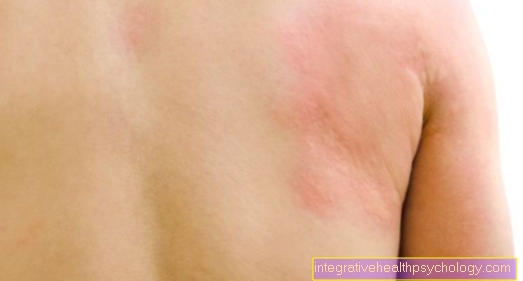
Rash on the upper body
definition
A rash describes a skin irritation that can arise from a wide variety of causes. In technical jargon, the rash is also called rash. In this case, the rash appears on the upper body. An exanthem can arise spontaneously and also spontaneously regress. A chronic rash can also occur with certain clinical pictures. Sometimes symptoms such as itching and pain can occur.
Read more on the topic: Skin rash
causes
The causes of a rash on the upper body are varied. On the one hand, it can be due to harmless causes. The sensitivity of the person concerned also plays a decisive role here. If the skin is very sensitive, soap, detergent or a certain substance can irritate the skin. This form of rash is not dangerous in itself, but it should always be watched. The use of a new shower gel can lead to skin irritation and rashes, especially on the upper body, as this area is more likely to be soaped.
A rash on the upper body can also be caused by exposure to the sun. The UV rays of sunlight lead to cell damage in the skin, which is repaired or broken down by the body in the form of an inflammatory reaction. This inflammatory reaction becomes visible to us as reddening of the skin. Sometimes there is pain, overheating and peeling of the skin. Stress can also trigger rashes. Especially if the affected person has problematic skin anyway, rashes develop more quickly under stress.
In addition to the causes mentioned, however, infectious diseases can also be the reason for a rash on the upper body. The childhood diseases measles, scarlet fever, rubella, rubella, three-day fever and chickenpox can lead to skin rashes.
Shingles also often results in rashes in a ring-shaped pattern (like a belt) around the body. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (also the trigger for chickenpox) and occurs when the immune system is weak. However, the infectious diseases are usually easy to diagnose based on other symptoms or specific patterns of the rash.
Read more on the topic: Causes of a rash
allergy
In the case of an allergy, the rash is a classic symptom. Here the body reacts to a specific substance, which actually does not pose a threat. This substance then becomes Allergen called. The allergen leads to an inflammatory reaction of the mucous membranes and the skin. This inflammatory reaction is triggered by the body's immune reaction causing a lot of histamine (a messenger substance) from mast cells (Immune cells) is distributed.
This histamine ensures that the skin is reddened and swollen. The histamine also causes increased pain perception and itching. The allergic skin rashes can in principle appear all over the body. They occur on the upper body when there has been contact between the skin and the allergen.
You might also be interested in the topic: Allergy rash
diagnosis
The rash is a visual diagnosis. This means that the diagnosis can be made just by looking, as rashes are usually easy to recognize. In addition, the anamnesis (asking for important information) is of great importance. Symptoms such as itching or pain must always be inquired about.
Here the doctor can also determine whether a certain cause is related to the rash. For example, the use of certain medications or the consumption of special foods can cause the rash. Other symptoms such as fever or general health are also important for a diagnosis.
Read more on the topic: Rash after antibiotics
Concomitant symptoms
On the one hand, the rash leads to reddening of the skin. This can take several forms. Primary fluorescences can occur in the form of spots, vesicles, pustules, wheals or papules (nodules). However, differentiating these from one another can be difficult for a person with no dermatological experience. The secondary efflorescence often results in crusts, scales, ulcers or scars. The shape of the rash often suggests a cause.
In addition to the rash, there may be other symptoms. For example, fever, increased sweating, nausea or dizziness can occur. Breathing problems, coughing and swollen mucous membranes are also sometimes observed.
Itchy rash
Itching is a common symptom of the rash. It's an urge to scratch or rub your skin. Scratching and rubbing the skin often worsens the rash, as the already irritated skin is additionally stressed by mechanical impact. The itching is mainly triggered by the messenger substances histamine and prostaglandin. These are released from mast cells in inflammatory reactions.
Typical skin diseases that cause itching are e.g. the infectious diseases rubella, chickenpox and scarlet fever which can also trigger rashes on the upper body. However, these infections usually occur in childhood and can be distinguished from one another by the shape of the rash.
Psoriasis also leads to itchy rashes, which can appear on the upper body. White flakes of skin can usually be seen here. Neurodermatitis also has a very itchy character, but tends to occur in the crooks of the arms, hollows of the knees and the face.
Read more on the topic: itchy rash
Rash without itching
The rash without itching can also have various causes. Measles (Morbilli) have no typical itching as a symptom. However, they cause a rash, which can also spread over the upper body. Measles is a viral infection that usually occurs in children. Nowadays vaccination protection covers the measles virus.
A rash that occurs due to medication is often not itchy, but it can vary widely. Sensitivity reactions such as New shower gels, detergents, etc., or allergies can trigger a rash on the upper body that occurs without itching.
When infected with the HI virus or immunosuppression (e.g. through chemotherapy), skin rashes often occur, which are caused by the growth of skin fungi. The skin fungi can grow due to the weakened immune system and occur on the upper body mainly in skin folds in obese (overweight) people.
Read more on the topic: Skin fungus such as Detergent allergy
Rash with red spots
If a rash with red spots occurs, it is first necessary to distinguish whether the spots are small and in a large number or as a larger area. The red spots are often an allergic reaction of the skin to an allergen. In many cases there is also a sensitivity reaction or an intolerance to certain substances in the form of red spots.
A skin disease that typically occurs on the upper body is rose lichen (Ptyriasis rosea) to be found. This rash lasts for about 8 weeks and is not contagious. If the spots are also itchy, it can be infectious diseases such as Act chickenpox or rubella. However, these spots mostly appear all over the body.
A syphilis infection in the second stage can also be characterized by red spots on the upper body. However, an ulcer should have appeared on the genital organs beforehand.
Read more on the topic: Rash with red spots - what is the cause?
Rash on the side of the torso
The rash on the side of the torso can have various causes. As with the rest of the body, most rashes can appear on the side of the torso. For this reason, it is difficult to draw conclusions about the actual disease based on the localization of the lateral upper body. When a person has scarlet fever, it can cause rashes in the area under the armpit. However, there is also a so-called "raspberry tongue". In addition, a rash appears in the groin area and on the cheeks.
Rash on baby
Infectious diseases such as chickenpox, measles, rubella, rubella and three-day fever are particularly common in babies. In most cases, the rash is found all over the body, not just limited to the upper body. Measles in particular, however, is the beginning rash that can be seen mainly on the upper body.
Read more on the topic: Rash on baby
therapy
The treatment of the rash goes hand in hand with finding the cause. If the rash occurred on the upper body because the skin was sensitive to a substance or a stimulus, this trigger should be avoided as far as possible. In the case of shower gel or detergent, it is better to go back to the tried and tested products.
In the case of an allergy, specific immunotherapy should be started as early as possible in order to eliminate the allergy in the best case. Apart from that, avoiding the allergens and using drug therapy can help Antihistamines (Histamine receptor blockers) or cortisone will be a good success. In general, the skin can be cooled to reduce the rash. This can be done using poultices or gels. If there is a suspicion of an infectious disease, in most cases the disease will have to heal for the rashes to subside. If in doubt, a doctor should be consulted here!