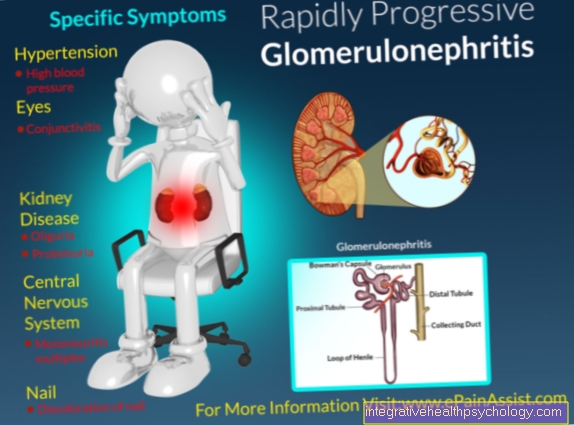
Causes of dizziness
Synonyms in a broader sense
Medical: Vertigo
To form: Positional vertigo, vertigo, Vertigo,
English: Vertigo, dizziness
Definition dizziness
Dizziness (Vertigo) is the most common cause which is why a doctor is consulted. There are many reasons for dizziness. In general, you can differentiate between one
- vestibular dizziness
- non-vestibular vertigo
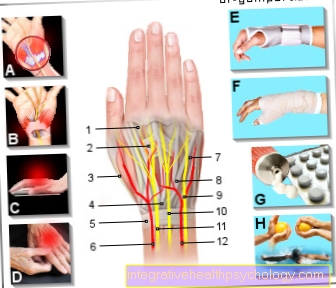
Vestibular dizziness goes on Balance organ (Vestibular organ) in the Inside ohr out.
Non-vestibular vertigo finds its origin not in the organ of equilibrium and can have many different triggers.

Causes of dizziness by sex
Causes in women
In young women, dizziness is often associated with low blood pressure on.
In combination with insufficient fluid intake, it comes to black in front of the eyes and unpleasant ones, especially when getting up too quickly Attacks of dizzinesswhich, however, usually pass quickly.
This phenomenon occurs, although less often, in people with normal blood pressure. Women of childbearing potential should consider a possible pregnancy if they experience attacks of dizziness accompanied by excessive tiredness.
Exercise can reduce the attacks by half in both cases. Another very common cause of dizziness in women is due to stress and provokes situations that they are afraid of.
In technical terms, this form of vertigo is called phobic vertigo and is one of the most common causes of dizziness in young people, women tend to suffer from it more often than men.
To better empathize with the situation, here is a small example:
"Imagine standing unsecured on the roof of a house. Suddenly the roof starts to move and sways back and forth like a ship"
This vertigo attack that those affected usually have no disease value, but is a complex reaction of the body to the psychological stress to which the person concerned is exposed.
In our example, almost everyone would react like this. However, women who suffer from phobic postural vertigo experience these attacks in everyday situations that they fear, such as in exam situations or when traveling by train Claustrophobia.
Furthermore, dizziness attacks occasionally occur as part of a migraine from which women suffer statistically more often. It is typical of this type of dizziness that it accompanies the characteristic, throbbing and unilateral migraine headache.
For the women concerned, it feels like a carousel ride that is too fast. One speaks of Vertigo. If sudden vertigo attacks occur in combination with Tinnitus and hearing loss should be observed in women between the ages of 40 and 60 Meniere's disease be thought.
Women suffer from the inner ear disease slightly more often than men (see: Dizziness from diseases of the ear). It is assumed that an increase in liquid (Endolymph) tear in the inner ear important membranes for balance and hearing.
The brain receives incorrect information and thinks it is constantly on the move, which explains the symptoms described above.
In very rare cases, the vertigo attacks occur as part of a Multiple sclerosis on. Women are about twice as likely to suffer from this condition, which leads to the destruction of the nerve sheaths.
In addition to dizziness, there are often visual disturbances, pain in the area of the eyes when moving and tingling or numbness in the arms and legs, and less often paralysis.
Another very common dizziness is the Positional vertigo, which also mainly affects women.
