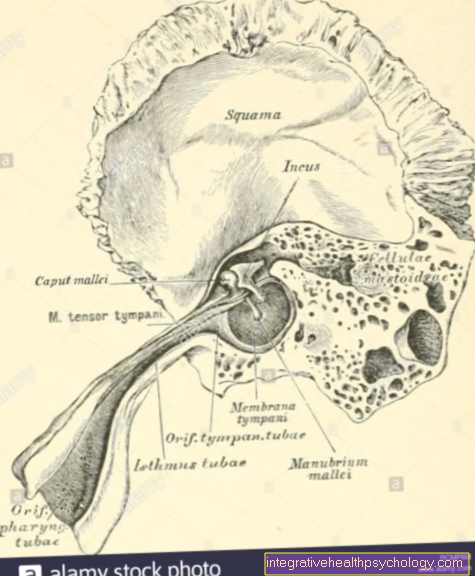
Inflammation stomach
introduction
Inflammation in the stomach is a widespread clinical picture, which is a not inconsiderable problem both for those affected and in our society in general. Every fifth in Germany was affected by it before. In other nations too, gastric mucosal inflammation with its many different characteristics and various causes is an issue. Not only do the food components and the infection of the stomach with certain pathogens play a role, but also risk factors such as Smoking, alcohol, stress etc. contribute a large part to this. It is therefore important to be aware of how inflammation occurs in the stomach, how to recognize it and what to do about it.
Symptoms

At a acute Onset of inflammation of the stomach are symptoms like nausea and pressure-like to piercing pain in the epigastric region in the foreground. In addition to nausea, you automatically feel less appetite. Quite often they occur as a result of nausea increased belching and Vomit on since the Gastric mucosa is very irritated by the inflammation. If the disease is severe, even Vomiting blood occur.
In addition, there is a general feeling of illness and weakness, which is related, among other things, to the reduced food intake due to the inflammation in the stomach and the inflammatory process in general. In extreme cases it can even lead to Gastric bleeding and a deeper damage in the stomach lining. Depending on its location in the stomach, this manifests itself as Vomit from blood (Hematemesis) or tarry stool (Miserere). The intensity of the pain varies greatly.
At a chronic inflammation of the stomach are the Symptoms not that clear. In many cases there are no symptoms and if they do, then in the form of unspecific Pain in the upper abdomen. In the Type-A- Stomach inflammation can progress to a Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia come. In some cases, those affected feel defeated and powerless. Identifying inflammation in the stomach is therefore not always that easy.
causes

Also with the causes of inflammation of the Stomach you have to between acute and chronic distinguish.
Among the causes of acute inflammation One of them is the excessive consumption of food or alcohol. Any overstretching of the stomach due to ingesting too much food or a constriction of the stomach outlet promotes the production of large quantities Stomach acid.
On the other hand, drugs of the group of irritants nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Acetylsalicylic acid (a headache reliever), but also drugs like cortisone or Cytostatics (chemotherapy) the Gastric mucosa. A Food poisoningcaused by bacteria ingested with food also leads to an inflammatory response.
Also plays stress plays an important role in causing inflammation in the stomach. One also understands stress Injuries or Burns of the stomach, which can occur during an operation, or one State of shock. But also psychological stress can subconsciously manifest itself in an increased production of stomach acid and lead to inflammation.
In the chronic Inflammation of the stomach lining three different forms of gastritis and thus also described three different causes:
- Type-A.Inflammation (A.utoimmun): The cause is unknown. However, in some cases there is a connection with an autoimmune disease, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus or Hashimoto's thyroiditis. In the course of a long-standing illness it comes through diminished Vitamin B12- Recording finally to one pernicious anemia.
- Type-B.Inflammation (B.Acteriell): This inflammation is caused by infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori triggered, which occurs with increasing age.
- Type-C.Inflammation (C.hemisch): By taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-Medication (see above) or with increased reflux of bile in the stomach this type of inflammation of the stomach occurs.
All the causes mentioned are based on two principles that damage the gastric mucosa:
On the one hand, cells in the stomach are stimulated to produce more gastric acid so that gastric acid is present in harmful concentrations and the environment becomes more acidic overall. On the other hand, the cells that produce the natural protective mucous layer are inhibited, so that infections now occur more easily.
therapy
In the acute Form of inflammation in the stomach, it is already helpful to the harmful substances such as alcohol easy to avoid. Also carries a Lunch break, the duration of which should be made dependent on the symptoms, for faster recovery of the Gastric mucosa at. A sufficient one Hydration but should not be neglected.
When the symptoms improve, diet can be restarted slowly. A drug therapy with so-called Proton pump inhibitorsshowing the release of Stomach acid or other gastric medication (e.g. Antacids) can be given at the same time. If the nausea and the Vomit If you don't go away on your own, you can use special medication against it.
In chronic inflammation Type B, in which the infection with Helicobacter pylori is in focus, the goal is this bacterium kill. Two different so-called "Triple therapies"Used, each of which consists of a combination of three drugs: a proton pump inhibitor (Gastric acid inhibitors) and two antibiotics. This therapy takes about seven days and has a high success rate.
Also with the Type A inflammation Helicobacter pylori treatment may be helpful. Does it come in addition to the Vitamine B12 deficiency, this vitamin can be replaced with medication.
Treatment of the Type c-inflammation primarily includes that Drop of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and taking Proton pump inhibitors.
diagnosis

