Denture of the upper jaw
Synonyms
Full denture, total denture, 28th, "The Third"
introduction
A large part of prosthetics deals with the dentures with complete tooth loss. In the course of life it can come to that due to different influences, such as Caries, periodontal damage or loses his teeth in an accident.
If you only lose part of the teeth, they can be replaced with a bridge or one Interim prosthesis be provided.
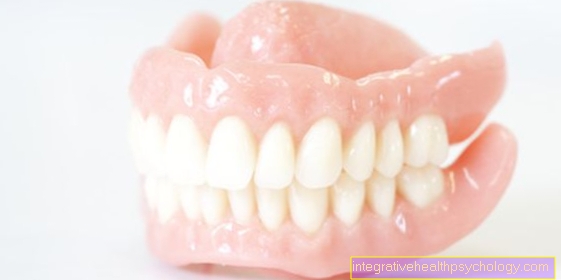
However, if there is no longer any tooth in the upper jaw, these dentures are no longer available. To still the Chewing and speaking function To enable and also to achieve a good aesthetic result, there is the possibility of either replacing the missing teeth Implants to replace or one Full denture to make. Alternatively, a full denture can be attached to implants for improved hold and more comfortable comfort. Placing implants, however, is a very time-consuming, lengthy, complicated and costly surgical procedure, especially when all teeth have to be replaced.
Since many patients shy away from this procedure or do not have the financial means, it is usually one Full denture, also 28er called, the drug of choice. She also provides the Standard supply which is covered by the health insurance companies. But how exactly is such a full denture made and why does it not fall out of the mouth?
The anatomical structure of the upper jaw
In order to understand which parts of the upper jaw are covered by the full denture and which parts are important for manufacture, knowledge of the anatomical structures in the upper jaw is important. The part where the teeth were present is called Alveolar ridge. It is covered by the mucous membrane and consists of bony alveoli in which the teeth used to sit. In the event of incorrect, excessive or non-stressing, the bony structures break down, which can be one of the reasons for a subsequent loss or poor “fit” of the prosthesis. There's one along the middle Center line (Raphe Palatini), which has a bone bulge, the Torus palatineus.
The general bony basis forms the Maxilla. The is divided palate into a hard (front) and soft (back) palate. The prosthesis will later cover the hard part. The mucous membrane that covers the structures is connected to the underlying part to different degrees and is equipped with different glands. So she finds the front more likely Adipose tissue and facing the pharynx a tissue occupied by many glands. These parts can also be pressed in with different degrees of pressure, what is called Resilience designated. In the area of the wisdom teeth, the maxilla has a kind of elevation, the Tuber maxillae.
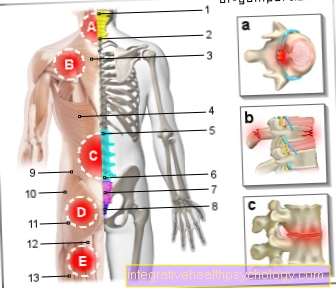
Figure upper jaw
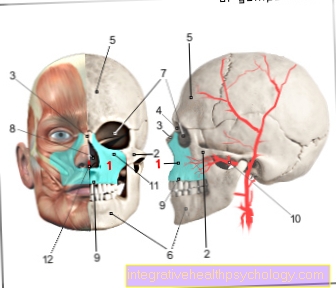
- Upper jaw -
Maxilla - Zygomatic bone -
Os zygomaticum - Nasal bone -
Nasal bone - Tearbone -
Lacrimal bone - Frontal bone -
Frontal bone - Lower jaw -
Mandible - Eye socket -
Orbit - Nasal cavity -
Cavitas nasi - Upper jaw, alveolar process -
Alveolar process - Maxillary artery -
Maxillary artery - Under eye cavity hole -
Infraorbital foramen - Ploughshare - Vomer
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
The components of a full denture
As soon as it has been inserted in the patient's mouth, the full denture should not be distinguishable from natural teeth. Regardless of whether the patient smiles, speaks or eats, the prosthesis should simulate normal gums and natural teeth as well as possible. Until then, however, it's a complex and lengthy manufacturing process, which also requires a lot of time in the dental laboratory to determine whether to manufacture the prosthesis. Usually the prosthesis consists entirely of plastic. Both the gums and the teeth are made of plastic. This makes it possible to use any type of tooth color and shape and also to make the gums as natural as possible.