In technical terms, the form of vertigo is called benign paroxysmal positional vertigo designated. Paroxysmal means that dizziness occurs suddenly when moving the head, such as when lying down, standing up and, above all, when turning the head, for example when turning over in bed.
Typical for this form are violent vertigo attacks, which, if the person concerned remains lying still, quickly disappear, but reappear the next time the head is turned.
The cause lies in small stones in the inner ear, the Otolithsthat have detached themselves from their place of origin and slide around in the inner ear arch canals with every movement. Through the Otolith movement the balance organ gets mixed up and sends incorrect information to the brain, resulting in the symptom dizziness.
Causes of dizziness in men
Men can generally suffer from dizziness due to the same conditions as women. However, they are usually inferior to women in terms of percentage, i.e. women fall ill more often and thus suffer more often from dizziness and vertigo attacks.
Men suffer from the frequent phobic postural vertigo, which occurs in very stressful and uncomfortable situations for the person concerned, at a later age than women.
Stress cause dizziness

stress is one of the most common dizziness triggers, especially in young people for whom pathological changes in the balance organ in the ear and brain are unlikely.
The dizziness can sometimes be so severe that everyday tasks can no longer be carried out. Those affected by no means imagine the dizziness.
It is the reaction and response of the body and the brain to sometimes extremely psychologically stressful situations, such as the death of a loved one, but also in test situations with people Exam anxiety.
The brain tries to use this reaction to distract from the bad feelings. In addition, many people affected by dizziness have the experience of getting out of situations such as an unpleasant conversation "to free“To be able to. So they subconsciously draw a positive benefit from their dizziness, which is why the brain falls back on this aid during the next unsightly conversation, whereby the dizziness, as I said, is not imagined, but real.
As a rule, the attack is perceived as vertigo, as if one were standing on a ship in heavy seas. Those affected often also suffer from Anxiety disorders, Panic attacks or depressions.
In spite of all of this, diseases of the brain or the ear, in which part of the equilibrium organ is located, should not be disregarded and should be investigated if suspected.
Causes in the neck
Permanent tension in the neck and throat muscles can also cause dizziness.
The sustained contractions of certain muscle groups in the neck usually predominate in a stiff neck, which leads to the unconscious kinking of the neck to this side.
This change in position of the head means that the equilibrium organ in the ear sends false signals to the brain, which now assumes that the head is in motion.
In the long run, these processing errors lead to vertigo attacks due to the convulsive incorrect posture of the neck and throat. Even tension in the muscles in the legs and back can trigger dizziness in this way.
Read more on the topic
- Tension in the neck
- Atlas correction
Causes of the eyes
The eyes offer a wide range of diseases, each of which can have dizziness as a symptom.
Dizziness through Diseases of the eyes or their muscles is rare.
The causes are usually visual defects, mostly as a result of axis misalignments of the eyes. Due to the misalignment, the eyes send incorrect information about the environment to the brain, which can cause dizziness.
The eye centers there are connected to the center of equilibrium via several interconnections. Squint is such a misalignment and can be new as a result of Eye muscle paralysis occur.
Eye muscle paralysis in turn comes as a reaction to various diseases, such as Inflammation, Brain tumors, Strokes, Autoimmune diseases or through Accidentsin which the brain or eyes are affected.
Another cause of eye-related (ocular) Dizziness can be so-called Nystagmus disease be.
The jerky eye movements can also be the result of various diseases, including problems of the balance organ, but also congenital brain changes. Dizziness can also occur when fitting and wearing new glasses.
Some people experience attacks of dizziness and nausea while watching a 3D movie or playing a 3D game. This phenomenon can be explained in a similar way to the nausea and dizziness that can occur while driving.
The eyes report three-dimensional images to the brain, most of which also move quickly, while the equilibrium organ in the ear reports calm because you are sitting. This "disagreement“Then leads to the symptoms mentioned above in people who are sensitive to it.
Causes on the cervical spine / head
Whiplash, especially after a car accident, can lead to dizziness for days after the accident.
