Procedure of an MRI
General
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is also known as magnetic resonance imaging. This is an imaging examination method which, in contrast to X-rays and computed tomography (CT), is not based on X-rays and therefore offers the advantage that the patient is not exposed to any radiation. The images that are made during an MRI are created by applying a strong magnetic field. This affects hydrogen atoms in the human body, which in turn emit radio waves. These radio waves can be detected by a computer and the MRT images are created from them. These are sectional images of the human body that show the corresponding body region in great detail. This makes it possible to detect very small changes in the tissue and to diagnose a disease at an early stage.
reasons
The MRI scan is used to diagnose many different diseases diagnose or to exclude. Also for Sales control or MRI can be used to check the success of the therapy. Basically, a magnetic resonance tomography delivers more detailed images than a computed tomography. Some organs, such as the lung, but do not reproduce as well there.
The MRI is particularly suitable to Changes in the soft tissues of the body. These include blood vessels, tendons, muscles, ligaments and cartilage. The brain, the spinal cord, the intervertebral discs and the internal organs can also be shown very well on the recordings. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging plays a major role in the Tumor diagnostics. Tumors and metastases can be detected from a very small size.
An MRI scan can be done on different areas of the body. In the head area, bleeding and cerebral edema can be recognized quickly and the course of certain diseases, such as Multiple sclerosis (MS) to be controlled. Many organs, such as the thyroid, heart, liver, kidney, adrenal gland, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, large intestine and the genital organs can be examined for the smallest changes. Joints and bones can also be assessed very well.
preparation
A special preparationsuch as sobriety or purging is prior to an MRI scan not necessary. There will be an upfront one Educational talk carried out, in which the doctor explains the procedure of the examination to the patient, inquires about his state of health, shows him risks and gives the patient the opportunity to ask questions.
Before performing the examination, the patient must put down all metal-containing parts. These could be from the strong magnetic fieldwhich is generated during the examination, dressed become and to bad injuries to lead. These include, for example, jewelry, metal parts on clothing, keys, money and credit cards, glasses, braces and dentures. Metal parts that are in the body, such as surgically inserted screws, wires or joint replacements, artificial heart valves and also tattoos with metallic colors must be announced before the examination.
Read more on the subject here MRI and tattoos and Clothing in the MRI - what should I wear?
In the examination room, the patient has to lie on a couch and is usually given headphones that are supposed to dampen the loud knocking noises generated by the examination device.
Contraindications
Magnetic resonance imaging cannot usually be performed on patients with cardiac pacemakers or implanted defibrillators (ICD), as this can damage the implants and the patient. This also applies to patients with built-in insulin pumps or inner ear implants (Cochlear implants).
Read more on the subject at: MRI with a pacemaker
execution
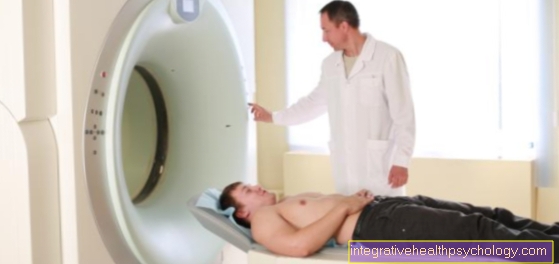
The patient lies in the examination room on a couch that can be moved into the tubular examination device. Depending on which part of the body is examined, the couch is fully or only partially retracted. During the examination, very loud knocking noises occur, which are muffled by the headphones.
When the radiological-technical assistants have made all the preparations, they leave the room. However, they remain in contact with the patient via an intercom system and are located behind a pane of glass so that they can see the patient during the entire examination. In addition, the patient is given an emergency button that they can press if for any reason they need to be driven out of the tube.
When the examination begins, the patient should try not to move so that the images become sharp. During some examinations, the patient is asked to hold their breath briefly in between.
Read about this too MRI - How far do I have to put my head in?
Duration
The duration of an MRI scan is depending on what is to be examinedl and how many recordings need to be made. Magnetic resonance imaging usually takes time to perform about 15 to 30 minutes. Is a Administration of contrast medium necessary, the investigation may also longer last.
In addition, the waiting time and the preparation time should be planned.
Contrast media
Because some tissues, such as Muscles and blood vessels, which are quite similar to the MRI images, it is necessary for some examinations to do a Contrast media to use whichever the Differentiate structures better from one another leaves. Also Foci of inflammation or Tumors can be better recognized by the administration of a contrast agent.
Usually the contrast agent is used during the examination injected into a vein in the arm. It will be a Contrast agent that does not contain iodine used, which is usually very well tolerated. Just very rare to step allergic reaction on. In patients with a Kidney disease however, it should not be used.
MRI of specific body regions
MRI of the cervical spine
If an MRI scan of the Cervical spine (Cervical spine) is performed, the patient becomes drove his head into the examination tube. On the recordings Changes in the vertebrae, of the Band washers and des Backmarks detect. You can also Damage to the vessels and Tumors recognize in this area. Changes due to various diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) can help to assess the course of the disease.