At the beginning, the dentures are made for the upper jaw set up in wax. This means that those taken by the dentist and taken by the technician with plaster cast impressions in a Articulator (a device for simulating the chewing movement). The appropriate teeth are then placed in wax. These have been tailored to the patient beforehand. So a small, round person gets different teeth than a big, thin one. The concept of the setup varies from dentist to dentist (bilateral balanced or anterior canine guidance). The teeth are placed in the wax in such a way that they correspond to the optimal way as in real dentition. Once the teeth have been set up, the different Tooth movements carried out. This ensures that the patient can later easily move the jaw to the right, left, front or back. If this is correct, more wax is applied and that Gums modeled. This means that the wax is processed with various instruments so that it looks like real gums.
The next step will be Wax model transferred to plastic, the finished end product. Various plastics and manufacturing processes are used. So it can stuffed cold or injected warm become. Thus the wax disappears and is replaced by liquid plastic, which hardens. The teeth remain in their position.
In the next step, the prosthesis is processed. It gets a high gloss polished and thus simulates the dentition in the upper jaw. Also the different movements are checked againso that the denture can end up being placed in the patient's mouth. Modern plastics have already developed to such an extent that they are no longer harmful to the body. However, intolerance or allergies can occur.
Materials of a full denture
Dental prostheses or also called full dentures consist of one Plastic base. This base is pink and lies against the palate. The materials for the teeth, which are anchored in the palatal plate, are either made of plastic or ceramic, like the base. Plastic teeth are softer and wear out after a while. Ceramic teeth are much more robust and resilient and have a longer service life. In telescopic prostheses, the telescopes and the counterparts that are incorporated into the prosthesis are made of metal alloys.
The hold of a total endoprosthesis

At first glance, it seems a bit puzzling how a full denture /Denture can hold in the upper jaw at all, because after all there are no longer any teeth to attach them to. Nevertheless, it is possible to talk to her and eat her without her falling out.
There are three important factors for this. The first factor is based on the occlusal stabilization. This means that the row of teeth from the lower jaw, be it normal teeth or also a full denture, in the closed mouth and sometimes also during movements, Contact with the teeth in the upper jaw to have. So is a static stabilization secured.
The second factor is that Storage of the full denture in the surrounding soft tissue. The prosthesis is made so that it lies perfectly on the alveolar ridge and covered on the sides by muscles and cheeks becomes. This is also known as Muscle grip. For example, the posterior tooth areas of the prosthesis are designed to be convex and the anterior tooth area to be concave in order to give the tissue and muscles the opportunity to snuggle up.
For the third and last factor, which is also the most important one for the hold, a little excursion into physics has to be undertaken. The whole thing can be imagined as a kind of valve, in which a negative pressure is generated, which causes the hold of the denture. Between the prosthesis to be placed (Prosthetic base) and the fabric underneath (Denture warehouse) are located Air bubbles. These are expressed when inserting the prosthesis. If the edges of the prosthesis are optimally designed, the air can no longer return, so that the said negative pressure is created and the The prosthesis. To the outside, to the surrounding structures, there is a External valve, inside, i.e. from the edge of the prosthesis to the middle of the alveolar ridge Internal valve.
In some cases, however, the The hold of a prosthesis wears off and wearing it becomes more uncomfortable. This can be caused by different factors. For one, a inaccurate work by the dentist or dental technician lead to the fact that the prosthesis does not fit optimally on the alveolar ridge. On the other hand, it can Ratio of denture base to denture bearing is unfavorable so that the hold is not optimal. The main cause is however Changesthat take place in our oral cavity. If the prosthesis is incorrectly loaded, i.e. one side is exposed to stronger chewing pressures than the other, for example, the side on which the stronger chewing pressures act tends to recede. This shows that the The ridge recedes, the greater the incorrect loading is. But in general it is also the case that the missing teeth transfer all of the force to the alveolar ridges and these regress with age. This is different for each patient.
