Herniated disc at the level of L5 / S1
Synonyms
Lumbar disc herniation, disc prolapse L5 / S1, lumbar disc prolapse
introduction
Many people with persistent and severe back pain assume that it could be a herniated disc. In fact, however, it can be observed that real herniated discs relatively rarely lead to persistent, severe back pain.
In most cases, the symptoms are caused by muscular tension or pinching of nerves.
Read more about this under Back pain in the lumbar spine
In addition, it should be noted in this context that a herniated disc does not necessarily have to cause pain.

A herniated disc between L5 and S1 is often discovered by chance without causing any symptoms beforehand. This is a herniated disc between the last lumbar vertebra and the first sacral vertebral. There can be a variety of causes for the development of a herniated disc.
The exact location of the prolapse therefore plays a decisive role in the search for the cause.
If the herniated disc occurs between L5 and S1, a Wear-related change in the intervertebral disc itself or the adjacent vertebral bodies be detected. For this reason, one usually speaks of a prolapse between L5 and S1 degenerative disc herniation.
In addition, you can permanent improper strain on the lumbar spine lead to this deep herniated disc.
People who often sit at their desks in a stooped position or have to do heavy physical work are particularly at risk.
Besides the pain you can Loss of sensitivity, tingling sensations and muscle weakness be an indication of the presence of a herniated disc between L5 and S1.
People who notice typical complaints should Consult a specialist in orthopedics or neurology as soon as possible. If there is a herniated disc, this can be determined during the extensive diagnostics.
In addition, surgical treatment of the herniated disc between L5 and S1 after an early diagnosis may be possible with the help of physiotherapy exercises be bypassed. In the case of a late diagnosis, however, the herniated disc usually has to be treated with surgery.
causes
The causes for the development of a herniated disc between the 5th lumbar vertebra and the 1st sacral vertebra can be varied.
In most cases, however, it can be assumed that the herniated disc between L5 and S1 is a wear-related disease of the spine.
In the course of aging, more or less pronounced deformations occur in the area of the individual intervertebral disc segments. In this way the intervertebral disc can change its original position and on the spinal cord or individual nerve fibers to press.
It can therefore be assumed that herniated discs are a rarity in young people. On the other hand, with increasing age, the risk of suffering a herniated disc also increases.
In addition, the risk of a herniated disc between L5 and S1 can be increased by various factors.
In this context, it is important to note that the intervertebral discs between the individual vertebrae primarily act as shock absorbers. In this way, loads can be cushioned without affecting the bony vertebrae or the spinal cord.
The reason for the shock-absorbing properties of the intervertebral discs is theirs high water content. With increasing age, however, it can be observed that the water content within the intervertebral discs steadily decreases. In this way their deformability and buffer capacity are reduced. The risk of developing a herniated disc increases rapidly.
Appointment with a specialist for a herniated disc?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
A herniated disc is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
Therefore, treating a herniated disc requires a lot of experience.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Especially with one Herniated disc in the lumbar spine area (e.g. between L5 and S1) Incorrect or overloading of the spine accelerate this age-related process.
Persistent incorrect loads, for example at heavy physical work, can cause the Gelatinous nucleus of the intervertebral disc relocated to the spinal canal.
In the course of this, the affected patient develops a Compression of the spinal cord or individual nerve fibers emanating from it.
The sustained compression can cause typical symptoms such as Back pain, numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness be evoked. The wear and tear of the intervertebral disc between L5 and S1 can be accelerated by other factors.
Among the most important Risk factors counting very overweight, improper or excessive strain on the spine, weak back and abdominal muscles and spinal injuries.
Symptoms
The symptoms that are caused by a herniated disc depend primarily on the exact location of the prolapse. In addition, the position of the intervertebral disc in the spinal canal after slipping also plays a decisive role.
In the case of a central herniated disc between L5 and S1 without lateral emphasis on the leaked disc tissue, the affected patients mainly describe local back pain. This back pain typically increases in intensity when the upper body is bent over. Numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness are not to be expected in these cases.
In the case of a herniated disc between L5 and S1 with lateral emphasis in the spinal canal, however, the nerve roots or individual nerve fibers branching off from them can be pressed off. This can lead to numbness, tingling, muscle weakness and even symptoms of paralysis in the affected patient.
