Transient osteoporosis
definition
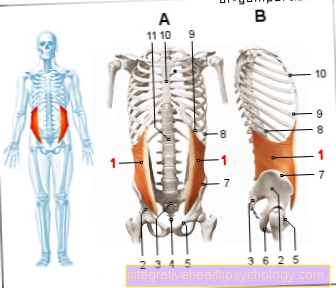
Transient osteoporosis defines a disease of the bones with increased water accumulation, which, as the name suggests (transient = temporary), occurs for a limited time and is a special form of classic osteoporosis. The infestation of the is typical of transient osteoporosis Hip bones. Other bony joint involvement, for example of the ankle and knee, occurs only in rare cases. The transient osteoporosis is also under the synonym "Bone marrow edema syndrome" (KMÖS) listed. In the literature, the transient osteoporosis is described on the one hand as a separate entity, but on the other hand as a reversible precursor of the Osteonecrosis. Men are typically three times more likely to be affected by the bone disease than women. However, both sexes develop transient osteoporosis at the same time, around the third and fifth decades of life.
root cause
The exact causes for the occurrence of a transient osteoporosis have not yet been clarified, so that one is often from a idiopathic genesis speaks. In some cases, however, possible explanations for the development of the clinical picture are available. Severe overloading of the hip joints, for example, can be the reason for transient osteoporosis, as well traumatic eventslike falls on the hip.Also the aspect of the reduced and disturbed blood flow to the femoral head, so a so-called Microcirculatory disorder, causes transient osteoporosis in some cases. In contrast to one Femoral head necrosis In transient osteoporosis, there is only a short-term and no definitive insufficient blood supply to the femoral head, on which a better prognosis is based. The transient osteoporosis can ultimately also be secondary in the context of other underlying diseases such as Sudeck's disease, rheumatism or other degenerative diseases arise. Also the fact of pregnancy can increase the likelihood of transient osteoporosis.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.

diagnosis
The diagnosis of transient osteoporosis can already be made clinically. In a physical examination, an objective assessment of the mobility in the hip is carried out using the neutral-zero method. Roughly speaking, the amount of movement for splaying (abduction), bending (flexion) and internal rotation are reduced. The subjective restriction of movement is usually felt to be much more extreme by those affected due to the severe pain.
You can also read more on the subject below: Normal value of the joints
One might think that with a bone disease, this is the main problem roentgen suitable as a diagnostic tool, but this is not the case. You can only start with a loss of 40% of the Bone density Obtain meaningful findings on X-rays. Instead, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) plays a crucial role in diagnosing transient osteoporosis. Depending on the weighting, the typical fluid accumulations, i.e. the Bone edema, describe. The signal intensity is reduced in the so-called T1 sequence, but increased in the T2 sequence. A sharp demarcation of the signals and the typical localization in the femoral head and parts of the femur are characteristic of the Bone marrow edema syndrome or for transient osteoporosis. To rule out an important differential diagnosis “femoral head necrosis”, both an MRI scan and a Skeletal scintigraphy be performed. Compared to transient osteoporosis, femoral head necrosis also forms a “necrosis zone”, i.e. an area in which the bone is destroyed.
Symptoms
The Leading symptom Transient osteoporosis is the spontaneously occurring pain in the hip in otherwise healthy adults, especially those affecting the musculoskeletal area. Of the pain Classically increases with exercise and occurs only in very rare cases at night or at rest. Sometimes the pain radiates to neighboring parts of the body such as the groin, buttocks and lower legs. In addition to the pain symptoms, transient osteoporosis can also be a limping gait provoke. In addition, those affected complain that the Hip joint mobility.
therapy
Fortunately, transient osteoporosis is a disease with good prognoses, which self-limiting and is almost never chronic. Therefore, the conservative therapeutic approaches should be in the foreground. This includes drug treatment and protection with consistent relief of the hip joint. Common painkillers are drugs from the group of so-called "non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs“ (NSAIDs), how Ibuprofen or Diclofenac. These are mainly used in pain therapy, but also in orthopedic diseases, including transient osteoporosis, due to the pain-relieving (analgesic) and anti-inflammatory (anti-inflammatory) Effect to application. Besides the painkillers, there are also those Bisphosphonates established in the treatment of transient osteoporosis, as they inhibit bone-degrading cells and thus stand for bone preservation. A third medication targets the circulatory disorder as a possible cause: the prostacyclin analog Iloprost. So far, however, this has only been prescribed for “off-label use”, which means that the use is carried out in a way that does not require approval. Forearm crutches are often prescribed to relieve the hip joint. A swift start of treatment and close monitoring are always important, since in addition to the outcome of full genesis, there is also always the transition to a Femoral head necrosis is possible.
