Inflammation of the salivary gland
introduction
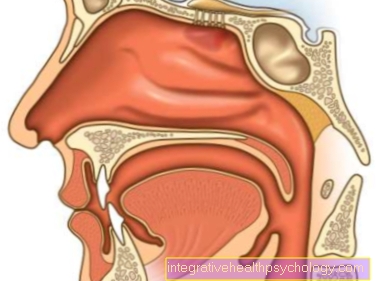
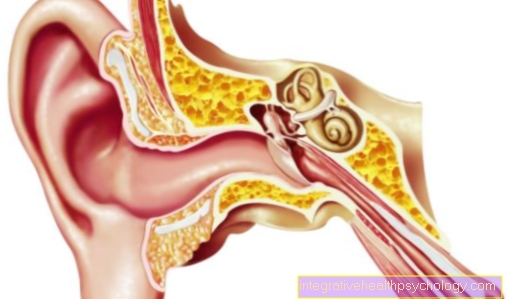
The paired salivary glands, especially the three large ones on both sides of the ears, under the tongue and on the lower jaw, perform numerous tasks in our everyday lives. They moisten the oral cavity and thus play a major role in eating, speaking and cleaning, as well as protecting the oral mucosa from bacteria and viruses.
Like any other organ, the salivary glands can become inflamed. This disease is technically referred to as Sialadenitis. 'Sial"is the Greek translation for saliva,"Aden"for gland and the ending -it is denotes the inflammation.
The most common are the large salivary glands and of these the parotid glands most likely (Parotid gland) affected by inflammation. Inflammation specifically of the parotid gland is called, based on its technical term Parotitis. Usually only one of the paired salivary glands becomes inflamed. Bilateral inflammation of the glands can be observed in around 20% of those affected.
Epidemiology
Most often people get sick between the ages of 20 and 50 at a Inflammation of the salivary glands.
However, there are two exceptions that stand out from the age spectrum. This is for one mumps, also colloquially as Goat peter called, probably the best known viral related inflammation of the salivary gland, the especially in childhood occurs, and on the other hand one purulent, bacterial inflammation of the parotid glands, usually people beyond the age of 50 get sick.
Causes and Risk Factors
As a trigger of Salivary gland inflammation become infectious and non-infectious Differentiated causes.
The infectious inflammation will be through bacteria or Viruses conditional, being bacterial inflammation through Staphylococci or Streptococci, which also in healthy people mouth- and Pharynx can occur, are more frequent.
To the non-infectious causes of salivary gland inflammation counting Autoimmune diseases, as the Sjogren's syndrome, an inflammation caused by radiation in the head and neck area (Radiation adenitis) or as a result of a Radioiodine therapy at Thyroid adenomas. The radiation or radioiodine therapy damages the mucous membrane, what Dry mouth with the consequences already described.
Furthermore are still acute from chronic Differentiated forms.
The acute Kick shapes within days or even suddenly and heal relatively quickly, especially with treatment. It is mainly from bacteria and Viruses triggered. So will mumpswhich is triggered by the mumps virus and mostly both parotid glands infects included. Mumps is the most common viral inflammation of the salivary glands and occurs especially in Childhood on. Other viruses are possible, but very rare.
From one chronic Shape is spoken when there is recurring, often in Spurts, leads to inflammation of the salivary glands. This is usually the case immunocompromised People or those who have an autoimmune disease like the one mentioned above Sjogren's syndrome suffer, observed. With Sjogren's syndrome, most of all Women over the age of forty are affected, the body mistakenly produces antibodywho the Salivary and lacrimal glands attack. As a result, those affected suffer from eyes- and Dry mouth, pain, and inflammation of saliva. In this case too, the parotid glands in particular are affected by the latter. This disease usually occurs in combination with other rheumatic complaints.
