Magnetic resonance imaging / MRI
Synonyms
Magnetic resonance tomography, magnetic resonance tomography, magnetic resonance tomography, nuclear spin examination
English: NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
Definition of MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging, also known as magnetic resonance imaging (MRT), is a diagnostic technique used to visualize internal organs, tissues and joints with the help of magnetic fields and radio waves.
As a second step in magnetic resonance imaging, this stable alignment is changed by radiating electromagnetic high-frequency energy in the form of a radio signal at a specific angle to align the hydrogen protons. The hydrogen protons are set in motion by the radio signal from the MRI. After the radio pulse has been switched off again, the hydrogen protons return to their original position and in the process give off the energy that they absorbed from the radiated radio pulse. In the third step, the energy emitted is generated by receiving coils (Principle of antennas) measurable. With a sophisticated arrangement of these receiving coils, it is possible to measure precisely where and when which energy has been emitted in a three-dimensional coordinate system. The measured information is then converted into image information by powerful computers.
Procedure
In magnetic resonance tomography (MRT), a complicated sequence of stimuli and measurements (see magnetic resonance technology) serves as the basis for creating (sectional) images of the inside of the body.
The measured signals are converted into image information with the help of computer processes such as those already developed for X-ray recordings, computed tomography and axial computed tomography.
For the behavior of the hydrogen atoms, it is essential whether they are bound in liquids or in solids, whether they move, e.g. B. in the blood, or not. Due to the different content and presence of hydrogen atoms, healthy and diseased body tissue and healthy tissue can be differentiated from each other like no other method in medicine.
By changing the measurement conditions, the display of certain types of tissue such as fatty tissue or cartilage can be enhanced or suppressed.
If the delimitation of tissues is not easily possible, well-tolerated contrast media are available with which further statements can be made about the examined body region.
These contrast media do not contain iodine but have mostly been developed on the basis of gadolinium compounds (Gd-DTPA, gadolinium is a so-called rare earth).
Risks of the MRI
Since magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) only uses magnetic fields and radio waves, there is no health risk to the patient according to the current state of knowledge. Possible risks are from metallic foreign objects such as Coins or keys are given, which are drawn into the magnetic field and which can cause injury to the patient due to their acceleration.
Therefore, all metallic objects must be handed in before the start of the MRI examination. Metallic foreign bodies inside the patient such as Fixed dentures, artificial joints or metal plates, after treatment of a fracture, usually do not pose a risk. With cardiac pacemakers, malfunctions can occur in the magnetic field, so that certain factors must be observed in patients with cardiac pacemakers.
Read more on the subject at: MRI with a pacemaker
Vascular supports such as stents or vascular clips, artificial heart valves, insulin pumps, hearing aids etc. should always be indicated.
Magnetic cards such as Check or credit cards are deleted when entering the room in which the nuclear spin system is installed.
A tattoo can also be problematic for an MRI. Read more about this on our website MRI and tattoos.
Read more on the subject at: Is an MRI harmful?
Procedure of the investigation
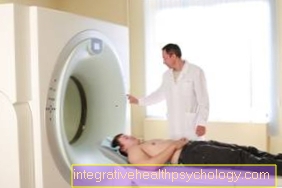
During the examination of the magnetic resonance tomography you lie on a movable couch, which at the beginning moves slowly into the magnet. The device has openings measuring 70-100 cm on both sides. Depending on the examination region, the patient is completely, e.g. when examining the head, or only partially, e.g. during an examination of the knee joint, in the device. When the pictures are taken, relatively loud, knocking noises are generated, which can sometimes be perceived as annoying. In order to muffle these noises, the patient is given earplugs or closed ear protection. You can often listen to music during the exam, just ask for it.
There are patients who suffer from so-called "claustrophobia" (claustrophobia) Suffer. If you have problems in this regard, you should discuss this beforehand with your family doctor or the local radiologist. In general, you can assume that the head lies outside the device when examining body regions below the navel. In very difficult cases it may be necessary to perform a short anesthetic during an MRI.
In that case, however, you have to come to the examination accompanied by someone, because you are no longer allowed to drive the whole day afterwards.
Read more on the topic: Procedure for an MRI examination
Duration of an MRI examination
An MRI scan usually takes between 20 to 40 minutes.
