Rhinoplasty
Reasons for a nose job

The nose job (Rhinoplasty) describes a procedure in which the outer nasal framework, i.e. both cartilage and bone, is surgically corrected. Usually congenital malpositions of the nose are corrected here (hump nose, saddle nose, crooked nose), but also deformations that have arisen from nose corrections that have already been carried out can make another operation necessary. Nose corrections are not always carried out for purely aesthetic reasons, because a correction of the outer nasal framework can also be justified in the course of nasal fractures caused by trauma (accidents etc.).
In the past, women tended to undergo a nose correction more often, but this trend has been reversing significantly for some years now, and men’s appearance is becoming increasingly important and they are therefore deciding to have a nose correction.
Basically, a correction of the nose is not a health insurance benefit, but it makes sense to consult a specialist in ear, nose and throat medicine in addition to the cosmetic surgeon. There is a simple reason for this, because many people suffer from a curvature of the nasal septum, the correction of this can in most cases be carried out together with the rhinoplasty and in such cases the health insurance will cover at least part of the costs. In particular, the stay in the hospital, the aftercare treatments and the main part of the anesthesia do not have to be borne by the patient himself.
Surgical methods and procedure
Basically, all aesthetic treatments follow the same scheme. In advance a consultation carried out, then the actual operation takes place and then the patient receives post-operative care.
During the consultation, it is important that the patient describes to the doctor as precisely as possible what bothers him about his "old" nose and what the "new" nose should look like. It is quite common for patients to bring pictures of their “dream nose” with them for this reason. The doctor will then discuss possible Complications enlighten and after Appraisal explain to the nose what correction options are available. The thickness The nasal skin plays a decisive role here, because with very thick skin you will not be able to form an extremely narrow, delicate nose and with very thin skin there is a risk that bone edges will become apparent after the operation. Lots Plastic surgeon make photos of the face for better illustration, on which they demonstrate simulations of the possible surgical outcome. However, the patient should be aware that this is only a simulation, even the best plastic surgeon cannot guarantee that the end result will look exactly the same.
The actual operation usually takes place under general anesthetic instead, but with small corrections it is also possible to just one local anesthesia to undertake.
A nose correction (rhinoplasty) can basically be performed in two different ways, as an open or as a closed operation.
In most cases, however, the closed surgical method is chosen. For this, the cosmetic surgeon makes an incision inside the nose (endonasal access). This procedure has the advantage that there are no externally visible scars. Due to the limited visibility, this method is particularly suitable for less extensive rhinoplasty, for example for removing Nasal humps or judging Crooked noses. If extensive changes are to be made and / or the cartilaginous tip of the nose is to be corrected, so is one open Surgical method is usually unavoidable. In addition to the incision inside the nose, the cosmetic surgeon will make another incision along the bridge of the nose (between the two nostrils).
So there is one permanent scarwhich however is small and in most cases fades very quickly. After the incision has been made, the doctor gently lifts the skin from the cartilage and bone during both a closed and an open rhinoplasty. Now the nasal framework can be reshaped. When the nose is reduced or narrowed (also when the cusps are removed), excess bone and cartilage material is removed. The procedure is somewhat reminiscent of the chiseling work of a stonemason, because the surgeon cuts the bone with the help of a chisel and then brings it into the right shape. If a nose that is too small is to be enlarged, additional tissue is used. In most cases, this additional tissue is body's own Cartilage, either from the nasal septum (Nasal septum) or from the Ribs is won. After modulation, the nose is sewn with a few stitches and is supportive plaster cast created (this usually remains 14 days on the nasal framework). Also, because of the initial bleeding Tamponades inserted into the nostrils.