In addition to pain relief, the goals of the therapy are to prevent possible bone fractures due to the unstable bones in the event of further stress. The small fractures could on the one hand exacerbate the pain and on the other hand the risk of a larger fracture like that Femoral neck fracture, climb. It is important to know that 3 to 6 months can pass before the relief leads to a noticeable alleviation of symptoms or an improvement. It is therefore essential that patients follow the therapy consistently and protect their hips, because this is the only way to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. If conservative measures are not sufficient, an operative procedure may be indicated. The aim is to "drill" (core decompression) of the bone to drain the bone marrow edema and thus reduce the pressure, which leads to immediate symptom relief. In general, of course, the cause of the occurrence of transient osteoporosis must be taken into account in order to be able to treat underlying or concomitant diseases in a secondary form of transient osteoporosis or to be able to adapt the medication accordingly.
Treatment with bisphosphonates
The bisphosphonates belong to a group of drugs that are used in the therapy of osteoporosis. About an inhibition of the so-called Osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, bisphosphonates cause a reduction in bone breakdown. Since the bone substance is also disturbed in transient osteoporosis due to the formation of bone marrow edema, they are used in drug therapy for that disease. It is important to know that bisphosphonates are present in the pregnancyin which transient osteoporosis or pregnancy-associated osteoporosis can also occur, contraindicated are. In addition, bisphosphonates should be taken at least half an hour before meals, as otherwise undesirable effects such as complex formation with calcium ions from food can occur Mineralization disorders with hypocalcemia and the risk of one Kidney failure can come. The drugs alendronate, ibandronate and zoledronate are currently being prescribed in particular.
Duration of treatment
It is difficult to make a precise statement about the duration of transient osteoporosis. Fortunately, it is generally one self-limiting and healing Illness. How quickly the body can ultimately fight the disease and how well the respective therapeutic measures work varies from person to person. On average one can heal with 6 to 8 months calculate. Even up to 12 months of persistence of symptoms, the chances are still good that the transient osteoporosis will heal. It is also important to know that there is never a transition to a chronic form.
Places of manifestation of transient osteoporosis
Hip / femoral neck / femoral head
The main places of manifestation of transient osteoporosis are the Hip joints. The findings can be bilateral or just unilateral. The latter is typical of transient osteoporosis during pregnancy. In the x-ray of the hip, a maximum of slight decalcification can be seen in the area of the femoral head with the bone cortex that is difficult to define (Cortex) represent. Since changes with a bone density loss of more than 40% are meaningful in the X-ray image, no reliable diagnosis can be made on the basis of the images. Much more specific for the diagnosis of transient osteoporosis is the MRI image of the hip. Here you can see the characteristic Bone marrow edema prove. The edema is localized in the femoral head, but can also migrate into the femoral neck and between the two rolling hills (trochanter major and minor). In the T1-weighted sequence, the signal intensity of the fluid accumulation, i.e. the edema, is greatly reduced. The signal intensity is typically increased in the T2 sequence. A special weighting (STIR) suppresses the fat signal so that the bone marrow edema can be mapped even better. In addition, in the area of the joint surface under the cartilage surface, i.e. subchondral, isolated changes can be seen, which are often classified as small fractures in the context of transient osteoporosis.
Close monitoring is important in order to assess the decrease in bone marrow edema, which should be the case within 10 months at the latest. The femoral head as a manifestation site in particular makes precise diagnostics necessary in order to rule out possible differential diagnoses. These include femoral head necrosis, rheumatic diseases and the Coxitis, an idiopathic inflammation of the hip joint in childhood. Above all, femoral head necrosis must be ruled out, as transient osteoporosis shows changes that are to be assessed as a preliminary stage of necrosis.
Foot / ankle / talus
In addition to the hip, transient osteoporosis can also manifest itself in the distal area of the lower extremity, i.e. the foot and ankle. In the rare cases in which such a localization of transient osteoporosis occurs Men more often affected than women. Bone marrow edema typically develops in the ankle. Here it manifests itself primarily in the lower ankle joint, more precisely in the talus (= ankle bone). As with the other places of manifestation, the MRI is the most specific diagnostic tool for visualizing bone marrow edema. The control and diagnosis are important, because the transient osteoporosis actually heals spontaneously at this point, but the development of one arthrosis in the ankle must be prevented by timely therapeutic interventions.
Transient osteoporosis in pregnancy
A transient osteoporosis in pregnancy is not with that pregnancy-associated osteoporosis, in which the occurrence is directly causally related to the pregnancy. Primarily women in the third trimester are particularly predisposed. Occasionally, transient osteoporosis only occurs postpartum, so after giving birth, while breastfeeding on. The Leading symptom As with non-pregnant sufferers, the spontaneous pain in the hip, which becomes worse with stress. A limping gait and restricted movement of the hips must also be described. The only difference is that transient osteoporosis can also provoke resting pain during pregnancy. The exact cause of the occurrence of transient osteoporosis during pregnancy has not yet been clarified. You should therefore at least clarify a circulatory disorder, nerve compression or increased stress as the cause. The diagnostic procedure, like the therapy, corresponds to that of transient osteoporosis, which occurs independently of pregnancy. The only restriction is the medication of bisphosphonates, which must not be taken during pregnancy. However, a sufficient supply of vitamin D and calcium play an important role, especially during pregnancy.