Physiotherapy / physiotherapy
Synonyms in a broader sense
Remedial gymnastics, movement therapy, physical therapy (sub-area of physiotherapy / physiotherapy), physical therapy
The term physical therapy has replaced the designation since 1994 physiotherapy and is thus based on international language usage. In the following topic I will use both terms synonymously, since physiotherapy is still used very often in common parlance.
definition
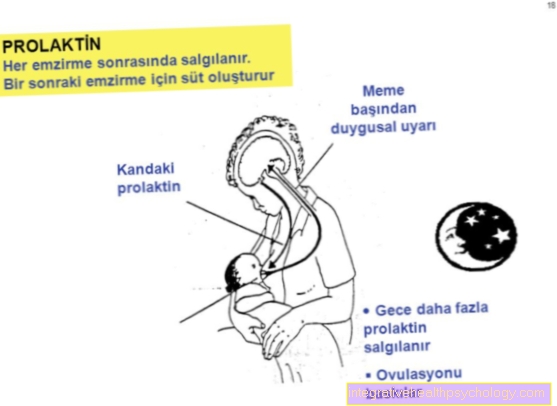
The word physical therapy is from Greek words physio = nature and therapeia = treatment / accompaniment derived.
Physiotherapy / physiotherapy is an after medical diagnosis prescribed, consisting of many different forms of therapy Remedieswhich aims to maintain or restore the greatest possible mobility and functionality in the physical (= somatic) and in the mental (= psychological) sense of a person.
The ability to move and function can be impaired by illness, accident, congenital disorders or misconduct in everyday life.
This goal is based on the definition of the World Health Organization (WHO), the health referred to as a state of physical and mental well-being.
The application of various active and / or passive forms of treatment (description follows) can be used in humans Eliminate pain, healthy (physiological) movement sequences or restore substitute functions, unbalanced muscle strength ratios (compensate for muscular imbalances and one for children promote physiological development. She gives the patient a tool (Helping people help themselves) with on the way, active and independent the Healing process to support to continue and to prevent new problems.
The history of physiotherapy / physiotherapy
Already in ancient times was the relaxing effect of gymnastic exercises, Massages and Medicinal baths known, thermal and mineral springs were used. Hippocrates (around 400 BC), who viewed the living body as an organism, health as equilibrium and illness as a disturbed physical (physical) and mental (psychological) overall condition, took the medical view that nature has its own healing power. This principle can be found today in many forms of physiotherapy, which stimulate the body's self-healing powers.
As early as the 18th century, a Swedish sports teacher developed specific therapeutic gymnastics from physical exercises, in the 19th century the use of therapeutic baths, water aerobics and health education etc.Sebastian Kneipp, the father of hydrotherapy (water therapy) growing in popularity. At the beginning of the 20th century, a Berlin doctor brought "Swedish therapeutic gymnastics" to Germany and defined the profession of "gymnast".
Due to wars and an increase in work and occupational accidents, the need for treatments increased and the application of physiotherapy expanded to various areas of medicine, such as the surgery, neurology.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.
Physiotherapy / physiotherapy - a broad field
Under the term of Physiotherapy / physiotherapy hides a wide field of therapeutic measures and fields of activity. Today is the physical therapy an important component of modern medicine and many treatment successes in practice, hospital and rehabilitation would not be achieved without physiotherapy.
It can be used at any age and is even more effective and less risky for some problems than drug therapy. Due to the increasing awareness of many patients that they want to actively participate in their recovery process and weigh the benefits and risks of other therapeutic procedures, a treatment that activates the body's own self-healing powers is becoming increasingly important.
Areas of activity
The areas of application of physiotherapy / physiotherapy mentioned in the following section contain only a selection of the most common clinical pictures.
Orthopedics: non-surgical (= conservative orthopedics)
- Back pain caused by functional disorders (no permanent changes) in the musculoskeletal system after improper or excessive strain and / or lack of movement
- Permanent (= structural) changes to the skeletal and muscular system such as Spinal curvatures, malformed feet, intervertebral disc problems, wear and tear (arthrosis) Etc.