Since general anesthesia always carries a health risk, it is common for the patient to stay in the clinic for at least one night under observation. The following day these tamponades are removed and the patient discharged home, thus entering the postoperative phase. About a week after the operation, a new appointment at the doctor's office is necessary, during this appointment the sutures are pulled if they do not come out self-dissolving Material and a new plaster cast applied. Putting on a new plaster cast is a bit uncomfortable, but necessary because the initial swelling of the nose has already subsided and the old cast can no longer provide reliable support. As a rule, the doctor will give the patient a look at the "new" nose at this appointment. It should be clear that at this point the nose is still very swollen and appears much larger than the final result.
After another week, the plaster of paris is finally removed and a small adhesive bandage is applied to the nose. These adhesive strips can be removed by the patient independently after a few days. Since the nose suddenly tends to swell up again so soon after the operation, it can be taped again independently in this case. Approximately 14 days After a rhinoplasty, the patient is considered to be “fit for work and social again”. At this point the final result is about 80% noticeably, the nose takes a long time (up to a year) to swell completely. The final result is only achieved after about a year.
Risks
A nose job (rhinoplasty), like any other operation, always involves risks. On the one hand, there may be rather unspecific sequelae, i.e. those that can generally occur as a result of operations of any kind. These include heart, circulatory and / or breathing problems during or after the operation.
In addition, thrombosis can form after the rhinoplasty due to the length of time the patient is in hospital, or a wound infection can form due to the surgical incisions.
Especially with rhinoplasty, heavy bleeding and sensory disturbances (numbness) of the nose can occur. In addition, most patients develop bruises (hematomas) around the nose, cheeks and especially around the eyes. Scar growths inside the nose can occur, and these growths can impede breathing.
A risk that should not be neglected is depressive moods that occur a few weeks after the operation. This sounds strange at first, because the "new" nose should make the patient happier and more self-confident, but the face draws a person enormously and the face in turn is strongly influenced by the appearance of the nose. The “new” nose seems strange to many patients at first and for some time they cannot identify with the overall effect of their face.
Find out more now: Scar care
Pain
Many patients worry about possible rhinoplasty surgery PainHowever, these worries can be taken away from them. An operation on the nose is one of the operations that cause the least pain in the healing phase. Most patients report mild pain shortly after surgery, but with the help of Painkillers can be quickly mastered. Severe pain is extremely rare. The pressure of the plaster cast is uncomfortable, but certainly not painful.
Behavior after the operation
Immediately after the rhinoplasty, the area below the eye should be particularly good chilled this reduces the development of strong ones Swelling and Bruising. Unfortunately, they cannot be completely prevented.
In the first few weeks you should try to sleep on your back, if possible, with your upper body raised. So it happens less often Bleeding and the freshly operated nose is not deformed during sleep (but the risk is generally very low thanks to the plaster cast).
Strong pressure on the nose should be avoided in any case, so it is advisable to wear glasses after the operation contact lenses to change or attach the glasses to the forehead with an adhesive strip so that they do not touch the nose.
Figure nose
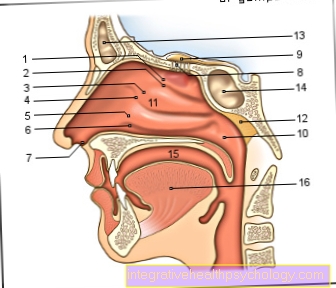
- Upper turbinate -
Concha nasi superior - Upper nasal passage -
Superior nasal meatus - Middle turbinate -
Concha nasi media - Middle nasal passage -
Meatus nasi medius - Lower turbinate -
Concha nasi inferior - Lower nasal passage -
Meatus nasi inferior - Atrium of the nasal cavity -
Nasal vestibule - Olfactory threads - Fila olfactoria
- Olfactory bulb - Olfactory bulb
- Rear opening of the
Nasal cavity - Choana - Nasal cavity - Cavitas nasi
- Pharyngeal almond -
Pharyngeal tonsil - Frontal sinus - Frontal sinus
- Sphenoid sinus -
Sphenoid sinus - Oral cavity - Cavitas oris
- Tongue - Lingua
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations


.jpg)