If the L5 nerve root is compressed, the affected people typically notice sensory disturbances on the inside of the lower leg, the back of the foot and the big toe. In addition, the lifting of the toes and the abduction of the hips may be restricted.
If, on the other hand, a herniated disc leads to compression of the S1 nerve root, corresponding sensitivity disorders occur in the area of the outer rear lower leg and on the outer edge of the foot. Affected patients also notice a weakness when rolling the foot.
In the case of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine, it must also be noted that, depending on the exact location, the urinary bladder and / or the intestine can be impaired. Because of this, some of the affected patients suffer from urinary and / or fecal incontinence.
Read more on the subject below Symptoms of a herniated disc of the lumbar spine and S1 syndrome
The herniated disc in the lumbar spine can also trigger a so-called cauda equina syndrome, which should be recognized urgently and, if left untreated, can lead to permanent paraplegia. We therefore recommend our website for further information: Cauda equina syndrome - do I have paraplegia?
Numbness and dermatomes
With a herniated disc between L5 and S1, numbness may occur in the dermatome of the L5 nerve root. The corresponding dermatome of the L5 nerve root extends over certain areas of the thigh and lower leg.
For this reason, people with a herniated disc between L5 / S1 may experience numbness and / or pain in the back of the thigh.
In addition, the outside of the knee, as well as the anterior and lateral lower legs, belong to the dermatome of the L5 nerve root.
If a herniated disc leads to numbness, a specialist must be consulted urgently and appropriate treatment initiated.
Without therapy, permanent damage to the nerve fibers and the associated permanent numbness in the dermatome of the nerve root L5 can occur.
Read more on the subject at:
- Numbness after a herniated disc
and - Numbness in the leg
- Dermatome
Impairment of key muscles
In the case of a pronounced herniated disc between L5 and S1, which leads to severe damage to the corresponding nerve root, in addition to the sensitive failures, impairment of the Identification muscles to be watched.
Identification muscles are muscles that are supplied by a specific spinal cord segment and that can indicate the location of the damage in the event of failure.
Will the motor nerve fibers damaged by the herniated disc between L5 / S1, the function of the Extensor hallucus longus muscle (long big toe extensor), des Tibialis anterior muscle (anterior tibial muscle) and des Gluteus medius muscle (glutes middle muscles) impaired.
If these identification muscles are damaged, affected patients can No longer lifting the big toe adequately.
In addition, an impairment of the anterior tibial muscle as one of the L5 / S1 muscles that is responsible for the Foot no longer adequately turned inwards (so-called Supination), spread outwards (Adduction) and raised towards the tip of the nose (Dorsiflexion) can be.
In those affected, a so-called “stepper gait” can be observed due to the damage to the nerve fibers of these characteristic muscles.
Displacement of the intervertebral disc to the right
If there is a herniated disc between L5 and S1, the disc can move out of its normal position in various ways.
Patients who experience a dislocation to the right usually experience similar symptoms.
By shifting the intervertebral disc to the right, it mainly occurs in the Severe pain in the area of the buttocks and right leg.
In addition, the sensitivity disorders can only be perceived on the right in those affected.
At the Stand on tiptoe the left foot is usually unaffected, while the right is a discrete one Palsy of the foot (slight paralysis of the Extensor hallucus longus muscle; long big toe extensor) can be observed.
The right calf muscles can also be affected (S1).
Shift of the intervertebral disc to the left
If, however, the intervertebral disc moves increasingly between L5 / S1 in the case of a herniated disc Leftthen the symptoms appear on the left side.
Affected patients typically feel pain in the area of the left buttocks and left thigh. In addition, the L5 nerve root dermatome loss of sensitivity or S1 Left.
Motor failures cannot be observed on the right leg, but only on the left.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of a suspected herniated disc between L5 / S1 usually comprises several steps. First, a detailed doctor-patient discussion (anamnese) help to narrow down the diseases that may be present.
During this conversation, the patient concerned should describe the symptoms he has observed as precisely as possible.
In addition, various lifestyle habits (e.g. sporting activities), the job and existing previous illnesses play a decisive role in this doctor-patient conversation.
An orienting neurological examination should then be carried out.
