Oily hair from hormones
definition
Every single hair is associated with a sebum gland.
This produces a small amount of secretion that keeps the hair and scalp supple. It is used to protect against infections, as pathogens can easily penetrate the body through dry skin. If the sebum glands secrete an excessive amount of secretion, the fatty film settles on the hair, sticking it together and making it look stringy.
Causes of oily hair

The male and female sex hormones affect the sebum glands. Androgens, the male sex hormones, increase the growth rate and secretion production of sebum glands. Estrogens as representatives of the female sex hormones have an opposite effect to androgens. Especially during puberty, when there are changes in the hormonal system, imbalances can occur that lead to greasy hair.
Only in rare cases is there an underlying cause that requires treatment. One example is polycystic ovarian syndrome. Typically, the focus here is on bleeding disorders or an unfulfilled desire to have children, as well as pain in the lower abdomen. The "masculinization" and greasy hair are also observed.
Another hormone that affects the appearance of hair is cortisol, which is produced by the adrenal gland. Cortisol is a vital stress hormone that keeps the metabolism in balance. In higher doses, it also has an anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effect, which is why it is important in the treatment of cancer or autoimmune diseases, for example. In addition to the positive effects, there are also negative effects if a larger amount than necessary is formed or if long-term therapy with cortisone in tablet form is required. In addition to oily hair and oily skin, osteoporosis, diabetes, fat redistribution from the extremities to the trunk, the full moon face, water retention and a disturbed menstrual cycle are among the more well-known complications.
Read more on the topic: Oily hair during pregnancy
Symptoms
In addition to excessively oily hair, one can increased testosterone levels a "masculinization" takes place in women. *
This includes a increased hair growth, which can also show up in the form of a beard (so-called Hirsutism). The body can more muscular become and the voice deeper. Kick frequently Skin problems as acne on.
In serious cases the Menstrual cycle and thus the Woman fertility disturbed. Insulin resistance can also be observed. This means that the body can no longer absorb its fuel sugar into the cells. There is a Diabetes mellitus of type 2.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of oily hair is primarily based on the Look in the mirror posed.
To find out if the Hormones bear complicity, this can be determined in the blood count or in the urine. If there are no other, more serious symptoms besides the oily hair, further diagnostics are not necessary.
therapy
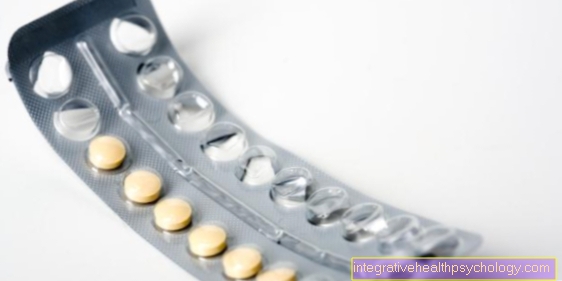
For women with the pill prevention, after consultation with the gynecologist a preparation can be prescribed that the excessive Sebum production inhibits. These not only reduce the appearance of greasy hair but also oily skin and acne.
In cases of overproduction of Androgens there is the possibility of drug intervention. Medicines inhibit the androgen receptor, which transmits the effects of excess hormones to the body's cells.
To improve the oily hair it is important not to overuse it. Loads like a Excess of care products, hot blow drying, frequent wearing of a hat or that Wash with strong degreasing shampoos should be avoided. The use of degreasing shampoos in particular creates a vicious circle that is difficult to break. Through the artificial dehydration of skin and hair the sebum glands are constantly stimulated to form more secretions, so that the hair becomes more and more greasy over time and faster and faster.
Instead, the hair should be washed in the morning with mild shampoos and lukewarm water.