The exact duration depends on the one hand on the type of MRI examination and on the other hand on:
- possible waiting times
- Complications and
- of the Cooperation of the patient from.
- That used MRI machine as well as the clinical question and the body section to be examined also play a role in the duration of the examination.
Usually this is no longer than 15 to 20 minutes. In clinics, the start and duration of the examination can be postponed if, for example, emergencies have priority and must be examined first.
Another reason for a longer duration is insufficient cooperation on the part of the patient.
Some people cannot relax enough or prevent the exam by not lying still. This can make it necessary to repeat the examination.
For the actual duration of the examination:
- Preparatory- and
- Follow-up time
be included in the planning.
Preparation includes removing metallic objects such as piercings, jewelry, glasses or removable dentures.
Digital data carriers and credit cards are also not allowed because they are damaged by the magnetic field of the MRI examination.
Waiting times may arise if, as already mentioned, other patients have priority, e.g. due to an emergency situation. Technical problems can also lead to delays. In the follow-up time, usually made an initial discussion of the findings. This can take different lengths of time depending on the type of finding.
An MRI examination with contrast agent also takes a little longer than an examination without contrast agent. As a rule, two recordings of the structures to be imaged are made, namely before and after the application of the contrast medium.
Do you have to be sober for an MRI?
It is usually not necessary to come for an MRI exam on an empty stomach.
In the case of special examinations or questions, however, it may be necessary to carry out the examination soberly.
This means that you are not allowed to drink or eat anything a few hours before the examination.
Usually 6 hours of food and 2 hours of fluid are necessary. You should then only drink a little water in sips.
This is for example at MRI examinations of the abdominal organs (Intestines, gall bladder, stomach etc.) necessary.
However, you will be explicitly informed about such a peculiarity in advance. Unless otherwise communicated, there is no need to appear sober.
However, if you are unsure, it is advisable to ask about the information in advance of the examination.
indication
The question of whether magnetic resonance imaging is justified is subject to a certain number of criteria and considerations that should be carefully assessed.
On the one hand, this is due to the fact that an MRI is one of the most expensive imaging procedures and consumes an enormous amount of energy.
Mainly, however, the indication for an MRT examination is narrowed down, as there is only a small number of devices available.
Computed tomograph (CT) and X-ray machines in particular are standard in most hospitals today, MRIs are only used in larger hospitals or radiological practices.
It must therefore be ensured that the rare places are made available for actually relevant patients and emergencies.
Nevertheless, there are a number of indications that make an MRI useful, as it is superior to other examinations in terms of the quality of the display or because you want to prevent excessive exposure to X-rays, as occurs with CT.
A typical indication for an MRI scan is the accurate visualization of soft tissues, such as:
- Musculature
and - Tendons
- connective tissue
- cartilage
- Brain parts
such as - Spinal cord
and - Band washers.
The assessment of tumors, which can be easily assessed in the MRI for size, extent and the infiltration of neighboring organs, is of particular importance (Staging).
The primary search for a tumor can also be used as an indication. Above all, the female genital organs such as the ovaries, uterus and also the breast are often examined with an MRI if a tumor is suspected.
The kidneys or the pancreas are also in focus here.
New growths in the brain can be seen extremely well on an MRI of the brain.
In the case of an oncological indication, a contrast agent is often used to better visualize specific structures.
The MRI is currently the safest method to rule out or diagnose a tumor disease.
Read more on the topic: Ultrasound of the abdomen
In addition to this department, the Assessment of the muscular and skeletal system, i.e. the musculoskeletal system, the majority of the MRI examinations initiated.
A typical indication here would be the suspicion of one disc prolapse or one Protrusion of the intervertebral discthat has not yet been recorded with clinical certainty.
Here, an MRI scan can make the diagnosis with certainty, although the patient's symptoms and not the MRI findings must be treated.
In addition to the intervertebral discs are often also Joints examined, with almost every joint clearly visible with the MRI.
An important indication here would be the suspicion of damage to the articular cartilage Knee joint, the so-called Menisci.
One of the most common indications in this context is the clarification and precise assessment of the injury in one Cruciate ligament tear.
Please also read our topic on this MRI for a cruciate ligament tear.
The differentiation between inflammatory, wear-related or metabolic pathological processes can also be an indication.
At Effusion in the jointAnother indication, an MRI can often detect signs of damage earlier than conventional procedures such as Ultrasonic or clinical examinations.
