You can recognize a magnesium deficiency by these symptoms
introduction
Magnesium is a metal that occurs in the body as a mineral and fulfills vital tasks. Magnesium is involved in numerous metabolic processes and its function is closely related to that of calcium. It slows down the function of calcium, which takes on functions especially on muscles and nerve cells, but also on numerous other organs.
Magnesium levels can be measured in the circulating blood, even though only a small amount of the mineral is outside the body's cells.
A magnesium deficiency can have various causes, most of which are related to an impaired absorption or supply of magnesium in the intestine. The resulting symptoms can be different for each person and present themselves differently, especially in different age groups.

These are the typical symptoms of magnesium deficiency
The first signs of a magnesium deficiency appear primarily in the muscles and the heart. Typical symptoms are muscle cramps and muscle twitching, so-called "Tetania“, Which can be traced back to an over-excitability of the muscles. Due to the lack of magnesium, the calcium can accumulate in the cells, which leads to a faster or permanent activation of the affected cells.
Read more on the topic: Eyebrow twitches - is that dangerous?
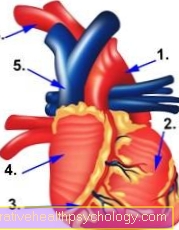
Spontaneous additional heartbeats and delays in the conduction of excitation can occur in the heart at an early stage. Although these are rarely consciously perceived, they can typically be recognized early in the ECG examination. In the further course, neurological symptoms such as irritability, restlessness, tiredness or confusion can follow.
Dry skin
A magnesium deficiency can be responsible for dry skin. The skin is subject to many harmful influences every day. Numerous regeneration and repair processes maintain the intact skin barrier and protect the skin. Magnesium can alleviate small inflammatory processes on the skin and act as an antioxidant.
As a result, it not only prevents the skin from drying out, but also promotes hair growth, works against pimples, inflammatory skin diseases and rashes and smooths the skin. Many cosmetic products for the skin also contain magnesium.
Read more on the topic:
- Skin care
- Baby skin care
- Skin care for men - care tips for men
cramps
Cramps are one of the most typical symptoms of a magnesium deficiency. In the muscle, the mineral directly counteracts any over-excitability caused by the influx of calcium in the muscle cells. In the case of a magnesium deficiency, on the other hand, the muscle can be very stressed and tense even from small exertions, which manifests itself as an uncomfortable and painful cramp.
Read more on the topic: Cramps despite magnesium - what can I do?
Athletes in particular, but also heavily stressed, stressed or pregnant people lose a lot of magnesium in everyday life, which is why muscle cramps can occur despite sufficient intake of the mineral. In these cases, only a conscious increase in magnesium intake through certain foods or dietary supplements will help.
Read more on the topic:
- Diet and exercise
- Palpitations during pregnancy
- Diet in Pregnancy
- Food supplements in pregnancy
a headache
Headaches are a very unspecific symptom that every person suffers from occasionally. However, frequent headaches or even migraines can be attributed to a magnesium deficiency.
The nerve cells are also in a close balance of minerals and electrolytes. The magnesium deficiency disrupts the fragile balance and the nerve cells can be excited, which can lead to numerous neurological symptoms. The sensitive nerve cells of the meninges can be easily irritated and trigger a pain impulse. In these cases, a slightly increased intake of magnesium can alleviate the frequent headaches.
Read more about: Therapy for migraines
Muscle twitching
Muscle twitches are closely related to the so-called "Tetany“, The muscle cramps. Both speak for excitability of the muscle without clear signals from the nerves. The excitation and activity of the muscles is always accompanied by an influx of calcium into the cells. In order to relax the muscles during rest phases, the magnesium maintains a balance in which the cells cannot be excited.
The magnesium deficiency leads to twitching, cramps and subsequent pain in the muscles due to unconscious stress. Small magnesium deficiencies can appear particularly through high levels of stress during stress or after exercise.
tingle
The body's sensitive nerve cells can transmit signals to the brain through pressure, vibration and small touches of the skin, which creates sensitive sensations. Many different mechanisms can disrupt the sensitive perception on its way to the brain and thereby trigger abnormal sensations in the affected part of the body. An example of this is the magnesium deficiency. Due to the low excitation threshold, the nerve cells can apparently be excited without stimulation and trigger tingling sensations. A magnesium deficiency can cause tingling sensations, especially in the sensitive areas of the fingers or face.
Read more on the topic: Leg tingles - what's behind it and burning in the face
Brittle fingernails
Brittle fingernails can indicate numerous causes and physical illnesses. In addition to serious illnesses, there can also be harmless mineral or vitamin deficiencies. A magnesium deficiency can also cause damage to the fingernails in the form of brittle, brittle and discolored nails.
Magnesium triggers metabolic processes in these nails, hair or bones, which lead to a strengthening and better energy supply for these tissues. Brittle fingernails can particularly affect pregnant women or athletes who have a latent magnesium deficiency.
Read more on the topic:
- Brittle fingernails - what's behind it?
- Dry skin during pregnancy
Indigestion
Digestive problems can often be traced back to a magnesium deficiency and are related to numerous muscular processes in the body. The main effect of magnesium is on muscle and nerve cells. Digestion also depends on the close interaction of the nerve plexuses and smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract.
A severe magnesium deficiency can lead to cramp-like and spastic movements of the intestinal muscles. In many cases, these only manifest themselves as digestive complaints or slight constipation. In an emergency, however, digestion can be impaired, which can lead to an intestinal obstruction. In addition to relaxing the intestinal muscles, the magnesium in the stool binds the water, which can make the stool softer.
