Burning in the chest
introduction
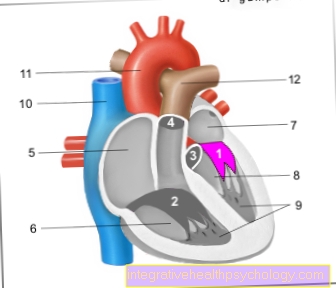
A burning sensation in the chest can not only be painful, it can also lead to far-reaching complications. In order to understand where the burning sensation in the chest can come from, it is worthwhile to discuss the anatomical conditions in the chest. The two lungs, the heart, the esophagus and - as bony and muscular borders of the organs - the chest itself are found here. Each of these compartments can cause pain or a burning sensation in the chest in various ways.
Read more on the topic Burning in the lungs
causes
A burning sensation in the chest is not a very specific symptom. This means that it can indicate a large number of possible diseases, but is not clear evidence of a specific disease. A large number of organs are localized in the thorax and, accordingly, many diseases project into the chest.
For example, the burning sensation could be caused by the heart. A Angina pectoris (Narrowing of the coronary arteries), a heart attack or inflammation of the pericardium (Pericarditis) can be the cause.
The lungs are also located in the chest. A burning sensation may indicate pneumonia (pneumonia), an occlusion of one of the large pulmonary vessels (embolism) or indicate a tear in the lung membrane (Pneumothorax).
You might also be interested in this topic: Air embolism
But the stomach or esophagus can also, for example, be affected by acid regurgitation (Reflux) or an inflammation of the stomach lining (gastritis) be the cause of the burning sensation.
In addition, rib fractures, bruises or dislocations should not be ignored. In addition, sore muscles or blockages in the thoracic spine can cause a burning sensation.
In addition to the organic causes, psychological causes should also be considered. A detailed questioning of the patient is therefore important in order to be able to rule out a fearful and stressful situation. If a burning sensation occurs in the chest, a doctor should be consulted in order to recognize and treat dangerous processes.
Concomitant symptoms
If the burning sensation comes from the heart, breathing difficulties (for example Dyspnea) and limited performance are often also present. Patients who have a heart attack usually also have extreme anxiety and sweats. In addition to the burning sensation, there are frequent pains in the chest and upper body area.Basically, any form of complaint can be associated with a heart attack: pain that radiates into the arms, neck, back or even the upper abdomen or nausea.
If the lungs are the cause, patients also experience shortness of breath and painful breathing. Coughing and an increase in heart rate may also show up. In some cases, pulmonary embolism has a previous thrombosis, e.g. the leg veins.
If the muscles, the ribs or the vertebral bodies are involved (in the sense of a blockage), the pain is usually movement-dependent and can be intensified or triggered by pressure or rotational movements. Patients often adopt relieving positions to relieve pain. If you ask more carefully, you will usually find an event (sport or wrong movement) that explains the problem.
If the stomach is the cause of the discomfort, additional symptoms include an unpleasant taste in the mouth (sour or bitter) and a dragging sensation into the throat and mouth. Symptoms intensify after large meals, increased consumption of sweets, lying down or during physical exertion (such as bending over or lifting).
If there is a psychological cause as the reason for the occurrence of chest pain, there are often many other symptoms that have an identical basis (e.g. sleep disorders, depressive mood, insecurity). Very often the psyche is not recognized as the cause and it is treated incorrectly. If no reason can be found after excluding the dangerous acute courses, then a psychological or psychosomatic genesis should also be considered as the cause of the burning sensation in the chest.
Read more about the topic here: Tension in the chest
Duration
Burning under a Angina pectoris, which occurs due to a temporary narrowing of the coronary arteries, is usually a short-term for a few minutes ongoing happening. The burning occurs through the Insufficient supply of the heart musclewhich is otherwise supplied by the constricted vessel. By using Nitrates, either as a spray or capsules, patients can usually reduce the symptoms.
At a Heart attack is the vessel against it completely laid. The burning sensation and pain arise during an acute event and usually do not resolve spontaneously. The patients have acute acute pain that is still present when the doctor arrives and must be treated with painkillers.
Should the patient have a lung infection have it Burn long term and it changes with the general symptoms of pneumonia. At a Pneumothorax (Tear of the lung membrane) are the burning or the pain and the shortness of breath acute eventthat it remains until medical treatment.
