Whiplash
Synonyms
Cervical spine - whiplash, whiplash phenomenon, acceleration injury of the cervical spine, Cervical spine syndrome, Cervical spine, cervical spine strain, cervical spine distortion
English: whiplash injury
Definition of whiplash
Under a Whiplash (Cervical spine distortion) one understands a - often caused by a rear-end collision - Soft tissue injury of the Cervical spine (Cervical spine). The unforeseen strong flexion and overstretching of the cervical spine results in distortions, painful steep postures and muscle tension in the neck and throat muscles. Under certain circumstances, tears of the anterior longitudinal ligament or injuries of the Intervertebral disc be evoked.
Whiplash is always a strain (Compression, dislocation) of the Cervical spine fundamentally.

root cause
As already mentioned, the most common cause of whiplash injuries is a traffic accident. The head is moved from front to back or vice versa without the person being able to counteract it. After the impact, the head at a Whiplash moved jerkily again in the opposite direction.
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
Whiplash in a rear-end collision
The jerky forces that act on the muscles and the involved cervical vertebrae can sometimes cause complex injuries.
Whiplash cannot always be externally proven, so that this clinical picture appears again and again with great controversy with regard to claims for pain and suffering. There is a tendency to describe the clinical picture not as “whiplash” but as a cervical spine distortion in order to better differentiate the psychosomatic accompanying symptoms (“if I have a whiplash, then ...”) from the physical injuries.
Of course, the clinical picture of whiplash is not limited to car accidents. Whenever jerky movements are unintentional, there is a risk of whiplash, for example in martial arts, but also when visiting amusement parks or the like (roller coaster, ...).
Symptoms
After a relative period of time without symptoms, after a few hours, possibly even a few days in the case of whiplash, pain in the neck area, combined with a feeling of stiffness in the muscles and a headache, on. The pain radiates to the back of the head and a perceived heaviness of the Head may occur as side effects. Depending on the severity of the trauma, other symptoms are possible in addition to the "common" symptoms, which are listed below without any description:
- dizziness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Sleep disorder
- Visual disturbances
- Ringing in the ears (Tinnitus)
- Numbness in the area of the arms, face and shoulders
Also read more on the topic: Herniated disc cervical spine symptoms
dizziness
After a whiplash, dizziness is common. This often lasts for a few days to weeks and can have different causes. If dizziness occurs, for example, when the head is turned or the body position changes, it is known as paroxysmal positional vertigo. This is caused by irritation in the organ of equilibrium and can be easily and effectively treated with positioning exercises.
However, in rare cases, the dizziness can be caused by more severe damage to the brain. Therefore, if dizziness occurs, a doctor should be consulted to clarify the cause.
Read more on the topic: dizziness
Tinnitus
In some cases, after a whiplash injury, tinnitus, i.e. noises in the ear without an external cause for the sound, can occur. The reasons for this are irritation of the muscles and nerves that are directly involved in hearing or are in the immediate vicinity.
After a whiplash, tinnitus can become chronic and recur over the years. It is therefore important to identify and treat the symptoms early on. For this purpose, certain infusions are used in particular, which ensure better blood flow to the inner ear.
Please see our main article for full details: Tinnitus
treatment
There are several treatment options for whiplash. The therapy is usually conservative, so there is usually no need for an operation. Depending on the symptoms and their severity, different treatments are in the foreground.
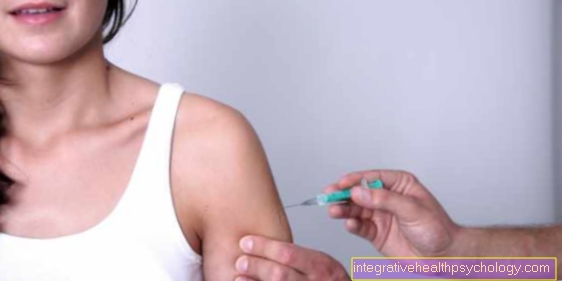
If the whiplash causes pain in the neck area, various painkillers can be taken against it. These include common drugs such as ibuprofen or diclofenac. If the pain persists, a doctor may give a local anesthetic or a muscle relaxant (a substance that relaxes the muscles). This is done with the help of a syringe in close proximity to the painful area.
Heat treatments and massages can be helpful in strengthening the overused muscles and reducing tension. Depending on the symptoms, electrotherapy, in which the damaged nerves are activated through the skin, or psychotherapy for prolonged emotional stress, may also be considered.
The mobility of the joints and the strengthening of the muscles can be supported by physiotherapy. This is also important to avoid long-term damage and should always be part of the treatment, depending on the symptoms.
You can find detailed information at: Therapy of a whiplash trauma
physical therapy
Physiotherapy is an important part of treating whiplash because it can prevent long-term damage to muscles and joints. This includes the massage of the tensed muscles due to the whiplash and the targeted treatment of the so-called trigger points, which cause the greatest pain in the affected area.
In addition, the movement of the joints in the cervical spine is promoted through exercises that can be carried out at home in addition to physiotherapy, in consultation with the therapist. In order to avoid possible damage caused by starting physiotherapy too early, the therapy should always be carried out in consultation with the attending physician.