One of the most important Risk factors for the development of salivary gland inflammation is the Decrease in mouth moisture due to reduced saliva production. As already mentioned cleans of the saliva the oral mucosa and protects it from germ colonization. If the mouth is dry for a long time, it can develop bacteria and Viruses multiply and via the gland ducts in the Oral cavity end up infecting the salivary gland tissue. Consequently it comes to Inflammation of the salivary glands.
Older people in particular suffer from the technical language Xerostomia (Dry mouth), there the feeling of hunger and thirst decreases with age. It will less fluid taken in and subsequently also less saliva produced. There are also numerous medications, such as water tablets (Diuretics), those for heart problems (Beta blockers, Calcium channel blockers) and Antidepressants, which are mainly prescribed to the elderly and one dry mouth by Inhibition of saliva production favor. Also luxury foods, especially the excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages leads to a decrease in saliva production.
Another important risk factor for the development of inflammation of the salivary glands is Salivary stones. They arise mainly in the gland ducts of the Salivary glands in the Lower jaw (Submandibular gland; Glandula = Gland). The saliva stones are able to narrow or even clog the duct through which the saliva gets from the glandular tissue into the oral cavity. On the one hand, the resulting dry mouth favors the Germ colonization of the oral cavity, on the other hand, the saliva built up behind the saliva stone forms an ideal breeding ground for the Multiplication of these germswhich is described below in a Inflammation of the salivary glands can end. The Main ingredients of salivary stones, technically as Sialolites are designated Calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate. Both can be found in Teeth and bone. The formation of the sialolites is caused by a changed saliva composition in the context of Metabolic diseases or after already been through Inflammation and / or one already narrowed gland duct among other things, after going through mumps-Disease in childhood or as part of a Cystic fibrosis favored.
However, it is important to know that not every salivary stone directly leads to an inflammation of the salivary glands Has. As I said, arise almost all stones in the area of the lower jaw salivary glands. However, this is hardly affected by inflammation, in contrast to the parotid glands, in whose gland ducts only about 2 out of 10 stones arise. Nevertheless, a known stone should be watched in order to avoid worse consequences or to be able to contain them in good time. A bad Oral hygiene accelerates the inflammatory process in each of the cases, since the bacteria and or Viruses do not have to colonize the oral cavity first.
At the Heerfordt Syndrome, which is mainly observed in young women and like Sjögren's syndrome is counted among the autoimmune diseases, there is also one Antibody-related destruction of glandular tissue of the lacrimal and parotid glands. The symptoms are similar to those of Sjogren's syndrome. Women with Heerfordt syndrome often also have one Sarcoid.
Also in the context of Tumors in the field of Salivary glands and gland ducts that narrow or completely close the ducts can lead to recurring inflammation of the salivary glands.
Mumps (epidemic parotitis)

mumps is the most common viral inflammation of the salivary glands, more precisely that of the Parotid glands in childhood and adolescence and is through what is called Paramyxo virus triggered. Colloquially, the disease is also known as Goat peter, because the swelling of the inflamed parotid glands causes the ears to protrude forward during the disease. The infection occurs over germ-colonized air. For example, a sick person separates while speaking, Sneeze and to cough tiny small droplets, called Aerosols out. These aerosols contain the virus, which can eventually infect other children through inhalation through the air. For this reason, sick children should stay at home; on the one hand to protect yourself, on the other hand to avoid infecting other children with mumps.
The dangerous thing about the mumps virus, however, is that not only children are contagious who already have symptoms, because approx. one week before symptoms appear and one week after they have subsided, the affected child sheds the virus. The virus usually attacks and infects both parotid glands. Once the virus has penetrated a previously healthy body, it takes some time to multiply and settle. This time is known as incubation period. With the mumps virus it is two to four weeks.
At the beginning the children act, as with other viral infections, tired and limp. You also have no appetite. In the course swell the parotid glands in the majority of children and are enlarged and painfully palpable. In the course of the sick child, it can be mild Temperature increase come. However, there are also fewer children who are also involved mumps have infected and have no symptoms or feeling of illness.