If the alveolar ridge recedes, the prosthesis that was made some time ago no longer fits properly. The tissue and the bone have changed, the prosthesis remains the same. All the factors that determine the hold of the prosthesis are getting weaker and weaker. Among other things, the valve effect can no longer work properly or the surrounding tissue cannot optimally support the dental prosthesis. However, since this is normal and can occur with every prosthesis, regular visits to the dentist are advisable, as it is then possible to "reline" the prosthesis. This means that the prosthesis base is adapted to the new conditions in the oral cavity so that it fits properly again. Even if the prosthesis breaks, it can be repaired in the dental laboratory. A visit to the dentist is advisable as soon as you notice that the prosthesis is no longer holding properly, is loose or disturbs while eating.
Implants can improve the hold of a denture, but are not applicable to everyone and are a surgical procedure. If one should consider such an improvement, a detailed discussion with the trusted dentist is important. In advertising, different prosthesis adhesives, so-called adhesive creams, are often advertised, which are supposed to improve the hold. If a prosthesis is optimally adapted to the situation in the patient's mouth, these are superfluous. In the short term, they can be used to compensate for the onset of loosening. Many denture wearers use adhesive cream for years because they shy away from visiting a dentist, even if they find the adhesive cream uncomfortable.
If you notice changes in the prosthesis hold, a visit to the dentist is the better and safer solution to restore the hold than permanent use of these agents.
This article might also interest you: Inflammation under a denture
costs
The cost of a denture can vary in a certain range from dentist to dentist, however, are used by the Health insurance subsidized. The health insurance subsidy can be increased by having a Bonus booklet leads.
The total is made up of three pillars. These are the Dentist's fee costs, the Laboratory and material costs. For the upper jaw you can on average with 430-500 € count on what the cashbox approximately 300€ (without bonus) takes over.
If you need both in upper jaw as well as in Lower jaw a full denture, the costs are approx. 1200 €. After deducting the health insurance contribution, between 500 € and 700 € personal contribution. The personal contribution can be increased if you special treatment methods wishes. So can a special electronic temporomandibular joint determination carried out or the modeling of the prosthesis be refined.
Palate plate
A denture is im Upper jaw with a palatal plate fitted. There is no such plate in the lower jaw because the tongue must still have enough space.
Through the palate plate the upper denture also holds better than the denture in the lower jaw. This has to be done frequently lined or be made from scratch.
The denture has one through the palate plate in the upper jaw larger contact surface, can include more of the palate and thereby get a higher strength. Without the palate plate, the prosthesis would not have sufficient hold. A disadvantage of the palate plate, however, is that it “bulkier“Makes, thus as more uncomfortable can be felt when worn, it covers several glands and has a negative effect on the taste sensation, as a large area in the mouth is covered with plastic.
Dental prosthesis without a palatal plate
For dental prostheses in the upper jaw, the palatal plate not only takes getting used to for many users, many patients cannot cope with it at all. If there are no own teeth in the upper jaw, it is not possible to create a palate-free prosthesis. In this case, the palate plate is there to ensure the hold of the prosthesis on the upper jawbone and to distribute the chewing load evenly. The only option for an edentulous jaw to wear a palate-free prosthesis is to insert Implants. For this, 6 implants are required in the upper jaw to ensure the perfect statics for a prosthesis without a palate plate.
In the dentate jaw can be with a Telescopic prosthesis A palate-free variant can be created, provided that 6 or more teeth are ground as telescopes. The ground teeth get one conical metal crown, as Primary elementst serves. The Abutment forms the Denturewhich in turn have built-in telescopes that fit exactly onto the ground teeth. So the prosthesis is true removable, but palate-free and it offers the patient a well-holding restoration in the upper jaw, which is comparable to an implant-supported prosthesis.