- Painful restriction of movement of the spine or extremities after an accident or with diseases of the rheumatic type
Orthopedics / surgery: operational procedures
- all forms of joint replacement surgery (e.g. artificial knee joint or artificial hip joint)
- surgical supplies one Fracture , Injuries of the muscle-tendon-ligament apparatus, joint misalignments etc.
- disc prolapse
- Relief operations at Shoulder pain, Knee problems Etc.
Neurology:
- Stroke (apoplexy)
- chronically progressive diseases of the nervous system such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease
- Symptoms of paralysis caused by an accident, disc prolapse Etc.
- Skull brain traumas
Pediatrics = paediatrics
- congenital or acquired disorders of central coordination in infants and young children
- Developmental delays in children in the various areas of perception
- degenerative muscle diseases
- Diseases from the field of orthopedics and surgery in children
Pain Therapy:
affects various areas of medicine
- chronic pain symptoms such as
- Headache
- Facial pain
- Back pain
- chronic pain throughout the musculoskeletal system (Fibromyalgia), see also under Psychosomatics
Internal Medicine:
- Functional disorders of the internal organs, e.g. in the Cardiovascular system or the internal organs
- Structural changes in the cardiovascular system such as B. Heart attack
- Respiratory diseases such as asthma, Chronic bronchitis
- rheumatism
- Functional disorders of the vascular system
- Neurological diseases such as stroke, see under neurology
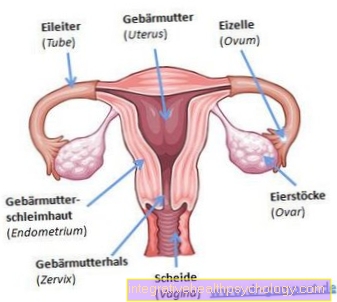
Gynecology / Urology:
- pregnancy- and Puerperium
- Incontinence
- Operative procedures e.g. with subsidence complaints
psychiatry / Psychosomatic disorders:
- Anorexia / obesity
- Chronic pain / fibromyalgia (see pain therapy)
- depression
Sports physiotherapy / sports medicine:
- Sports injury
- "Aftermath" from training and competition
- Training optimization
Prevention:
- Prevention of diseases, functional impairments and risk factors e.g. Prevention of back pain due to misconduct in everyday life through a Back school
- Prevention of the recurrence of an already existing health problem (relapse prophylaxis) e.g. Preventing another herniated disc over medical strength training
Rehabilitation:
Rehabilitation serves to regain and secure the best possible physical and mental abilities. It can be carried out immediately after an acute event (e.g. surgery, stroke) or at a later point in time. Following rehabilitation, the patient should be able to take his place in society and work as independently as possible and possibly learn to live with chronic illnesses or disabilities in the long term.
- Rehabilitation after illnesses in the field of neurology:
- Skull brain traumas
- stroke
- Etc.
- Rehabilitation after diseases in the field of orthopedics
- Endoprosthetics
- Spinal disease
- Etc.
- Rehabilitation after illnesses in the field of internal medicine:
- Heart attack
- Respiratory disease
- Rehabilitation after illnesses in the field
- Broken bone
- Endoprosthetics
- All departments
- Cancers
Goals of physiotherapy
The goals of physiotherapy treatment depend on the individual problems of each patient, i.e. the age and general condition, the clinical picture and its progressive stage and the individual requirements in everyday life.
- Pain relief over the Regulation of muscle tension, Elimination of functional disorders, improvement of mobility, increase in muscle strength / Muscle building and improving the coordination of motion sequences
- Training of sensorimotor skills by optimizing the interplay of sensory perception, balance and movement
- Improvement of the cardiovascular system and organ functions via Endurance increase and breathing regulation
- Developing compensation options in the event of permanent disability or illness
- Improving the quality of life at work and in everyday life
- Helping people help themselves