Due to the impact, the head is suddenly accelerated and decelerated again, which on the one hand concussionas well as neck tension.
Both in turn can present symptomatically with dizziness, in worse cases coupled with nausea and vomiting.
Misalignments of the cervical spine and the head lead to the fact that the equilibrium organ of the ear transmits false information about the position of the head to the brain. This interprets this information as head movement, even if the head is held still. The "Information imbalance“Ultimately leads to dizziness in those affected.
Bad posture of the cervical spine and head occurs on the one hand when the cervical spine is worn out, especially in older people in connection with a arthrosis and Disc wear or through cramp and permanent tension in the neck muscles.
In addition to the symptoms of dizziness, those affected often feel pain in the neck and back of the head.
Cervical spine syndrome
Tension and pain in the neck and shoulder area are typical for a spinal column syndrome of the cervical spine, also known as the cervical spine syndrome. In some cases, irritated nerves also lead to a tingling or numb feeling in these areas. In the extreme case, paralysis can even occur.
Sometimes, however, with the cervical spine syndrome, in addition to the symptoms already mentioned, dizziness can also occur. In addition to dizziness, tinnitus, headache or visual disturbances can also occur as further symptoms. If several of these symptoms occur, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible.
A cervical spine syndrome can arise from various causes (cervical spine syndrome causes). On the one hand by constricted or irritated nerves. This narrowing can occur, for example, in the context of a herniated disc or a tumor. Sometimes, in the course of a mass, not only a constriction of a nerve but also a constriction of a blood vessel occurs. If it is an artery that supplies the brain with blood, there is an insufficient supply of the brain, which can lead to symptoms of dizziness.
A cervical spine syndrome is often caused by stress. Stress also promotes the development of a feeling of dizziness, so that this can also be favored by the simultaneous existence of a cervical spine syndrome and stress.
Also read our topic: Cervical spine syndrome and dizziness
Causes of the heart
Numerous Cardiovascular diseases can also have dizziness as a symptom.
Other symptoms accompanying the dizziness and the underlying illness are typical, such as Sweats, Drowsiness to Faint, Racing heart or flickering / asterisks in front of the eyes.
The underlying mechanism of dizziness is common to almost all cardiovascular diseases, namely a temporary reduced blood supply to the brain.
Possible heart diseases that can cause dizziness are Heart failurein which the heart eventually becomes too big and is no longer able to throw out enough blood, Cardiac arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, congenital heart defects and coronary artery disease, which is now widespread in Germany, which results in calcification of the arteries supplying the heart (Coronary arteries) and in the worst case to Heart attack can lead.
The latter disease leads to a reduced blood supply to the heart muscle, which as a result no longer achieves its original force of contraction, which in turn leads to a lower blood output with the symptoms mentioned above.
Possible circulatory diseases are high blood pressure or that Subclavian steel syndrome, in which there is also a temporary insufficient blood supply to the brain as a result of the narrowing of the clavicle artery from which arteries supplying the brain arise.
Causes of dizziness while lying down
Generally, dizziness improves while lying down and becomes worse especially when you stand up and move around.
There is, however, one important exception, namely vertigo, which is technically known as benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Or, for a moment, just positional vertigo. "Benign" stands for a benign cause and "paroxysmal" for seizure / sudden. Positional dizziness typically occurs in people between the ages of 60 and 80. Women are affected more often than men.
In this positional vertigo, there are ear stones within the semicircular canals of our equilibrium organ, which have formed through deposits within our inner ear. Ear stones then irritate the semicircular canals and cause dizziness. The dizziness usually occurs while lying down, especially when rolling over in bed. In addition, it can also occur when sitting up from lying down or when bending over quickly.
In contrast to other vertigo diseases, vertigo attacks are only very brief during positional vertigo. The seizure is usually over on its own within seconds. The vertigo is sometimes accompanied by nausea and / or visual disturbances.