At heartburn the burning is usually not permanent, but above all after eating occurring or also layingwhen gastric juice can more easily get into the esophagus.
Burning left or right in the chest
A burn on the left side of the chest speaks for one Involvement of the heart or the esophagus. But also that left lung can be affected.
Basically you have to distinguish whether the burning suddenly occurred or already for several days / weeks consists. In the case of an acute event, a distinction must also be made between in what situation the burning occurred.
Classic for a burning sensation in the chest Left (see: chest pain left) is a so-called "Angina pectoris", So a"Chest tightness". The burning sensation is partly over the left rib cage, but often also extends over the Sternum down to the right side of the rib cage. Less often the pain also radiates to the left or right poor out. With angina pectoris there is a short-term one Reduced blood flow of the Coronary arteries. Can trigger mental stress, but also heavy ones physical strain be. Depending on the severity, angina pectoris can also occur without any prior physical strain. Angina pectoris is primarily not yet dangerous, the burning sensation disappears by itself after seconds to minutes. However, angina pectoris is a typical one Heralding a heart attack and should therefore absolutely medically clarified become.
Some patients know the little red ones Pump sprays, Which Nitroglycerin contain. In the case of chest tightness, the burning sensation and tightness disappear within a few seconds when the pump spray is applied - it is then most likely one Angina and not about one Heart attack.
Another cause of burning in the left and / or right rib cage can be the Damage to the lungs be. This can be done, for example, in the course of a embolism come, in this context then also "Pulmonary embolism" called. A pulmonary embolism refers to one Vessel stopperthat is a more or less big one vessel relocated in the lungs and thus cut off the blood supply to the corresponding segments of the lung. This is not only problematic in that the affected segment is no longer in the oxygenation of the Blood can participate - the body escapes oxygen-rich blood. Depending on its location in the chest, pulmonary embolism can also cause pain, burning and Shortness of breath cause. The larger the embolus, the earlier it settles in the vascular system of the lungs and the more lung tissue evades oxygenation of the blood. In addition, a vascular occlusion in the lungs increases pressurethat that Heart must counteractwhen it throws blood. The heart has to constantly fight against increased resistance, which is the case with a chronic pulmonary embolism structural changes in the heart. One then speaks of one Right heart failure.
A severe burn localization to the right or left rib cage tends to be uncommon for damage to the heart or lungs. Most of the time, the burning process cannot be limited to a specific section and extends over the entire rib cage.
Burning in the center of the chest
A burn central localized in the chest, so behind the breastbone (retrosternal), is a sign of heart involvement. The heart lies behind the breastbone and with its tip in the left rib cage. If there is a central burn over you longer period always with burden for several minutes, this indicates a narrowing of the heart vessels, which leads to a CHD (coronary heart disease) can lead. The burning sensation is not the only symptom. Additionally come Pain in the chest, arms, jaw, upper abdomen and other area. Patients have nausea, Fears to death and Cold perspiration.
In the case of less pronounced forms, a general one shows up Chest tightness. If such symptoms recur over the long term, you should speak to your family doctor or cardiologist.
At acute Burning, pain and other symptoms just mentioned (mostly in stronger expression) in the middle of the chest, an emergency doctor must be called immediately. Because here is probably a Heart attack in front.
continue reading: Symptoms of a heart attack
Tension
Is that burning movement dependent and kick strictly localizable at one point on the rib cage, so must a muscular activity should be considered. For example, it is often a simple one Tension. But what exactly is meant by the term “tension”?
When there is tension, it comes to permanent and painful reinforcement of muscle tone - so the muscle tension - in one Muscle group. A tension can go through wrong movement patterns or overload to be triggered. Classics here are, for example, gardening or overexertion in sports. Because of the burning sensation and the pain caused by the tension, the affected person automatically takes one Relieving posture a, which in turn can strain other muscle groups to an unusually high degree - a Vicious circle arises.
Such tension can be particularly annoying on the chest, as it becomes noticeable with every movement and every breath. The good news here: Except for the burning sensation and the pain in the chest no other organs affected. So it's a painful one, but harmless clinical picture.
The therapy is to break the above vicious circle. This succeeds with Painkillersthat take the pain away, dissolve the relieving posture and thus enable the regeneration of tense muscle groups.
A possible complicationthat should be kept in mind when there is tension in the chest is this Chronificationwhich then makes a multimodal treatment concept necessary.