Exercises
There are various exercises that can help strengthen the muscles of the shoulders and neck after a whiplash injury. On the one hand, it is important to stretch the muscles to improve mobility and, on the other hand, to strengthen the muscles. The exercises can also be instructed by a physical therapist or practiced in a gym with a trainer.
One possible exercise is, for example, folding your hands behind your back with your arms straight.
warmth
For many people who suffer from whiplash, treatment with heat has a relaxing and pain-relieving effect. A heat pillow, which can be heated in hot water or the microwave and then placed on the back of the neck, is a simple and effective way of heat treatment. The increased temperature increases the blood circulation in the area of application, which means that the muscles are better supplied and can relax. In addition, the warmth has a calming effect on the whole body.
diagnosis
In particular, if unconsciousness, amnesia, nausea and / or vomiting occur, the patient should contact the doctor IMMEDIATELY. As part of the diagnosis, the doctor will try to draw up an anamnesis, in the course of which the patient explains the "accident" and the accompanying symptoms.
In the event of whiplash, the doctor will then initiate a physical examination in which the exact extent of the illness is determined and, if necessary, further illnesses such as injuries to the spine with bone involvement or skull and brain injuries are confirmed or negated. In order to be able to assess this precisely, the cervical spine is x-rayed in the vast majority of cases. In particular, any bony involvement of the cervical spine can be recognized and diagnosed.
If there is also a suspicion of involvement of the ligament structures of the cervical spine (Cervical spine), magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) of the cervical spine can be used as a further imaging method in addition to the X-ray image. Magnetic resonance tomography, however, is not a standard procedure for such a disease. Only in exceptional cases and with regard to the suspicion described above can an MRI (magnetic resonance tomography) of the cervical spine provide further information.
Further information on this topic can also be found at: MRI of the cervical spine
In addition to the physical and radiological examination, the nerve status should always be checked. Eye mobility is also of great importance in whiplash, as it can under certain circumstances provide evidence of a concussion. This is especially the case in which the head was not only "thrown" jerkily twice in different movements, but also the head was slammed against an object.
The examination of the physical stature, the preparation of an X-ray, as well as the examination of nerve status, eye mobility and the balance organ are routinely included in the delimitation of the clinical picture.
In cases where an injury to the nervous system cannot be ruled out, further diagnostic measures may be necessary. Such examinations include, among others, examinations from the field of neurology such as measuring the nerve conduction velocity (NLG), electromyography (EMG) or an MRI of the cervical spine. MRIs are primarily created when there are indications of soft tissue injuries.
In rare cases, imaging of the brain by means of MRI or CT, an ultrasound examination of the large cervical artery or CSF diagnostics (examination of the cerebral fluid / nerve fluid) may be necessary. These examinations are only used in exceptional cases, which is why they will not be discussed further here.
Course of the cervical spine distortion
The figure shows the timing of a whiplash / cervical spine distortion in a rear-end collision.
classification
Depending on the symptoms, the whiplash is divided into different degrees of severity according to the so-called Quebec classification, where grade 0 means that there are no symptoms. In grade 1, neck pain is in the foreground, which usually lasts a few days to weeks. Muscle tension is part of grade 2, although the duration here is usually longer and often lasts for several weeks. In grade 3 there is additional damage to the nerves, which has a significant impact on the duration. Depending on the severity and early treatment of the damage, the symptoms can even persist for several years. The 4th and last degree describes the most severe type of injury involving the bones, for example a fracture. For this it is difficult to make a statement about the duration, as this can vary greatly.
Duration of whiplash
Whiplash can have different characteristics, which means that the symptoms last differently and for different periods of time. Most whiplash injuries usually last between two and four weeks. If symptoms persist, a doctor should be consulted again to clarify whether there is a possibly more severe injury than was originally suspected. The symptoms usually occur within the first few hours after the whiplash injury. In some cases, however, further symptoms can appear after 3 days.
Are you interested in this topic? Read detailed information at: Duration of whiplash
Consequences of whiplash
Whiplash can have many different consequences. These depend essentially on the type and severity of the trauma itself and on the symptoms it causes. In more than half of all those affected there are no more symptoms after a few months. The whiplash often has no consequences and there are no long-term damage that can have a negative effect.
However, if the whiplash is more severe, longer-lasting symptoms may develop. The most common consequences include long-term shoulder or neck pain and irritation of the muscles and nerves.
Very serious whiplash injuries can also lead to fractures and injuries in the cervical spine, which can lead to serious and sometimes life-threatening consequences.
Some people experience emotional distress after whiplash because the trauma from a traffic accident is a dangerous situation. Psychotherapy should therefore be considered if necessary for long-lasting conditions characterized by stress and anxiety.
forecast
Long-term effects as a result of whiplash are rather rare. Studies have shown that only a very small percentage of around 2 to 3% still have severe complaints two years after the injury, which hinder or severely impair their work. Most patients can cope with whiplash without any subsequent adverse effects.
Since the neck pain is persistent for a certain time and only slowly recedes. In another study, it was also confirmed that certain factors, such as:
- older age
- female gender
- Sensitivity to pressure in the neck and neck muscles
- a headache
prolong the healing process. As a rule - regardless of the severity of the whiplash - one assumes a recovery time of about one month. With only about 10% the pain period extends over a period of about half a year.














.jpg)