The diagnosis of acute inflammation in the stomach is made on the basis of the symptoms in connection with a gastroscopy and sampling. The sample that was taken from a suspicious stomach area during gastroscopy is then examined histologically. This means that the fabric, supplemented with special colors, is viewed and assessed at a large magnification. If more white blood cells can be seen in the upper layer of the mucous membrane and this layer is no longer intact, this supports the suspicion of inflammation of the gastric mucous membrane.
The chronic form of inflammation in the stomach urgently requires a gastroscopy and testing for Helicobacter pylori for diagnosis, as the symptoms are not always indicative. Here, too, a sample of the gastric mucosa should be taken during the gastroscopy in order to be able to assess the tissue and the extent of the inflammation more precisely histologically. Testing for the bacterium is usually carried out two weeks after the antibiotic triple therapy.
The bacterial pathogen can be detected in different ways. One possibility is to detect it by taking a sample of the mucous membrane. There is also the option of a breath test, in which a certain concentration of labeled carbon dioxide in the exhaled air is evidence of Helicobacter pylori. In addition, either the bacterium itself or antibodies to it can be sought in stool and blood serum.
Ultimately, however, only the sample taken from the gastric mucosa is conclusive.
Read more on the topic: Ultrasound of the abdomen
forecast
The acute Inflammation in the stomach usually heals spontaneous and leaves no major traces or damage to the gastric lining.
In the chronic Inflammation is more careful. Depending on the severity, major gastric mucosal changes can occur in the course, such as Ulcers or even to malignant tumors. In addition, the treatment and follow-up examinations are significantly more time-consuming compared to acute inflammation. While one case may require lengthy treatment Stomach acid blockers and a Vitamin administration is bound, can be an elimination treatment of the stubborn Helicobacter pylori remain unsuccessful for a long time due to resistance to the drugs. Especially in the case of an inflammation with Helicobacter Pylori, a Breath test or a gastroscopy can be done after about two months of treatment.
In general, for all chronic gastric mucosal inflammations after successful therapy, regular checks should still be carried out, for example in the form of a Gastroscopyto rule out stomach ulcers and malignant changes such as cancer or to be able to treat them in good time.
Furthermore, the Type A - inflammation a anemia to be clarified in the course.
Overall it is the case that with chronic gastric mucosal inflammation, the quality of life of those affected is significantly reduced due to the associated symptoms, which should be taken into account by the doctor during treatment.
prophylaxis
To avoid inflammation in the stomach To prevent this, it helps if you avoid substances harmful to the stomach as much as possible or if you only consume small amounts.
Typical Gastric acid stimulators are alcohol, coffee, nicotine and certain Painkiller. It also includes foods that are highly acidic.
Gastric acid blockers are often used therapeutically, but from a gastroenterological point of view are not always for prophylaxis, at least not for permanent prophylactic purposes Ingestion suitable.It is important to take care of your stomach and to consult a specialist doctor as soon as possible if you have complaints.