Cluster headache
definition
Synonyms: Bing-Horton syndrome, Bing-Horton neuralgia, erythroposopalgia, lightning headache;
engl .: cluster headache.
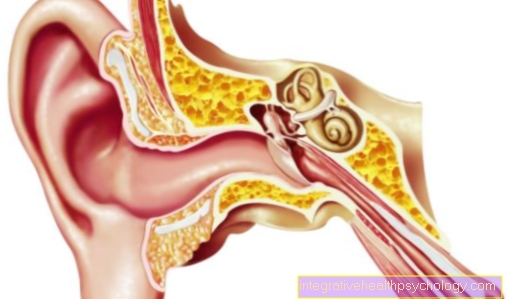
The cluster headache is a form of recurring headache. It usually occurs unilaterally in the eye-forehead-temple area and shows some peculiarities compared to other forms of headache:

Symptoms
In cluster headache there is an increased occurrence of severe pain episodes over a period of 1-2 months alternating with symptom-free periods of 6 months to 2 years. A pain episode usually lasts 15 minutes to 2 hours and can occur up to 10 times a day, accompanied by eye reddening and tears, a drooping eyelid on the affected side or a runny nose. The pain occurs particularly at night and in the morning hours; a seasonal increase can be observed in spring and autumn. In some cases, the pain is caused by alcohol (even small amounts), bright lights, or certain medications. The great intensity of the pain and the frequency of the episodes can mean immense suffering for those affected!
root cause
The cause of the recurring headache episodes is ultimately unclear. While some explanatory approaches assume a non-pathogen-related inflammation in the area of the cerebral vessels, others see e.g. B. the cause in disorders of the local vessel size regulation.
An episodic headache (see also headache) can also occur symptomatically as a result of another underlying disease. Here come z. B. cerebral sacs (aneurysm) or tumors in question.
To find the cause of cluster headaches, documentation in a headache diary is also suitable, in which you write down when, how where, how severe the symptoms occur over a certain period of time. The neurologist can then use the evaluation for diagnosis and therapy planning.
Read on below: Headache diary
What are typical triggers?
Most cluster headaches have no identifiable trigger. However, it has been found that many of the patients have inflamed veins behind the eye, which may irritate the nerves at that point. This could be an explanation for the cluster headache exiting. During a period in which the pain attacks occur frequently, it can be observed that alcohol is often a trigger for such. In addition, staying at high altitudes, such as in the Alps, is recognized as the trigger for the attacks within a cluster period. Other triggers can be the drug nitroglycerin, which is used to dilate the blood vessels in the heart. The hormone histamine can also cause blood vessels to dilate. It is released by the body in the event of allergies and inflammation in order to increase blood circulation. All of these triggers are treated as the primary cluster headache triggers. The secondary triggers are tumors and vascular malformations that irritate the nerves and cause pain.
You might also be interested in: Headache with nausea - what's behind it?
What role does histamine play?
The histamine plays a role as a trigger factor or trigger of a cluster headache attack. This effect is primarily only observed during an existing cluster period. Histamine is an endogenous hormone that is released by the body in connection with allergies and inflammation. It causes the blood vessels to widen, which increases blood flow.
therapy
In the event of an attack, the patient is given high doses of oxygen through a face mask for a period of approx. 10 minutes. The administration of an ergotamine preparation as an injection under the skin or as a nasal spray can also prove helpful, and a lidocaine nasal spray can also be used. Unfortunately, the response rate to the individual drugs is sometimes rather low.
Various drugs from different groups of active substances are used to prevent further attacks. Verapamil (an antihypertensive agent), methysergide (a former migraine therapy), or valproic acid (used to treat epilepsies) are used. Short-term therapy with cortisone (cortisone) or the intake of lithium can also prove helpful.
Which drugs work best?
In acute therapy during a cluster headache attack, undiluted oxygen is given along with the drugs sumatriptan, which is injected under the skin, and zolmitriptan, which is given via nasal spray. These drugs are considered the first choice in attack therapy. The two drugs belong to the group of triptans, which cause the vessels in the brain to constrict. In the acute phase, lidocaine can also be given by nasal spray. It has a local effect on the triggering of pain and is treated here as a second choice. For prophylaxis, verpamil, a drug that has a vasodilating effect in the arteries and still works well, can be given as the first choice. As a second choice, lithium can be given for prophylaxis, which can positively change the brain metabolism and therefore also the nerve stimulation.