Once the treating physician has diagnosed the positional vertigo and identified the affected ear, it can usually be treated easily. The treatment is medication-free and can be done by the patient himself. With these exercises, the ear stones are ultimately transported out of the semicircular canals. There are two exercises that can be performed by the patient, one is the Sémont maneuver and the other is the Epley maneuver.
The Sémont maneuver is best performed with a second person to help. With this method, the patient sits upright while the head is rotated 45 degrees to the unaffected side.The second person then quickly tilts the patient to one side so that the patient lies on a couch with a view upwards. He then remains in this position for two to three minutes.
Then he stands up again and is abruptly lying on the other side, with the head remaining in the old position, so that this time the view is directed downwards to the couch. Then he is straightened up again and then remains in the upright position for about three minutes. Then the exercise can be repeated.
In the Epley maneuver, the patient sits with his legs stretched out in front of him. The head is again tilted 45 degrees to the side, this time in the direction of the diseased ear. The patient is then quickly repositioned in the supine position, with the head protruding over the couch / bed so that the head hangs. This causes dizziness. The patient should remain in this position until the dizziness subsides or the position is maintained for at least one minute. Then the head is turned 90 degrees to the healthy side and again waited until the symptoms of dizziness disappear. Finally, the patient turns on his healthy side and remains that way for about a minute. Then sit upright again.
It is best to keep your eyes closed while doing this exercise to avoid nausea.
In addition to positional dizziness, dizziness can also be present when our equilibrium nerves are inflamed. Due to the inflammation, the equilibrium nerve sends permanent signals to the brain, causing dizziness. However, the dizziness in this disease is also present when standing and sitting. This is not a brief attack of vertigo, but rather a permanent vertigo.
In pregnant women (dizziness during pregnancy), vertigo-inducing vena cava syndrome sometimes occurs.
The vena cava is a hollow vein that runs within the right half of the body and transports our blood back to the heart.
The waist circumference during pregnancy can compress this vena cava so that less blood is pumped back to the heart. Ultimately, this means that the heart can supply the body with less blood, so that less blood reaches the brain, which can cause dizziness. Vena cava syndrome is triggered when the pregnant woman lies on her right side or on her back. If you then turn on your left side, the vertigo disappears because the vena cava is no longer compressed.
Read more on the topic: Dizziness when lying down
Causes of dizziness in old age

Many people suffer from dizziness in old age.
The causes for this are very diverse and should always be considered. In old age, there is often a decrease in activity and muscle mass.
The elderly forget to drink during the day. Both together lead to a drop in blood pressure, especially when getting up. The brain is briefly poorly supplied with blood and those affected feel dizzy and often black in front of their eyes.
Such low blood pressure and the symptom of dizziness can also be a side effect of numerous medications that the elderly usually consume in sufficient quantities.
These drugs include, among other things, drugs for depression, sleeping pills, sedatives, and various drugs for high blood pressure.
A certain group of antibiotics can also have short-term effects on the balance organ in the inner ear as a side effect.
Various diseases, which older people suffer from more frequently, can also result in dizziness as one of their symptoms. They include numerous diseases of the cardiovascular system, diabetes, anemia (anemia), as well as disorders of the electrolyte and water balance as a result of kidney diseases.
Causes of Vestibular Dizziness
1. Benign positional vertigo
(Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo)
Benign positional vertigo is a common form of vertigo that occurs twice as often in women as it does in men. The likelihood of suffering from this form of dizziness increases with age.
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo shows up with
- short attacks of vertigo that last less than 30 seconds and are triggered by changing the position of the head
- Nausea (possibly)
- Visual disturbances
Visual disturbances that occur in the context of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo are so-called oscillopsia. It seems to the person affected as if fixed objects are trembling. The image that the person concerned perceives is similar to that of a shaky video recording.
For more information, also read: Causes of vertigo.
2. Vestibular migraines
In the course of a vestibular migraine, recurring attacks of dizziness occur that last for minutes to hours and can be associated with headaches.
Sensitivity to light or noise and auras, as in a classic migraine, can also be partially perceived. Despite the term "vestibular migraine", it is possible that only the vertigo attacks occur without a headache.