Burning sensation in the chest through the esophagus
A burning sensation in the chest caused by the esophagus is often the result of stomach acid rising up the esophagus. There can be various reasons for this advancement. One reason is excessive gastric acid production, which can be triggered either by stress, diet or medication such as acetylsalicylic acid. Another cause is weakness in the sphincter that separates the stomach from the esophagus. It is important that persistent stomach acid build-up is treated early. Persistent inflammation of the esophagus increases the likelihood of developing esophageal cancer. The aim of treatment is to reduce stomach acid and thus prevent it from rising up the esophagus.
heartburn
Part of the esophagus runs just behind the left atrium of the heart. One of the most common causes of left-sided burning in the chest is reflux - i.e. the backflow - of stomach acid from the stomach, through the esophagus, towards the larynx. The stomach acid also passes through the constriction behind the heart, which is why heartburn is often misinterpreted as a "heart problem".
This assumption is reasonable, however, since the burning sensation and the sharp pain caused by heartburn are reminiscent of a heart attack. However, patients describe the symptoms of a heart attack in such a way that they experience shortness of breath and fear of death, which - even with severe heartburn - is usually not the case.
If the burning sensation occurs immediately after eating, this is a further indication that speaks for heartburn and against a cardiac event. This type of pain is called “postprandial pain” - that is, pain after eating.
With heartburn, the acidic gastric fluid slowly rises up the esophagus and irritates the chemoreceptors of the esophageal epithelium (top layer of skin of the esophagus) - we then experience this as pain or burning in the area behind the breastbone.
While single heartburn is still harmless, repeated ascent of stomach acid into the esophagus can lead to permanent damage to the skin and mucous membrane there.
The stomach acid contains hydrochloric acid, one of the strongest acids found in nature. It is used to break down the food pulp in the stomach. However, while the stomach has protective mechanisms against self-digestion, the esophagus is defenseless against acid.
Complications of chronic heartburn include inflammation and burning, as well as bleeding and esophageal cancer.
Therapy for heartburn consists of taking antacids, i.e. acid-binding drugs, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). A well-known representative from the group of PPIs is pantoprazole, or a general drug with the ending -prazole.
Read more on the topic: Burning behind the breastbone.
Burning in the chest through the stomach
The stomach can also be responsible for an uncomfortable burning sensation in the chest. This is usually based on one gastritis - so one Inflammation of the stomach. One distinguishes three forms the gastritis.
A Type A gastritis is through autoimmune processes triggered - the body is fighting itself, so to speak. The reason for this is unknown. However, type A gastritis usually runs asymptomatic, so prepare no pain.
The Type B gastritis is bacterial conditional and based on an infection with the bacterium "Helicobacter pylori". This bacterium prefers to colonize in the stomach entrance - the "pylorus" - and takes care of one there inflammation and possibly also one increased production of stomach acid. Stomach acid, in turn, causes a burning sensation that can rise from the stomach area to the chest and cause severe pain. However, type B gastritis also runs mostly asymptomatic, only one unpleasant bad breath can occur more frequently. Therapy is carried out with a Antibiotics - Multiple therapy for which several different treatment regimens exist.
The most important representative of gastritis in this case is Type-C gastritis. She caused next to one Feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen additionally a constant belchingwhich, however, does not bring "relief", ie does not reduce the feeling of fullness. The constant belching leads to Reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus, causing a severe burning sensation in the stomach, chest and, less often, throat, in the larynx area. trigger for type C gastritis (chemically conditional gastritis) is generally said a unhealthy lifestyle. This includes besides Smoke also excessive Alcohol consumption, stress and the regular use of pain relievers NSAIDs-Group. This includes Aspirin®, Ibuprofen and Naproxen. The classic combination is high alcohol and cigarette consumption, for example when “partying” on the weekend, followed by a headache the next day treated with Aspirin® or ibuprofen. If the stomach is permanently exposed to this stress, it reacts with inflammation. The only sensible one therapy in this case is the reduction cigarette and alcohol consumption, avoidance of NSAID-class painkillers and avoidance of stress. Alternatively can Paracetamol be taken, as this affects the stomach less badly (but the liver…).
If the burning sensation in the chest occurs in combination with a feeling of fullness and frequent belching and if there is an increased consumption of alcohol, cigarettes and painkillers at the same time, gastritis - i.e. inflammation of the stomach - should always be considered.