MRI of the lumbar spine
An MRI scan of the Lumbar spine (Lumbar spine) is performed to bony changes the vertebrae, intervertebral disc protrusions or herniations. In addition, can also Spinal cord and vessels be judged in this region. Also Inflammation and Tumors can be seen on the recordings.
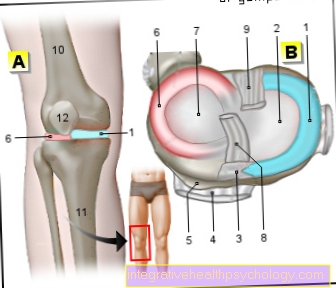
MRI of the knee
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to visualize both the bones and the other joint parts such as tendons and muscles on the knee Cruciate ligaments and the Menisci represent.
Injuries of any kind can therefore usually be detected quickly on MRI images of the knee. To the typical indications belong here Cruciate ligament tears, Cartilage or meniscus damage, as well as unexplained knee pain that lasts longer.
MRI of the shoulder
At prolonged pain in the shoulder an MRI scan can reveal the cause. Both the bony parts of the joint as well as the tendons and muscles can be seen well on the recordings and any Inflammation or cracks are well represented. The MRI also shows inflammation of the tendon or entrapment in detail.
Before the examination, the patient is placed on the couch with special pillows so that the shoulder's freedom of movement is restricted and the images are sharp.
Read more on the subject at: MRI of the shoulder joint.
Risks
Because in the MRI examination in contrast to a CT scan no x-rays are used, the patient is not exposed to radiation and the Risks are much lower. There are so far no side effects proven, pregnant women should however only in emergencies have an MRI done.
Only that Administration of contrast media can to allergic reactions which, however, occur extremely rarely.
Claustrophobic patients should discuss this with their doctor prior to the examination. Often the head is not pushed into the tube for the examination. If this is the case, however, the person concerned may need a brief anesthetic.
Cost of an MRI examination
The costs for medical services can be found in the fee schedule for doctors.
Put simply, it regulates how medical services that go beyond the contractual medical services are remunerated. These are amounts that self-payers or those with private insurance pay for services.
Statutory insurance also pay these amounts within the framework of individual health services or with the reimbursement procedure.
The costs for an MRI examination usually fluctuate. between 400 and 700 euros.
Depending on the effort and the indication of the examination, different amounts result. The cost of a MRI scan of the abdomen (belly) and / or basin amount to around 460 euros.
There is also one in the same price category MRI scan of the head.
Optionally, the neck is also shown. The recording takes place in two projections. At least one of these is recorded in the so-called T2 weighting.
A MRI of the chest amounts to around 420 euros. In the same area there are also MRI images of the extremities showing at least two large joints of the extremity.
The representation of sections of the extremities or individual joints costs around 250 euros. An image of the thorax and the organs it contains or the aorta in its entire length is around 450 euros.
In addition, there may be costs associated with the use of contrast media or additional services. That can increase the price by around 100 euros.
A change of position and / or the introduction of a new reel lead to a surcharge of around 60 euros. The use of computer-controlled analyzes such as a 3D reconstruction increases the costs by around 50 euros.
All costs are given a cost number and listed in the total invoice so that the total price of an examination can then be easily understood.
Summary
Before one MRI examination the patient is asked to put down metallic and magnetic objects that he / she is carrying.
These include glasses, removable dentures, piercings, jewelry, money or other items.
Furthermore, it is advised to also store digital data carriers or credit cards, as these will be damaged by the magnet of the MRT.
At the beginning of the examination, the patient is placed on a couch so that it is as comfortable as possible for him and the examination of the area to be imaged is optimally possible. Storage pillows can also be used for this. It is very important that the patient remains relaxed and still in this position during the examination so that the images are successful.
Then the patient is put into the housing opening ("tube“) Of the MRT in which the recordings take place. Sometimes it is not necessary for the patient to be driven completely into this housing opening.
When taking pictures of the lower extremity, for example, the upper body lies outside the tube. During the examination, very loud, booming or knocking noises can be heard, which are caused by the MRI.
In contrast, patients receive hearing protection that they can put on. The housing opening is open at both ends and fresh air is constantly flowing in, and it is also bright.
A fast-acting sedative can be given to patients with claustrophobia or anxiety. For small children or infants, an MRI scan is usually performed under anesthesia. During the entire examination time, the patient can ring the bell to draw attention to himself if he feels uncomfortable or wants to abort the examination.
The examiners also observe the examination during the entire duration.
Some MRI examinations are performed using a contrast agent. Recordings are made before and after the application of the contrast agent (please refer: MRI with contrast agent).
The contrast agent is injected into a vein in the arm. The contrast medium feels a bit cool. The injection is similar to drawing blood.