There mumps through a virus is triggered, only therapy that alleviates the child's symptoms and the symptoms of the disease makes sense. Unfortunately, there is no therapy that specifically attacks and destroys the virus. To the symptomatic therapy count among others cold envelopeswrapped around the head along the inflamed parotid glands. fever and Pain can be contained with the help of medication. However, it is still advisable to consult a doctor for detailed clarification of further therapy. The The disease heals within seven to fourteen days without consequences. After an infection, there is one lifelong immunity, which also explains that the Age peak the disease in Children and adolescents lies.
Symptoms

Acute and chronic forms of salivary gland inflammation also differ in some symptoms. Those affected who participated in a acute sialadenitis are sick, often complain of suddenly appearing, unilateral swollen, and often tender salivary glands. The infected gland feels coarse to hard when you touch it. The overlying skin may be overheated and appear red due to the inflammation. There is often significant swelling of the face. If the acute inflammation of the salivary gland is bacterial, pus can be drained into the oral cavity. In the case of viral inflammation of the salivary gland, both sides are often affected; in bacterial infections, usually one side. In contrast to bacterial inflammation, there is no purulent, but watery secretion.
The pain can increase when eating and chewing, as the salivary glands work harder when eating and produce more saliva to moisten and utilize the food and transport it into the oral cavity. Since the inflamed tissue swells up and hinders the outflow of saliva, this puts additional pressure on the already sensitive salivary gland, which subsequently causes it to swell even more and hurt even more. Some people experience pain so bad that they find it difficult to open their mouth or swallow. The corresponding muscles are located in the immediate vicinity of the glands and irritate the inflamed salivary gland tissue when moving.
The body reacts to the inflammation with a fever. The surrounding lymph nodes can also swell as a result of the inflammation of the salivary glands and be mistaken for them when palpating. By taking a blood count and assessing inflammatory parameters, such as the number of white blood cells, the attending physician can find information about the presence of inflammation.
Chronic salivary gland inflammation can drag on for several weeks. In contrast to the acute form, the onset is not sudden, but is characterized by a gradual worsening of the symptoms over weeks. In addition, a relapsing occurrence of salivary gland inflammation is typical of a chronic manifestation. Once the chronic inflammation has reached its peak, the affected salivary gland is painful and hard and palpable.Occasionally it secretes a milky, granular secretion, which can also contain pus.
Chronic salivary gland inflammation usually occurs on one side, but can change sides from one flare to another. If a salivary stone is the cause of the problem, depending on its size, it can occasionally be felt as a hardening in the gland duct. If you feel a tender and swollen, enlarged salivary gland, it is important to see a doctor and discuss the next steps with him. If you wait too long and the cause responsible for the inflammation of the salivary glands is not properly counteracted, a serious complication can result in an abscess, i.e. a purulent accumulation caused by the colonized bacteria. The danger of the abscess is that it can break into blood vessels and, in the worst case, the bacteria can subsequently trigger life-threatening blood poisoning.
Also read our topic: Symptoms of inflammation of the parotid gland
diagnosis
The doctor can usually make the diagnosis based on the clinical symptoms and in conversation with the person concerned or at least suspect it. An indication of the presence of an inflammation of the glandular tissue of the salivary organs is one Swelling and tenderness in this area and the Increase in discomfort when eating. An earlier one Irradiation in the head and neck area and the ingestion of certain Medication, combined with the corresponding symptoms, can be an indication of the presence of a salivary gland inflammation.