In addition, the associated tendons and muscle attachments are also examined using MRI if more detailed information is needed in the case of unclear pain or irritation.
The indication for an MRI examination is often made in the case of diseases or injuries to the head.
Play alongside the tumor diseases already mentioned Bleedingthat take place both within the brain and between the brain and the skullcap often play a role.
Also the clarification of a Ischemia, in other words, insufficient or no supply of parts of the brain in the sense of one Stroke, is a common MRI indication.
In addition, if the Closure of a vessel in the head MR angiography may be shown, a representation of arteries and veins with the help of contrast medium.
MR angiography can be used anywhere in the body.
Another indication is e.g. assessing the aorta, the pulmonary vessels if suspected Pulmonary embolism or the examination of vessels in the abdomen, pelvis and legs.
Read more about the topic here Angiography
Another important indication is the search for typical signs multiple sclerosis (MS) in the foreground, which are particularly visible in the MRI.
Be here for special MRT's for MS with contrast media prepared.
A rather rare, but all the more important indication for an MRI as a supplement to the Cardiac ultrasound is the capture of certain Diseases of the heart.
The main focus is on congenital malformations and the status of the coronary vessels, as well as structural defects or malignant neoplasms.
Theoretically, one can examine the whole body with the MRI from the head and neck area to the chest and stomach to the feet.
In many questions like the ones mentioned above, it offers a better recording and presentation of the disease than other methods.
However, there are also a number of indications for which the CT is superior to MRI.
In addition, many of the diseases or injuries can be identified and treated in advance. Only if more detailed clarification is required is an MRI examination considered as a supplementary means.
MRI according to location
MRI of the head
At the headMRI (Synonym: magnetic resonance imaging of the skull) is a radiological examination procedurewhere the Brain can be represented with the help of a magnetic field.
In the course of the head MRI you can also bony parts of the skull, the head blood vessels, the cerebral ventricles (cerebral cavities) together with the ones inside Cerebrospinal fluid (Cerebral fluid) and the remaining soft tissues of the skull are shown. A head MRI is now routinely performed for a variety of complaints.
The reason for this is the fact that this diagnostic procedure especially meaningful pictures supplies. In addition, when performing an MRI of the head, in contrast to conventional X-rays, does not cause radiation exposure for the sensitive brain structures.
Performing magnetic resonance imaging of the head can be useful for many different indications. Especially after one Accident event Head MRI can help with this possible Cerebral hemorrhage, Brain injuries and Craniocerebral trauma (SHT). An MRI of the head can also be helpful in the case of inflammatory changes (e.g. MS) or bleeding into the brain.
Other indications for a head MRI are:
- Brain tumors
- Cerebral infarctions
- Meningitis (Meningitis)
- Encephalitis (Encephalitis)
- Changes in blood vessels
- unclear a headache
- chronic a headache
Furthermore, with the help of a head MRI, the Eye socket (Orbit), the Inner ear including the ossicles and internal auditory canals, Malformations of the bony skull and changes in the area of the Temporomandibular joints being represented. Since it is essential when performing a head MRI that the patient remains in a certain position, he is given a so-called Head coil created.
In addition, the head must be fixed on the examination table. For this reason arises with Anxiety patients In particular, the head MRI is particularly difficult to carry out. In order to avoid anxiety or panic attacks during the preparation of the head MRI, it may be useful to take a light sedative. There are basically two methods of MRI of the head: The Image taken without contrast medium and the so-called Contrast medium absorption (MRI with contrast agent).
In most cases, head images without contrast media are first taken during the session. But if so special structures or the vascular courses must be shown, a contrast agent must also be administered during the examination.
In this case, before the patient is fixed in the device, a Indwelling cannula (peripheral venous access; PVC).
The usual ones apply to the head MRI Contraindications as for any other MRI exam. Especially for people who have a Pacemaker are supplied, it must be carefully considered whether the production of an MRI is justifiable. Even in patients with artificial heart valves With a few exceptions, head MRI may not be performed.