By checking the sensitivity in the skin areas assigned to the individual nerve segments, it is already possible to roughly estimate whether there is a herniated disc and at what level the change is.
In addition to the sensitivity test, the reflexes and muscle strength should also be checked.
Read more on the topic: Bragard test
If there is evidence of impairment of the nerve fibers, the nerve conduction velocity should also be measured.
Since various internal diseases can cause symptoms similar to the herniated disc between L5 and S1, the most important pulse points on both legs must also be checked. In this way, circulatory disorders of the legs (for example the so-called "peripheral arterial occlusive disease, pavK for short") can be excluded.
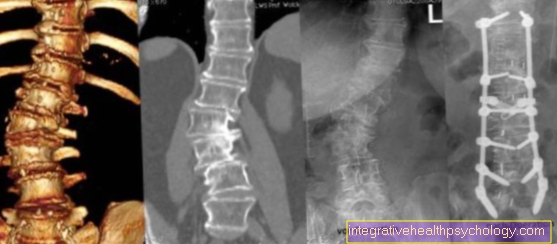
If the suspicion of a herniated disc between L5 and S1 is confirmed in the course of the diagnosis, imaging procedures must be ordered.
In particular, taking X-rays in different postures plays a crucial role in diagnosing a herniated disc between L5 / S1. A disadvantage of conventional X-rays, however, is the fact that only the bony vertebral bodies with possible signs of wear can be assessed in this way. The intervertebral disc itself cannot be assessed in these functional images.
For this reason, if a herniated disc is suspected between L5 / S1, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT) or so-called myelography should also be performed.
With the help of these imaging procedures, the spinal cord and nerve fibers can also be visualized and assessed. The imaging of these structures can be further improved by administering a special contrast agent.
Read more on the subject below MRI for a herniated disc
MRI of the lumbar spine
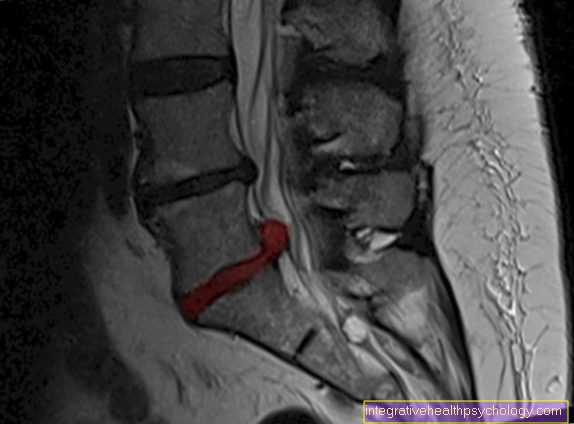
MRI image of a herniated disc L5 / S1
therapy
The choice of the most suitable treatment strategy for a herniated disc between L5 / S1 depends primarily on its extent and the symptoms.
If the herniated disc is diagnosed early between L5 and S1, one is usually done first conservative (non-operative) therapy.
Should the complaints perceived by the patient concerned change within a period of six to eight weeks do not mend, should have one alternative treatment strategy to be thought about.
The non-surgical treatment for one Herniated disc between L5 / S1 mainly includes physical rest (rest), one adequate pain therapy and the Change of risky lifestyle.
In acute pain, the spine should be immobilized if possible.
However, absolute bed rest for long periods of time can have a negative effect on the healing process. For this reason, the affected patient should always receive a Sport that is gentle on the spine be suggested.
Especially swim is particularly suitable for alleviating the symptoms.
In many cases, drugs that relax muscles can also be used successfully.
A operative treatment should only be considered in the case of a herniated disc between L5 / S1 if other therapeutic measures do not show the desired success. It can also be pronounced Impairment of the sensory or motor nerve conduction represent the justification for surgical treatment.
Conservative therapy
If a herniated disc is diagnosed early between L5 / S1, purely conservative therapy is completely sufficient in most cases.
In general, it can be assumed that approximately 90 percent of the affected patients respond well to conservative therapy and do not require surgery.
Conservative therapy should, however, after a period of three to four months The first signs of success, otherwise the treatment strategy must urgently be reconsidered.
The protection of the affected part of the spine plays a decisive role in conservative therapy. In addition, the patient should be asked to exercise the back muscles in the course of a special physiotherapy to be able to counteract the changes in the lumbar spine in this way.