Homeopathic Therapy
Homeopathy is said to be ineffective for cluster headache. Just like relaxation techniques, physiotherapy or other complementary medical measures. These techniques, such as homeopathy, are certainly justified for other pain disorders. The cluster headache, however, should be treated fundamentally differently, as it also does not respond to the common painkillers. With homeopathy it is generally the case that it does not have any side effects and therefore no doctor is against it. The patient should be informed that in this case homeopathy is not being used as effective, but he or she can decide for himself whether or not to benefit from it. "Kalium iodatum" is recommended by homeopaths in this case, as are some other remedies.
Read more on this topic at: Homeopathy for headaches
Therapy with oxygen
The cluster headache is still under exploration. So far, however, it has been shown that it can be treated by giving 100% oxygen. During a pain attack, the patient receives undiluted oxygen for inhalation directly from the gas cylinder or the gas connection from the wall. Together with the drug sumatriptan, which is injected under the skin and zolmitriptan, which is administered via nasal spray, it is considered the drug of first choice.
Home remedies for cluster headache
The cluster headache is one of the most aggressive pains that even the strongest painkillers such as opiates (morphine, etc.) cannot be treated and can only be controlled with other special drugs. All patients should therefore consult a doctor and be treated with modern means. But if you also want to do something against cluster headache at home, especially for prophylaxis, you should avoid nicotine and alcohol. This is particularly recommended during the cluster periods.
Treatment with nasal spray
Both the drugs zolmitriptan and lidocaine, which are used in acute therapy for cluster headache, can be administered as a nasal spray. In this way, the active ingredient is absorbed very quickly directly through the nasal mucous membranes, which is an advantage in acute therapy. Zolmitriptan constricts the vessels in the brain while lidocaine blocks pain transmission. Lidocaine is only given as a second choice in acute therapy.
forecast
The disease is often chronic and causal therapy is not possible. In rare cases, however, the disease comes to a spontaneous standstill.
Is Cluster Headache Curable?
The cluster headache is currently still being researched, as not all questions regarding its origin and therapy options have been clarified. At this point in time, the cluster headache cannot be cured, but it is possible to achieve good prophylaxis with modern drugs, so that it occurs only rarely, if at all. If the attacks are not reduced satisfactorily despite the medication, a blockage of the painful nerve can be resorted to, which rarely has to be done.
Diagnosis
It is important to collect the patient's medical history (anamnesis) and to precisely record the characteristics of the pain.
A neurological examination in the interval shows no abnormalities, in the pain attack the accompanying symptoms listed above can be found: eyelid swelling and drooping, runny nose, reddening and tears of the eye and sweating on the same side on which the headache shows. If necessary, further diagnostic measures have to be initiated to exclude underlying diseases. B. the preparation of an X-ray or a computed tomography of the head.
Exclusion diseases (differential diagnoses)
The causes of a symptomatic headache are increased intracranial pressure and space-occupying processes in the skull roentgen or Computed tomography (CT) can be excluded.
The also shows a similar localization of pain green star (med .: glaucoma), so that an ophthalmological examination may be advisable.
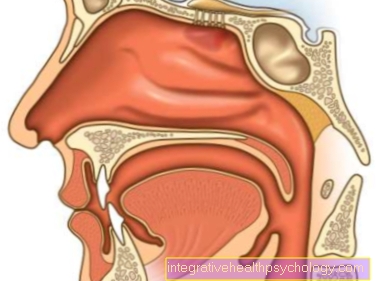
Also inflammation in the area of the Sinuses (Please refer Sinus infection) can lead to pain in the eye, forehead and temples, and differentiating between the various forms of recurring headache is not always easy. So can migraine, Trigeminal neuralgia or hemicrania continua (half-sided headache) show clinical symptoms overlap with the cluster headache.
How often does the cluster headache happen?
About 90/100000 people are affected by cluster headaches, men more often than women. The headache attacks usually begin around the age of 30.