Enter the inflammation again and again and the person concerned also suffers from diseases from the rheumatic Form circle, this indicates to the doctor a chronic form of inflammation. When inspecting the Oral cavity can affect some sufferers, especially those with bacterial and viral conditional Salivary gland inflammation, inflamed areas can be seen. If a bacterial infection is suspected, the doctor will try to massage the pus out of the glandular tissue and duct system to confirm his suspicion. A smear can be useful in the case of bacterial inflammation of the salivary glands to find out which one antibiotic the triggering pathogen responds in order to subsequently start a targeted therapy.
are Salivary stones Involved as a trigger, this can be done as part of a Ultrasound examination can be gently detected. Also Tumors or possible Abscesses can be seen with the help of these diagnostics. Imaging by means of MRI, CT or one endoscopic examination the salivary ducts using a small camera has been considered as a diagnostic tool. An endoscopic examination is indicated if one is suspected Autoimmune disease as the triggering cause, since during the procedure Sample material can be obtained and examined accordingly. Furthermore, as part of the examination, the gland duct can be flushed and freed of stubborn stones. The disadvantage of the investigation is that it is under local anesthesia must be done.
therapy
With the exception of viral conditional Inflammation of the salivary glands It is important to detect and treat the cause of this so that the glandular tissue can subsequently recover and heal. Stones should be removed from the glandular duct if possible to avoid recurrence of inflammation. Are diseases from the rheumatic Shape circle, like that Sjogren's syndrome, Cause of recurring inflammation, this should be treated with medication if possible.
As already said, a dry mouth the basis for the Colonization with pathogens. This colonization can be sufficient with Hydration and Oral hygiene be counteracted. During the illness it is recommended to stay on soft food resorting to so that chewing and swallowing doesn't hurt too much. The Saliva production can also by inclusion acidic foodslike sugar-free, sour candy or with the help of sour juices or water mixed with lemon juice, and in this way the gland ducts and the tissue are rinsed and cleaned. In many cases, smaller salivary stones can also be transported from the glandular duct into the oral cavity in this way, which makes endoscopic removal for the person affected Short anesthesia saved. Massages of the area in which the salivary stone is stuck in the gland duct can also help to loosen it and consequently facilitate its removal.
are bacteria The trigger of inflammation is on Antibiotics resorted to treatment. At a viral conditional gland inflammation stands the symptomatic therapy in the foreground. It includes that among other things drug treatment of pain and fever. Suitable drugs are Ibuprofen and Paracetamol. However, symptomatic therapy is also part of the treatment for other triggers mentioned above. Has become a purulent complication abscess formed, this must be opened to allow the pus to drain off and to break through into the Blood vessels and one possible Blood poisoning to prevent. Existing constrictions in the gland ducts should be removed, as these can also be the cause of recurring inflammations.
At repeated inflammation of the salivary glandthat heal hardly at all or only after a long period of time should have a Removal of the affected gland should be considered.
forecast
The forecast an acute, one-off Inflammation of the salivary glands is generally very good. If the trigger is found in good time and a targeted, symptom-oriented therapy is started, it heals within a few days without any problems or consequences out.
In the Removal of the salivary glands, especially that of the parotid gland, there is a risk that the facial nerves embedded in it will be damaged, which is a Facial paralysis the affected half of the face. However, the nerves are repeatedly checked for their function during the operation and by means of special surgical tool spared as much as possible to maintain their function.
prophylaxis
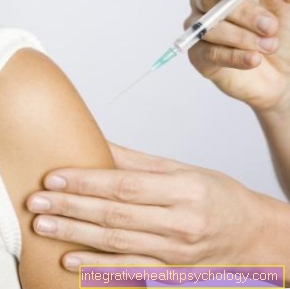
Prophylactic should be on one adequate hydration be respected to Dry mouth to prevent. Oral hygiene, especially after eating, prevents excessive colonization with harmful germs. Chewing gum and sour, sugar-free candies also stimulate the flow of saliva and clean thereby Salivary glands and execution aisles. Chewing gum also contributes to oral hygiene.
There is a possibility of children in combination with rubella and measles against the mumps-virus get vaccinated. As a result of vaccination the body produces antibodies which, like after a past mumps infection, give the vaccinated child protection and immunity against re-infection.