Whether an outpatient physiotherapeutic therapy is sufficient or a inpatient rehabilitation must be carried out, should be decided on a case-by-case basis.
Acute pain that occurs with a herniated disc between L5 / S1 can be avoided in the course of conservative therapy locally applied heat be alleviated. Special ointments and plasters are particularly suitable for conservative therapy in the case of a herniated disc between L5 / S1.
In addition, affected patients should follow a fixed schedule in the acute pain phase pain reliever medicines take in. The medication best suited to the symptoms and the dosage regimen tailored to the patient should urgently be identified Specialist agreed become.
An increase in symptoms under conservative therapy or at diagnosis, particularly pronounced Signs of paralysis can make an immediate operation of the herniated disc necessary.
Exercises and physiotherapy
Conservative treatment methods, such as special exercises and physiotherapy, can be particularly helpful in the case of a fresh or less pronounced herniated disc between L5 / S1.
The first attempts at therapy for a herniated disc between L5 / S1 should primarily serve to alleviate the acute pain symptoms.
In addition, the stability of the spine should definitely be increased through special exercises and physiotherapy.
Above all, exercises that serve to build up the back muscles can help improve the symptoms within a very short time.
Read more on the subject below Strengthening exercises for a herniated disc
In the case of a herniated disc between L5 / S1, however, the exercises should only be learned under the supervision of a specialist.
Otherwise, incorrectly performed exercises could permanently damage the spine.
In addition, in the conservative treatment of a herniated disc between L5 / S1 (for example with the help of physiotherapy), it must be ensured that the symptoms should improve within a few weeks.
If this is not the case, other treatment options must be urgently considered.
Operation of a herniated disc in the lumbar spine
A surgery is always an option for a herniated disc between L5 and S1 if conservative treatment measures are not effective or Nerve damage threaten.
Especially in patients with a herniated disc between L5 / S1 Loss of sensitivity or motor deficits surgery should be considered.
In general, the indication for an operation in the presence of a herniated disc is now only very cautious. In addition, it should be noted that due to the enormous risks of an open surgical procedure, now almost exclusively via so-called minimally invasive procedures is treated.
With the help of minimally invasive procedures, which may also be used in local anesthesia can be performed, however, it is not possible to treat advanced herniated discs between L5 and S1.
Especially the so-called "Chemonucleosis", in which the inner gelatinous ring of the intervertebral disc is liquefied with chemical agents and then sucked off, is now one of the standard procedures.
In addition, an operation with the laser with a fresh herniated disc between L5 / S1. With this procedure, the displaced intervertebral disc has to be removed with the laser. In this way, the pressure on the nerve fibers can be reduced or completely relieved.
Another and particularly popular surgical method for a herniated disc between L5 / S1 is the so-called "Percutaneous nucleotomy". With this method, the excess volume of the gelatinous nucleus is sucked off through the skin. Chemical substances are not used in this operation.
In contrast, advanced herniated discs between L5 / S1 usually require a conventional one open surgery. This often also applies to a herniated disc between L5 / S1, which has already caused pronounced sensory or motor deficits.
During open disc surgery, a large skin incision must be made and the relevant vertebral segment exposed.
Because of this, it may possibly increase after surgery Inflammation or wound healing disorders come. However, these possible complications can usually be treated without any problems in inpatient care.
Exercise for a herniated disc
Sport can significantly reduce the severity of the symptoms in people who suffer from a herniated disc between L5 / S1. In addition, can back-friendly sport Both prevent a herniated disc in the lumbar spine and inhibit its progression.
In this context, however, it must be noted that not every sport gently on the back affects.
For this reason, affected persons should urgently discuss with the treating specialist what kinds of sports can be practiced without any problems.
Especially swim is considered a sport that is particularly gentle on the spine and joints. In addition, exercises that strengthen the back muscles can help alleviate the symptoms of a herniated disc.
prophylaxis
A herniated disc in the lumbar spine (for example between L5 / S1) can be identified long-lasting incorrect and excessive loads lead back.
For this reason, targeted training of the stabilizing back muscles can help prevent such a slipped disc. In addition, members of the risk groups should be on a back-friendly posture and sufficient exercise respect, think highly of.