Other contraindications for a head MRI are:
- implanted defibrillator (ICD)
- Metallic foreign bodies in dangerous locations (e.g. near the eyeball)
- medical implants (especially Cochlear implants)
Further information can be found under our topics: Head MRI
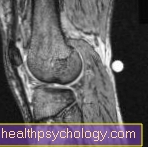
MRI knee
The high-resolution images created using the Magnetic resonance imaging can be obtained make this procedure the ideal diagnostic method Joint discomfort. Above all, illnesses that arise in the course of a traumatic event (for example during sports) or as a result of years of wear and tear can be optimally displayed with the help of the knee MRI. A knee MRI is usually done outpatient with a resident radiologist carried out. However, most clinics can also produce a knee MRI.
Before the actual exam, patients should remember to empty their bladder completely. An interruption during the recording is not easily possible. In addition, everyone must be in a changing room in front of the examination room Metal objects are deposited. This applies to both Jewellery and Hair clips, as well as for Piercings and removable Braces. The knee to be examined must then be placed in the MRI machine.
For people under Claustrophobia suffer, is that Knee MRI comparatively pleasant.
The reason for this is the fact that the upper body is completely outside the tube even during the examination. In addition, in most cases it is even possible to do a Companion to take with you to the examination room.This can be of great benefit, especially for young children and anxious patients. In contrast to the conventional X-ray the magnetic resonance tomograph does not work with X-rays. Because of this, this research method brings no radiation exposure for the patient with himself.
During the production of the MRI images, it should be remembered that any movement will result in the images becoming blurred and thus unusable. The investigation of the Knee joint Using an MRI for the knee takes no longer than in most cases 30 minutes.
The MRI examination on the knee does that Tissues near the joint, the ligaments and cartilage of the joint visible. For this reason, performing magnetic resonance imaging of the knee joint can be useful for a variety of diseases.
Especially with one Cartilage damage, one Cruciate ligament tear or Meniscus damage there is no comparable diagnosis to the MRI of the knee.
To the typical Indications of the knee MRI include:
- unexplained knee pain
- Meniscus damage
- Cruciate ligament tear
- Cartilage damage
The Jointoscopy (Arthroscopy) is considered Alternative to knee MRI. With this examination method, however, a small one must camera about a Skin incision be introduced into the knee joint. With this method, too, changes in the cartilage and damage to the menisci can be reliably depicted. The advantage of this examination method is the possibility of being able to correct some changes during the reflection. This means that slight changes in the cartilage can often be treated in the same session.
The disadvantage of a jointoscopy is the fact that it is a surgical intervention acts and therefore to the typical complications can come. Especially Wound healing disorders and Infections are among the most feared complications of a jointoscopy. In addition, in contrast to the MRI of the knee, the mirroring of the knee joint must in most cases be carried out in an inpatient setting.
In addition, the surgical incisions lead to a temporary restriction of mobility of the knee joint. The informative value of such an arthroscopy on the knee also depends to a large extent on the skills of the surgeon. The images of the knee MRI, however, can stored digitally and thus, in the event of unclear findings, can be interpreted by different specialists.
Further information can be found under our topics:
- MRI of the knee
- MRI of cruciate ligament tear
Cervical spine
The Magnetic resonance imaging (Synonym: Magnetic Resonance Imaging / MRT) is the ideal method for the section-by-section display of the Spine. For most diseases of the spine, the MRI is even considered the first choice of examination.
Since the MRI is also used in the Cervical spine (Cervical spine) delivers high-resolution images, pathological changes can usually be depicted down to the smallest detail. First of all, the fact that the roots of each Spinal nerves can be displayed without overlaying with the cervical MRI, offers ideal diagnostic possibilities. For this reason, diseases such as nerve compression and irritation that occur in the course of a herniated disc can be optimally assessed.
Further indications for performing an MRI of the cervical spine are:
- Herniated discs of the cervical spine
Please also read our special topic: MRI for a herniated disc - Broken bones
- Bone spurs
- Spinal stenosis
- Spondylolisthesis (vertebral sliding)
In addition, with the help of the cervical MRI, less common diseases, for example inflammatory processes or tumorsjudge optimally. At the MRI of the cervical spine a distinction must be made between two procedures. As a rule, images without contrast media are made at the beginning of the examination. Depending on the indication, a Contrast media administered. In this way, different structures of the cervical spine can be better represented. The contrast medium MRI of the cervical spine is mainly at Suspicion of the presence of inflammatory processes or tumors makes sense.
Performing a cervical MRI usually takes approximately 20 to 30 minutes. The patient to be examined is in lying position placed in the magnetic resonance tomograph. Since any movement during the examination leads to the recordings becoming blurred and therefore unusable, the patient's head must be on the examination table fixed become.