Read more on the topic: Home remedies for constipation and constipation therapy
Racing heart
The heart muscles and the cardiac conduction system are heavily dependent on the balance of minerals and electrolytes. Even small changes in calcium or potassium levels can cause life-threatening disorders. Magnesium also plays an important role in these processes. In these cases, the heart muscle can involuntarily contract, not exert adequate force or incorporate irregular beats into the rhythm. A racing heart is also not uncommon due to the excitability of the heart muscle. These are diseases that require urgent treatment and are to be taken seriously and should be treated immediately by a doctor.
Read more on the topic: Therapy of palpitations
depression
Different areas of the brain can also be affected by the changes in the mineral balance. In addition to the general over-excitability of the nerve cells, which is caused by a magnesium deficiency, individual brain functions can also be disrupted by enzymatic processes. In addition to its effects on the cell, magnesium also takes part in numerous chemical reactions in the body, which influences a number of body processes.
In the brain, the functions of the hypothalamus and the amygdala can suffer from the magnesium deficiency. The amygdala is responsible for feelings of fear, whereas the hypothalamus is an important switching function for vital hormones. As a result, in addition to feelings of fear, there can also be listlessness, weakness and a reduced general condition. Ultimately, this can cause or worsen depression. By replacing the magnesium, the hormone levels normalize quickly and the depression also subsides after a short time.
Read more on the topic: Bach flowers for fear
fear
For the feeling of fear, the so-called "Amygdala" responsible. If there is a magnesium deficiency, it is typically affected in its function along with numerous other brain areas and organs. Magnesium supports many reactions and metabolic processes in the nerve cells that are disturbed by the magnesium deficiency. This creates a feeling of fear. Together with a change in hormone levels and other effects on the nerve cells of the brain, sometimes severe neurological symptoms can develop. Medical treatment is urgently indicated in the event of neurological involvement.
Read more on the topic:
- specific fear
- Bach flowers for fear
- Anti-anxiety medication
Tremble
Trembling is one of the most common and typical symptoms of magnesium deficiency. Combinations of symptoms of muscle cramps, tremors, tingling, paresthesia, twitching and muscle pain can occur at an early stage. The tremor can often be misinterpreted as a muscular strain after exercise or in stressful situations. However, it is precisely in these situations that a magnesium deficiency can arise, which becomes apparent in the subsequent rest phases as tremors or muscle cramps.
Read more on the topic:
- Zinc deficiency
- Protein deficiency
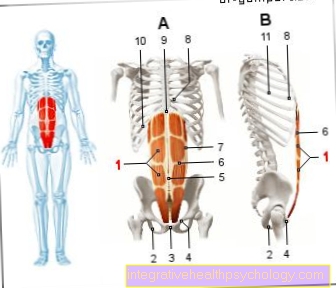
Back and joint pain
In some cases, even back pain and joint pain can be related to a magnesium deficiency. Most people experience occasional or permanent back pain or pain in the joints of their arms and legs. In the majority of cases, the back pain in particular is the result of muscular problems that lead to misalignments, spasms of the back muscles and unpleasant pain. A magnesium deficiency can lead to latent cramps in the back muscles. This can lead to blockages and severe movement-dependent pain, which are often misinterpreted as a problem with the intervertebral discs.
Read more on the topic:
- Back pain
- Effects of back pain
- Pain in the joints
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a very unpleasant symptom, which has numerous unexplained causes and is very difficult to treat.In many cases, inflammatory or degenerative processes are behind the development of the ringing in the ears. However, in a large number of cases, the origin of the troublesome tinnitus cannot be established.
The small hair cells of the inner ear also have receptors that need magnesium to maintain a balance with other minerals. If there is a magnesium deficiency, the hair cells are also overexcited, which means that noises can appear without any cause. Magnesium also plays an important role in the therapy of tinnitus, as it reduces the excitability of the cells and can thereby break through the tinnitus regardless of the cause.
Read more on the topic: Ringing in the ears and treatment of tinnitus
eye bags
In addition to magnesium, numerous minerals and electrolytes are involved in the maintenance of intact skin. Magnesium causes the skin to mineralize and thereby promotes repair processes for damage that occurs on the skin of every person in everyday life. If the skin lacks these minerals, it cannot regenerate itself sufficiently from everyday stress, which can lead to dark discolorations under the eyes. The dark circles are particularly noticeable after a busy day or in the morning. Many repair processes take place during the night. Dark circles in the morning indicate a significant disruption of the skin's ability to regenerate.
Read more on the topic:
- Dark circles - get away and remove
- Cream against dark circles
- Inject under dark circles
- Home remedies for dark circles
Nerve pain
Muscle and nerve cells are primarily affected by a magnesium deficiency. In addition to muscle spasms and twitches, the most common and typical symptoms are abnormal sensations in the nerves. This is due to the overexcitability of the nerves, triggered by an increased influx of calcium into the cells. This is usually slowed down by magnesium.
As a result, the nerve cells can be excited and pass on sensitive sensations to the brain, although no sensitive stimulus has occurred. These abnormal sensations can range from tingling and pins and needles to numbness and pain. In contrast to numerous similar neurological diseases, the pain and impairment of the nerve cells are reversible.
Read more on the topic:
- Nerve pain
- St. John's wort oil - the medicinal plant for calming nerves and more