Burning in the chest radiating to the arms
If the burning sensation affects not only the chest but also the arms, it must be urgently excluded that the patient does Heart attack Has. Most patients complain of pain in the center to the left of the chest. Quite a few patients also describe one tearing to stabbing pain that radiates into the arms. If there are also fear, nausea and cold sweat, everyone has to be careful and get one as soon as possible Emergency doctor communicate.
But this burning can also go through Tension or blockages in the cervical or thoracic spine be triggered. Blockages can be caused by bad posture, incorrect lifting or insufficiently trained muscles. It comes to one minimal misalignment of the joint, which one reflex tension and cramping the surrounding muscles. Depending on the location, this can lead to pain and burning sensation only in the spine or to large-scale complaints that affect the chest or arms.
Burning in the chest with back pain
Back pain can occur especially with a severe cough. The pain and burning then move from the chest to the back, causing pain there. Especially with cough and persistent coughing for hours is that entire lungs irritated, as well as the Chest muscles and Back muscles overexerted.
Cough represents a enormous burden for our body, there are sometimes pressures that Lung membrane can tear. So got there Air between the lungs and the chest - a pulmonary one emergency. Typical symptoms of this as "Pneumothroax“Are suddenly occurring Pain in the entire upper body, Shortness of breath and "hanging over" the affected side of the chest while breathing.
However, back pain can also just come off Nerve entrapment or Overexertion the muscles result from a coughing fit. Below each of our ribs runs one of a total of 11 pairs Intercostal nerveswhich supply the muscles and skin on the chest. By strong cough is one Entrapment these very nerves between rib and muscles conceivable. One then speaks of a "Intercostal neuralgia“.
Next Fractures and Spinal cord disease these also occur more frequently with lung diseases. The therapy takes place by means of Administration of painkillers, such as Protection of the rib cage. In addition, of course, the cough must be combated, for example with irritant cough tea or cough blockers.
Burning in the chest with a feeling of pressure
If there is a burning sensation in the chest combined with a feeling of pressure in the chest, action must be taken quickly. In the worst case, it is a heart attack. In this case, one of the vessels in the heart is blocked and some of the heart muscle is no longer supplied with blood. The no longer supplied area dies and serious complications can arise. If the feeling of pressure occurs under stress or only lasts for a few minutes, an angina pectoris attack is more likely to be considered, in which the vessels are not completely closed and the heart muscle is still sparsely supplied with blood. In any case, if there is a burning sensation in the chest with a feeling of pressure, the emergency services must be called as soon as possible, as the motto “time is muscle” applies. So no time should be lost to save as much heart muscle mass as possible.
You can find more information here: Pressure in the Chest - These are possible causes
Burning in the chest and throat
Burning of the chest up to the neck area either speaks for one Reflux from stomach acid rising up to the larynx or for one Respiratory disease. Diagnosis and therapy follow depending on the accompanying symptoms and development process.
Sore throat can also with warming envelopes, just as scarves and "coughs and bronchial tea" are remedied.
Is it a hoarse voice - for example after excessive stress or a night of partying - helps Protection and drink a lot (3 liters or more per day). The drink should preferably not contain carbon dioxide and should be taken warm rather than cold. It is particularly suitable for relieving a sore throat Camomile tea, which can also be mixed with honey if you like.
Burning in the chest with a cold and cough
Especially in the cold winter months, people like to catch a cold. Every cold also includes a cough, which from a certain stage can be quite painful. A heavy cough leaves a real burning sensation in the chest and upper airways. This is usually bronchitis.
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi, i.e. a section of the lungs in which the air is primarily transported.
In the early stages of bronchitis, the cough is often still dry, i.e. without coughing up mucus. Only later does the so-called “productive cough” occur, in which slimy sputum is associated with the cough. This phase is then accompanied by a stinging and burning sensation in the chest and neck region. In addition, it can lead to headaches, tiredness and a slight fever.
Bronchitis usually heals within two weeks without consequences - but patience is required: a cold can persist for several weeks. At least the uncomfortable stinging and burning sensation in the chest disappears relatively soon. If this is not the case, it may also be a more serious differential diagnosis. These include pleurisy, i.e. inflammation of the pleura. The two pleural layers rub against each other during breathing, causing severe, breath-dependent pain. In addition, there may be a feeling of severe illness and a fever.