This situation can be especially true for patients who are taking Claustrophobia suffer, be very stressful. However, possible anxiety attacks can now be relied on by taking one Sedative be avoided. In this context, however, it must be noted that operating vehicles after taking a sedative is not permitted for the time being. For this reason, the patient should bring an accompanying person to the examination.
Further information can be found under our topics: MRI of the cervical spine
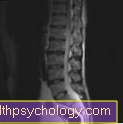
Lumbar spine
Since the Magnetic resonance imaging is best suited to depict the spine in the smallest parts, parts of the lumbar spine (lumbar spine) can also be depicted. Depending on the type and location of the complaints, cross-sectional images of the lumbar spine can be generated from every direction and in every plane. Based on these images, the specialist can make a quick and targeted diagnosis. In addition, additional images of the entire spine can be made for complaints that only affect the lumbar spine. This is very important mainly because Pain in the spine likes to radiate to other segments. Complaints that are perceived by the patient in the lumbar spine can possibly originate from the thoracic vertebrae or the hip joint and have no connection with the actual lumbar spine.
Especially the Overlay-free representation of the roots of the spinal nerves enables an optimal assessment of the extent of various diseases. This is especially true in patients who Crushed nerve roots or Nerve root irritation have an enormous advantage. In addition, less frequent causes of pain in the lumbar spine, such as inflammation or tumors, can be safely excluded with the help of the lumbar spine MRI. In addition to the production of a lumbar spine MRI without a contrast agent, recordings with a special gadolinium-containing contrast agent are now standard procedures.
Typical indications for the preparation of an MRI of the lumbar spine include:
- Herniated disc of the lumbar spine
Please also read our special topic: MRI for a herniated disc - Lumbar vertebrae fractures
- Vortex sliding
- Inflammation
- Tumors
For an MRI examination of the lumbar spine, the patient must be positioned on a movable couch. This couch is pushed into the magnetic resonance tomograph.
Since the MRT machine can be very noisy while the recordings are being made, the patient becomes a Ear protection created.
Further information can be found under our topics MRI of the lumbar spine
shoulder
This applies to most shoulder diseases Magnetic resonance imaging as the diagnostic agent of choice. With the help of the shoulder MRI, both the bony structures, as well as the Ligaments and muscles of the shoulder joint being represented. In addition, Changes in the cartilage area of the shoulder map true to detail.
An MRI of the shoulder takes a period of time in most cases 20 to 30 minutes in claim. During this period, the patient to be examined must remain in a certain position. If he does not do this, the MRIRecordings out of focus and useless for further diagnostics. For this reason, it is particularly important that the patient is fixed on a movable couch before the actual examination begins. Especially in the head and shoulder area, there must be no room to move. Swallowing too hard or accidentally sneezing can make the recordings unusable.
Fixing can be especially useful for people who want to Claustrophobia suffer, be very uncomfortable. For this reason, it is advisable, especially when MRI of the spine, the head and the shoulder, a light one before the examination Sedatives to take. In addition, it can help if the patient is up to the treatment room by one trusted person is accompanied. In addition, it must be noted that the Driving a motor vehicle after taking a sedative is not permitted for the time being is. For this reason, too, it is worthwhile for the patient not to come to the shoulder MRI appointment alone.
The most common conditions that can be diagnosed with shoulder MRI include:
- chronic Shoulder pain
- chronic overload of the shoulder
- chronic instability of the shoulder
- Torn long biceps tendon
- arthrosis
- Impingement Syndrome
- Tendinitis
Further information can be found under our topics: MRI of the shoulder
Cost of an MRI examination
Once performing an MRI medically necessary is (indication), all incurred Costs assumed. This applies both to those with statutory health insurance and to private patients.
If the attending physician sees no medical need for an MRT examination to be carried out, but the patient nevertheless wishes to have a magnetic resonance tomography, he must bear the costs for this examination himself.
The amount of the costs depends on the type of MRI. A MRI of the knee joint for example causes costs of approximate 500 - 600 euros. The cost of an MRI of the skull or spine, on the other hand, is usually higher. The costs vary within the facilities and the MRIs performed.
You can find extensive information on this topic at: Cost of an MRI examination









.jpg)