Also read on this topic: Dizziness and Migraines - Everything You Need to Know About Vestibular Migraines
3. Meniere's disease
This is a disease of the inner ear that occurs predominantly between the ages of 40 and 60. The cause of Menière's disease is still not entirely clear. One assumes an endolymph congestion (endolymph is a potassium-rich liquid), which causes excessive pressure in the cochlea.
Sick people typically suffer from the so-called Menière’s triad:
- Vertigo attacks
- unilateral hearing deterioration / hearing loss
- "Ringing ears" (Tinnitus aurium).
Read a lot more information under our topic: Meniere's disease
4. Vestibular neuritis
Vestibular neuritis is one acutely occurring one-sided functional restriction or even a Failure of the organ of equilibrium (vestibular organ). Reasons for this inflammatory process, especially between the 30 and 60 years of age occurs, are unclear. One goes from one
- Viral infection
- Virus reactivation of a dormant virus or
- Circulatory disorder out.
Vestibular neuritis presents symptomatic With
- acute onset of permanent vertigo that can even last for a few weeks
- Visual disturbances (Oscillops ien)
- nausea
- Vomit
- Tendency to fall to the diseased side
- horizontal rhythmic eye movements to the healthy side (Spontaneous nystagmus)
Hearing disorders do not occur with vestibular neuritis.
5. Acoustic neuroma
A Acoustic neuroma is a benign (benign) Tumor of the Schwann cells of the Equilibrium nerve. Patients with an acoustic neuroma
- a Hearing loss on the affected side
- Ringing in the ears (Tinnitus) and
- Balance disorders up to dizziness
6. Bilateral vestibulopathy
Bilateral vestibulopathy means that Balance organ and / or the Equilibrium nerve (Vestibular nerve) have failed on both sides.
Patients feel it
- Vertigothat occurs subject to movement
- Unsteadiness especially in poor light and ground conditions
- Visual disturbances (Oscillopsia)
- Spatial memory disorders
7. Vestibular paroxysmia
The cause of vestibular paroxysmia is one Compression of the equilibrium nerve (Nervus vestibularis) on its way from the ear to the brain. The reason for the compression is a tortuous or dilated artery. It comes to acutely occurring and Brief vertigo or vertigo.
8. Other central causes for a disturbance of the balance organ
- Circulatory disorders (e.g. due to atherosclerosis)
- Brain stem and cerebellar damage
- multiple sclerosis
- Parkinson's disease
- Alzheimer's disease
- Traumatic brain injury
can also be causes of dizziness.
Causes of Non-Vestibular Dizziness
1. Cardiovascular system
Many too Changes or diseases of the cardiovascular system can make you dizzy. Examples include
- low blood pressure (Hypotension)
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Diseases of the heartwhich ensure that a smaller volume of blood leaves the heart in a certain time (Valvular heart disease, Heart attack, Etc.).
2. Somatoform dizziness
Vertigo the psychosomatic conditional is called somatoform vertigo. Somatoform vertigo can have all different forms of vertigo
- Vertigo
- Vertigo
- Elevator dizziness occur.
Various diseases can be triggers:
- stress
- Anxiety disorders
- Panic disorder
- Phobias
- burnout
- Adjustment disorders
Even vertigo, which is primarily caused by an organic disease, such as Menière's disease, can later turn into somatoform vertigo.
3. Cervical spine
A so-called cervicogenic dizziness is a Vertigo of the cervical spine goes out.
4. Eyes
Ocular dizziness has its origin in the eyes and can be triggered, for example, by eye muscle paralysis and ametropia. However, this type of vertigo is usually of minor importance.
5. Other causes of non-vestibular dizziness
- Stroke (apoplexy)
- Panic attacks
- Anemia
- accelerated and / or deepened breathing (hyperventilation)
- Infections
- Medicines, such as anti-epileptic drugs, antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs (antihypertensive drugs)
- Sleeping pills
- Thyroid as the cause
- Drug and alcohol abuse
- Dizziness after exercise
are other causes of dizziness.
Read more on the topic: Iron deficiency dizziness