Therapy of lumbar sciatica
introduction
Lumboischialgia can be treated both conservatively and surgically. Conservative therapy is preferred to surgical therapy as long as there are no neurological deficits or symptoms of paralysis.
Conservative therapy of lumbar sciatica
The conservative therapy of lumbar sciatica is based on a multimodal therapy concept. This means that the therapy consists of different starting points and includes different approaches. These include the
- Medical therapy
- anesthesia
- physical therapy or physiotherapy as well as the
- Back school to increase the back muscles
Medical therapy
The right choice of medication for lumbar sciatica requires a thorough physical examination by the doctor. Drug pain therapy is based on the recommendations of the World Health Organization. This is roughly divided into three levels with the option of combining other medications. You start with the least potent pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, paracetamol or novalgin.
The next stage is less strong opioids and the third stage is strong opioids. These painkillers can always be combined with medications such as cortisone, antidepressants or muscle relaxants. For example, cortisone can be given as injections directly near the exit point of the nerve in lumboischialgia. It is important that the pain therapy is adapted to the needs of the patient.
When taking medication at home, it should be ensured that the pain medication is taken at regular intervals as prescribed. This achieves a certain level of the drug in the blood and prevents peaks in pain.
The drug therapy of lumbar sciatica consists in the administration of pain medication (NSAID) or muscle relaxants. In some cases, the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are insufficient to provide relevant pain relief. Centrally acting drugs may then have to be used, in some cases even morphine. In order not to irritate the stomach while taking pain medication, a stomach protector should always be used. Muscle relaxants are used when the back muscles cramp due to the relieving posture and lead to additional pain.
Read more on the subject at: Pain medication - the basis of drug pain treatment
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- Lumedis - your orthopedic surgeon
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at Dr. Nicolas Gumpert
anesthesia
Another option in the therapy of lumbar sciatica is the direct injection of local anesthetics and anti-inflammatory drugs. A puncture is made at the site of the inflammation using a small needle. Then the local anesthetic and anti-inflammatory drug are injected. Local anesthesia directly relieves the pain. The pain can also be treated permanently by means of anti-inflammatory measures. However, the effect of the medication diminishes again, so that daily injections must be made for effective pain therapy and causal therapy.
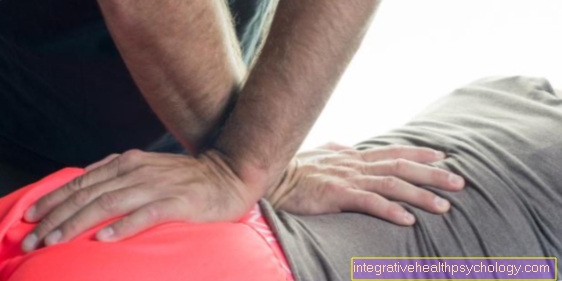
physiotherapy
As soon as the acute pain symptoms have subsided, physical therapy and physiotherapy are carried out to strengthen the back muscles. The physical measures include warm and cold therapies, manual therapy in the sense of a massage, positioning on a step bed and therapy using ultrasound waves. Bed rest and elevation of the legs are also recommended until the symptoms are relieved.
To prevent lumboischialgia from occurring again, the back muscles should be strengthened. This can be done as part of a back school, for example in the gym. During the training, not only should the back muscles be strengthened, but the correct posture and movement in everyday life should also be learned. This can prevent a new lumbar sciatica in many cases.
Surgical therapy of lumbar sciatica
in case of an Cauda Syndrome and if symptoms of paralysis occur (Paresis) there is a absolute surgical indication. Even in the case of Incontinence symptoms or treatment-resistant pain as a result of lumboischialgia, an operation is recommended. There are various methods to choose from:
- In the Microdiscectomy becomes the involved part of the vertebral bone or the intervertebral disc away. This is done using microsurgical technology so that no large access route has to be opened to reach the corresponding intervertebral disc. The subsequent Rehabilitation and healing proceeds with this method often quickly and without further complications.
- Also the Foraminotomy is a relatively small procedure that is performed in the prone position. Only the small part of the protruding tissue (Sequester) away. The intervertebral disc remains and the Vertebral bodies is not further impaired in its stability. So there is no need to use a placeholder instead of the actual disc. However, this practice is only with small herniated discs possible.
- As soon as a larger part of the intervertebral disc has slipped into the spinal canal, it must be completely removed (Laminectomy). Here the Vertebral arch and its spinous process removedto get to the intervertebral disc and remove it. There loses the spine, however stabilityso that there is always a placeholder or a Spinal fusion must be carried out.
- For this reason, in some cases only part of the vertebral body is removed (Hemilamectomy) to get another Residual stability to receive. We always try to choose the gentlest and smallest surgical method in order to maintain the stability of the spine. In addition, the access path for a laminectomy is significantly larger than for a microsurgical operation, as this requires a large incision to be made over the spine. In some cases, however, microsurgical surgery is not enough to relieve symptoms of lumbar sciatica.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy in the context of lumbar sciatica must be advised by a medical examination beforehand. If the clinical picture is based on an overload of the sciatic nerve, manual therapy can loosen the affected muscle groups and significantly support the course of therapy. This should go hand in hand with prescribed physiotherapy for faster mobilization and muscle building. Bad posture caused by gentle movements must always be prevented.
Whether manual therapy helps against the symptoms of lumbar sciatica must be found out individually by the patient. Fortunately, there is now a wide range of supportive therapy methods to choose from. In any case, however, it is important to consult the treating doctor to check whether there is a contraindication to a form of therapy. In the case of an acute herniated disc, for example, manual therapy in the directly affected area is not recommended, especially if neurological symptoms occur. The area itself should be manipulated as little as possible. If, on the other hand, the rest of the spine is affected by blockages, there are no concerns about manual therapy in these areas.
How long does therapy for lumbar sciatica take?
The duration of therapy, like the occurrence of lumbar sciatica, is strongly dependent on the cause of the nerve irritation. In some cases, the condition will improve after a few days. In the event of a severe herniated disc, however, the therapy can be extended over a few months.
Basically, the aim is to mobilize and reintegrate the sick person into everyday life at an early stage. Bed rest in the form of step positioning may only be carried out as briefly as necessary. Following this, the patient should try to move slowly while taking medication to relieve pain. Prolonged rest leads to increased immobility and increased restraint.
Length of sick leave
Like the duration of therapy, the length of sick leave also varies depending on the cause of the illness. There is no set time that should be adhered to until work is resumed after lumboischialgia. It must also be considered whether the activity at work could have caused nerve irritation and would hinder the healing process. If the lumbar sciatica is overloaded with nerve irritation as a result, the patient may be able to work again after a few days. In the case of a herniated disc, however, a long sick leave is usually required.