It is also possible to have remaining ones Combine teeth and implants and thus to produce a palate-free prosthesis. There are also again 6 carrying elements required. If there are fewer elements, whether tooth or implant, then the prosthesis must have a part of the palate in order to guarantee the statics and the hold. In the case of prosthesis variants with brackets, a palatal plate is almost always present.
Dentures with push button
Another variant one Palate-free upper jaw prosthesis are to be worn Snap fasteners, so-called mini implants. These mini-implants are essential shorter than normal implants and are also surgically drilled into the jaw. Matching locators are built into the prosthesis, which lock into place in the mini-implants using a lock and key principle, thus securing them. Many dentists prefer these mini-implants only as a temporary solution before correct implants are placed in order to achieve an optimal hold. However, it is not unlikely that these mini-implants will provide a lifelong supply with good healing and stability.
Dentures without brackets
The only way to guarantee an upper jaw prosthesis without a palate plate and without a clasp is that telescopic prosthesis with at least 6 teeth or one implant-supported prosthesis with 6 implants. The combination of the two holding elements is also free of clamps. The teeth and implants act as an "anchor" that supports the prosthesis. The prosthesis is supported by the specially ground conical shape of the teeth. This phenomenon is called friction, as the telescopes wedge themselves with their matching counterparts in the prosthesis.
Gag reflex
In most cases, gag irritation with upper jaw prostheses is caused by the palatal plate. The individual sensation is decisive here. There are patients who choke as soon as the posterior palate is touched and have to vomit.In this group of patients, a palate-free treatment of the upper jaw is essential in order to tolerate the strong gag reflex.
Prosthetic care
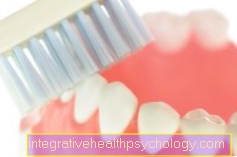
Even if a Lining in most cases unavoidable after at least 1 1/2 years and dentures are not "real" teeth, it is still very important that they to be cleaned thoroughly every day. bacteria can still use the Oral cavity settle and Inflammation and cause an unpleasant odor.
A clean and well-maintained prosthesis not only looks better, it also enhances yours Comfort and your durability. After every meal, it is advisable to rinse the denture under running water, as food scraps may have gotten under the denture. Thorough cleaning is recommended once a day, where you have to be careful so that the prosthesis does not fall out of your hand and maybe break. With a special Denture toothbrush the denture can now be cleaned thoroughly from all sides to remove food residues and plaque. It is recommended to special denture toothpaste to use, or everyday toothpastewhich has a small amount of abrasive particles, as otherwise the surface of the prosthesis could become roughened. Special cleaners in powder or tablet form can be used as a supplement, but not a substitute for manual cleaning. In addition, a regular check-ups at the dentist.
What should you do if a prosthesis breaks?
Since the base of the prosthesis is made of plastic, it is prone to breakage and can be damaged or even break through if it falls on the ground. This risk exists especially when the palate plate is designed to be filigree and thin. To strengthen the prosthesis, metal meshes can be incorporated into the plastic base of full dentures.
In the event of a break, regardless of whether it is a full denture, implant-borne denture or telescopic denture, it must definitely be repaired by a technician. It is often not enough to hand over the parts of the damaged prosthesis to the dentist, in many cases an over-impression must be taken to ensure the correct composition of the individual parts. It is important that you visit the dentist as soon as possible, since with telescopic prostheses the teeth can move as soon as the prosthesis is not worn for a long time.
Can I glue the prosthesis myself?
If a prosthesis is broken, regardless of the type of denture, it is not possible to repair it yourself. The use of adhesives is strongly discouraged, as the individual parts often cannot be joined without gaps and the prosthesis does not fit afterwards. In addition, the adhesive used is often toxic and not suitable for the oral cavity, which is why a visit to the dentist is inevitable.
Read more on the topic: Gluing dentures