed. If an antibiotic is prescribed, it is very likely that the tooth is infected and is being used to fight it.
Correct behavior after the operation
When can I smoke again?
Smoking not only has a damaging effect on the various tissues in the body, but also narrows the blood vessels due to the ingredients in the smoke. As a result, the tissues in the oral cavity are poorly supplied with blood and wound healing slows down. Fewer cells are transported to the wound site for healing. In general, you should refrain from smoking as long as the wound has not yet healed. You should wait at least 24 hours before smoking again. Smoking increases the risk of infection in the mouth.
Read more on the topic: Consequences of smoking
When can you drink alcohol again?
After a tooth extraction, alcohol should be avoided for at least 24 hours. It would be even better not to consume alcohol for two to four days after the operation. Alcohol increases the tendency to bleed and leads to impaired wound healing. It expands the blood vessels and thus increases blood flow. At the same time, it inhibits components of blood coagulation and thus reduces wound healing. There is an increased risk of bleeding. Furthermore, alcohol inhibits the effect of antibiotics that are often prescribed after an operation.
How long do you have to wait to eat?
After pulling a tooth you should wait until the local anesthesia from the treatment has worn off. Otherwise the risk of biting your tongue or lip while eating and injuring yourself is too great. Water or cooled tea is suitable for drinking during this time. After that, normal but digestible food can be consumed. However, care should be taken to ensure that it is not too hard and that the chewing muscles can be spared for the first few days. Furthermore, dairy products should be avoided for a few days. The lactic acid bacteria can dissolve the primary plug that is formed during wound healing and thus lead to impaired wound healing.
When can you start exercising again?
So that the blood pressure does not increase and wound healing is not disturbed, no sport should be played for about two to three days after the operation. Any kind of sport or physical exertion increases the bleeding tendency and lengthens the healing time. The increased blood pressure makes it difficult for the wound to close. Furthermore, there is a risk that the healing wound will break open as a result of the exertion during exercise.
When can I fly again after a tooth has been pulled?
Flying has, at least the opposite has not yet been proven, no negative impact on the wound caused by tooth extraction. If it is a longer vacation, it would be worth considering whether to get a prescription for an antibiotic as a precaution, which can be taken if complications arise.
What can you do about the fear of tooth pulling?
Many people are afraid of having a tooth pulled. They associate this with severe pain, are afraid of losing control or of the resulting temporary tooth gap. In any case, one should try to find out the reason for the fears. In the first step, it is always very useful to make an appointment with a trusted dentist. It is very important to explain your own concerns and worries to him and to be informed about all treatment steps.
Many practices and dentists nowadays have specialized and adjusted to the treatment of anxious patients. It is very important to trust the doctor treating you. If the fear is too great, general anesthesia is recommended during the tooth extraction. In this case, one does not notice anything about the treatment and cannot remember it afterwards either. Furthermore, a hand signal can be agreed with the attending doctor so that he can briefly interrupt the treatment. This is very useful if the fear is based on a loss of control and the feeling of being completely at the mercy. Another option is to practice relaxation techniques beforehand, which can help in the course of the treatment.
Read more on the topic: Fear of the dentist
What does a tooth extraction cost?
The cost of a tooth extraction is borne entirely by the health insurance company if the procedure is medically necessary and cannot be avoided. Patients only incur costs when the newly created gap has to be treated with prosthesis. It is difficult to flat-rate the cost of tooth extraction. Privately insured patients have to pay in advance for a tooth extraction and are reimbursed the amount depending on the amount of their deductible.
Which parts of the treatment are covered or reimbursed by private health insurance depends on the health insurance company itself and the tariff chosen. The cost of extracting a tooth varies widely. On the one hand, they depend on the dentist's expertise and tariffs. On the other hand, it depends on the position of the tooth to be extracted, the number of roots and any previous damage. The dentist calculates, among other things the consultation, the pretreatment, the x-ray, the anesthesia, i.e. the anesthesia, the actual extraction of the tooth, the number of its roots and possible complications, such as a pre-fracture of the tooth. Additional billing points can be added to these points.
In the case of privately insured persons, it is important to obtain a cost estimate from the treating dentist. Prices can vary widely.
Special circumstances
Can a tooth be extracted despite taking blood thinners?
The drugs known colloquially as ’blood thinners’ are in the actual anticoagulant. So they prevent the formation of blood clots in underlying diseases such as Arteriosclerosis, heart disease or thrombosis. However, a disadvantage of these drugs is the risk of increased bleeding. If wounds develop, there is a risk of losing too much blood, as blood clotting, which forms a kind of plug to close the wound, is inhibited.
To avoid the risk of high blood loss during tooth extraction, the blood thinners can be discontinued several days before treatment. As long as the so-called INR value (measure of blood coagulation) has been checked beforehand and it is not higher than 3.5, a tooth extraction can also be carried out without discontinuing anticoagulants. For this purpose, an advisory discussion should be held with the treating doctor.
Tooth extraction during pregnancy
Of course, toothache can also arise during an existing pregnancy and urgently require treatment.
Read more on the topic: Toothache During Pregnancy
Basically there is nothing wrong with dental treatments during pregnancy, and the extraction of a tooth poses no danger to the unborn child. However, it is particularly important that the treating dentist is informed about the existing pregnancy and can adapt the necessary treatment measures accordingly.
There are a few things to keep in mind while visiting the dentist. On the one hand, only those anesthetics should be used before pulling the tooth that do not pose a risk to the child and / or mother. On the other hand, it is imperative to refrain from taking an X-ray, because the rays used can damage the genome of the unborn child, especially at the beginning of pregnancy, and lead to disabilities in the child.
A single X-ray will not cause this, however, any radiation exposure that is not absolutely necessary should be avoided. The higher the radiation exposure during pregnancy, the higher the risk for the unborn child.
In addition, when visiting the dentist during an existing pregnancy, it is important to expose the expectant mother to as little stress as possible. The dentist arouses certain fears and worries in many people from the outset, and the announcement of a necessary tooth removal can put the patient under stress.
For this reason, the treating dentist will take a lot of time, especially for expectant mothers, to discuss all treatment steps in advance, answer questions, try to take away existing fears and act particularly cautiously. Pulling a tooth during pregnancy does not pose a threat.
If you wish to have children, it is generally advisable to have the entire set of teeth, the gums and the tooth supporting structure examined by a dentist. The necessary dental treatments can then be carried out before the pregnancy.
history
In the Middle Ages, so-called tooth breakers traveled from fair to fair to pull teeth on a podium. This was done as popular amusement for the visitors to the fair. The poor patients, however, had to endure terrible pain, because there was of course no anesthesia for tooth extraction back then. In addition, there were instruments that, in many cases, removed not only one tooth but also the neighboring teeth, as they were supported on them. The consequences were not only the removal of the teeth but often also the removal of parts of the jawbone.
Summary
Tooth extraction. takes place under local or central anesthesia. A distinction is made between the normal extraction of a tooth and the surgical one. In both cases, the tooth is first loosened with a lever and then removed with the pliers. In most cases, follow-up treatment is not necessary if the blood clot in the wound is not removed.











.jpg)