Chronic cough can also be caused by the widespread respiratory disease bronchial asthma. The main symptoms of bronchial asthma are a dry, i.e. unproductive cough that occurs particularly at night. In addition, there is a so-called expiratory stridor, i.e. a "rattling" breath sound that occurs during exhalation. An asthma attack usually happens suddenly, within a few minutes. This is also an important criterion to distinguish it from a cold that lasts for days. Asthma, like bronchitis, causes a burning sensation in the chest and a strong cough. In the case of an attack, however, therapy is carried out using spasmolytics, i.e. drugs that release the spasms in the lungs. A well-known representative of these antispasmodics is salbutamol, which is applied by inhalation and which provides immediate relief after just a few strokes.
However, a dreaded but rare form of productive cough is coughing up blood. Blood is also coughed up, which suggests severe damage to the lung tissue. Coughing up blood can occur in very severe forms of bronchitis, but more often in end-stage bronchial cancer.
In the past, blood when coughing was a sign of tuberculosis. With the eradication of tuberculosis in our latitudes, this differential diagnosis was pushed into the background. With the increasing influx of refugees from endemic areas, however, this diagnosis is coming back to the fore. Central Africa and the Middle East, in particular, are risk areas, which is why travelers must also be examined for this disease if they are suspected. Pulmonary tuberculosis at this stage is extremely contagious and requires urgent medical clarification.
additionally shortness of breath
If you experience shortness of breath in addition to the burning sensation in your chest, the symptoms are most likely caused by your heart or lungs. Heart disease that causes these conditions may include a heart attack or a Pericardial tamponade be. A heart attack is usually associated with a feeling of pressure behind the breastbone and radiating pain. At a Pericardial tamponade blood enters the pericardium and the heart can no longer achieve its full pumping capacity. The result is that not enough blood can be enriched with oxygen in the lungs and consequently shortness of breath. If the lungs are the trigger for the symptoms, one can think of a pulmonary embolism, with this there is a shortage of breath because the pulmonary arteries are obstructed and in this case too, not enough blood can be oxygenated. Another cause of the discomfort may be a pneumothorax, which is caused by the entry of air into the space between the lungs and the chest (Pleural space) arises.
You can find more information here: Causes of shortness of breath
Occur during exertion
A burning sensation in the chest on exertion is an important and common symptom of coronary heart disease (CHD). Those affected suffer from a narrowing of the coronary arteries, which supply the heart muscle cells with oxygen and energy. During exertion (e.g. walking upstairs), the narrowing means that the heart muscle no longer receives sufficient oxygen. Those affected often describe that they can only walk a certain number of floors before they need a break. A doctor can use this to estimate whether there is a possible CHD and, if so, how severe it is. If there is a burning sensation in the chest during exertion, it should be discussed with a doctor and an EKG, a heart ultrasound and, if necessary, further diagnostics performed.
However, the symptoms can also originate from the lungs. For example, if someone has smoked for many years and developed COPD, physical exertion can cause an uncomfortable burning sensation.
Read more about: End-stage COPD
Burning sensation caused by the thyroid gland
Also one Hyperthyroidism can cause a burning sensation in the chest. The thyroid pours Hormones from that a general Increase in the basal metabolic rate of the body. When overactive, the excessively released hormones lead to one Increase in heart rate (Tachycardia) or to Cardiac arrhythmias. This can be felt as a burning sensation in the chest. In addition, those affected are common restless, have trouble sleeping, sweating, as well increased blood pressure. Overfunction can have various causes and should therefore be clarified by a doctor.
Burning sensation in the chest during pregnancy
A burning sensation in the chest is common during pregnancy frequently through the stomach conditionally. Because the child takes up more and more space in the womb during pregnancy, the Stomach pushed further up. That can lead to heartburn occurs - i.e. the stomach acid passes into the esophagus. Since in addition the muscles and that tissue by the progesterone (important hormone during pregnancy) softer the sphincter muscles at the entrance to the stomach may no longer close effectively and the Stomach acid can rise more easily. The problem usually gets worse when lying down. If the burning sensation is accompanied by additional problems such as chest pain, shortness of breath and anxiety, then a doctor must be consulted so that heart and lung problems can be excluded.
That is found Burn rather in the Breasts and in the field of Burst warts, then this indicates a normal process during pregnancy. This means that the breasts through the Enlargement of the glandular body grow a lot, many women notice feelings of tension, pressure or even burning in the breasts and nipples. If the burning sensation does not go away or if further symptoms occur, the gynecologist or midwife should be contacted.



.jpg)