Inflammation of the uterus
introduction
A uterine infection can be very uncomfortable for the affected woman.
A distinction is made between inflammation of the cervix (Cervicitis) from inflammation of the lining of the uterus (Endometritis) and inflammation of the uterine muscles (Myometritis).
Overall, the uterine inflammation is often caused by ascending vaginal inflammation (Colpitis) conditional and mostly of bacterial origin.
With adequate and timely therapy, it usually heals without complications.
anatomy
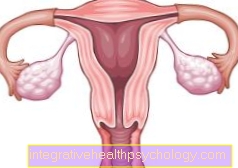
The uterus lies in the middle of the lower abdomen.
One fallopian tube opens into the body of the uterus on each side.
The uterus is down through the inner cervix towards the cervix (Cervix) locked.
The cervix is in turn separated from the vagina by the external cervix.
The external cervix is particularly important as it keeps pathogenic germs out of the uterus.
causes
The most common cause of uterine infection is one untreated vaginal inflammationthat spreads towards the uterus and finally through the cervix reaches the uterus.
Usually this is a bacterial inflammation.
Possible pathogens are Gonococci, Streptococci, Staphylococci, Chlamydia, Mycoplasma or Escherichia coli.
Usually such an ascending infection is favored by other factors.
For example, pathogens can more easily reach the uterus if the natural protective mechanisms of the vagina are disturbed.
There is usually one there acidic environment, which should make it difficult for harmful microorganisms to multiply there.
A too dry and alkaline vaginal environment can promote the colonization and reproduction of harmful bacteria and fungi.
Even during the Menstruation the risk of germs entering the uterus is increased.
Same goes for vaginal interventions, for example gynecological interventions such as the insertion of a spiral.
In the process, germs can be carried into the uterus, which continue to multiply there and lead to an inflammatory reaction.
Other factors that can promote the development of uterine inflammation are changes in the area of the uterus Cervixthat make it more permeable.
This includes Growths of the mucous membrane, for example Polyps and Fibroids.
After a vaginal birth or one Miscarriage the cervix can also be more permeable so that germs can spread into the uterus.
Sometimes remain after one pregnancy Remnants of the Mother cake (placenta) in the uterus, which can then cause inflammation.
Also one Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) can make the mucous membrane on the cervix less resistant to rising germs.
Last but not least, uterine inflammation can also develop in old age Prolapse of the uterus or the Adjustment of the hormonal balance develop.
The mirror sinks with age female sex hormones. As a result, the Uterine lining thinner, drier and therefore more prone to infection.
A uterine inflammation due to this hormonal change after the Menopause is also known as Senile endometritis designated.
Symptoms
The symptoms of uterine inflammation can be very non-specific.
Above all, they differ depending on how far the inflammation has progressed and which part of the uterus it has affected (only the cervix, the lining of the uterus, or the uterine muscles).
Cervical infection (Cervicitis):
If the Cervix the affected woman often experiences only mild symptoms.
This can be a increased or color-changed discharge out of the vagina, which often smells unpleasant.
The discharge can be a white-yellow to reddish-bloody color to have.
In some cases symptoms come like itching or a burning sensation in the vagina.
Otherwise, the cervical inflammation presents itself earlier few symptoms and is therefore often not recognized early.
Please also read our page Inflammation of the cervix.
Uterine inflammation (Endometritis, myometritis):
If the inflammation has already spread to the mucous membrane or muscles of the uterine body, other symptoms arise that may indicate the disease.
Affected women often complain Abdominal pain, or one discreet tenderness in the area of the uterus.
Also Changes in the control cycle can occur, for example the occurrence of Interstitial bleeding or spotting, as well as a increased or prolonged menstrual bleeding.
Inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries (Adnexitis):
Since the Hurry open into the uterus on both sides, in the worst case, uterine inflammation can also spread there and up to one Ovarian inflammation to lead.
This clinical picture is known as adnexitis and usually goes with one for the patients pronounced feeling of illness hand in hand.
Usually there are also severe pain in the lower abdomen and fever.
Complications
If a uterine inflammation is not recognized in time, various complications can result.
The inflammation may affect the initially Fallopian tubes and Ovaries spread and cause a serious clinical picture there (Adnexitis).
In the worst case, this can damage the ovaries so much that a infertility results.
The inflammation can very rarely spread to the entire abdomen. This state is called Peritonitis (Peritonitis) and usually goes with severe pain and high fever hand in hand.
Also the Accumulation of pus in the uterus or the formation of purulent settlements in the tissue (abscess) is possible.
Ultimately, the pathogens can also spread into the bloodstream and thus lead to a generalized inflammatory reaction in the sense of a Blood poisoning to lead.
Please also read our pages Fallopian tube inflammation and Inflammation of the ovaries.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of uterine inflammation is made by a gynecologist. There is also a vaginal exam necessary.
In this way, the doctor can examine the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix and examine them for signs of inflammation.
He can do one too smear which can then be examined microbiologically for pathogens.
With the so-called Colposcope the cervix can finally be shown enlarged. If the mucous membrane there is abnormal, the doctor can contact you directly Tissue sample remove and have it examined cytologically.
Especially if you are infected with human papillomavirus (HPV) must have the possibility of cervical cancer can be excluded as the cause of uterine inflammation.
To do this, a smear, as well as an Tissue sample (biopsy) from cervix taken.
In addition, the doctor is talking Risk factors for uterine inflammation ask, for example, previous vaginal interventions (Insertion of a coil, vaginal Operations), more frequent infections of the vagina, previous (Miss) births or the like.
In this way, the doctor can estimate the likelihood of an uterine infection.
therapy
If the uterine inflammation can be traced back to a specific cause, the therapy primarily serves to address it Eliminate factor.
The inflammation apparently originates from a previously started one spiral off, it must first be removed.
At remaining placenta in the uterus following a pregnancy these must be scraped off so that the uterus can recover.
If the uterine infection is severe, hospital treatment may be necessary.
Once the triggering factors have been eliminated, the actual treatment of the inflammation can begin. Bacterial uterine inflammation usually occurs Antibiotics used.
In the case of severe complaints, additional Painkiller can be used. It is important that the woman concerned much rest and give your body enough time to completely cure the inflammation in order to avoid complications.
prophylaxis
To avoid uterine inflammation, it is important to be on one adequate intimate hygiene to pay attention.
Since the uterine inflammation usually develops from a vaginal inflammation, it should be avoided.
In addition, washing with soap in the genital area should be avoided, as this attacks the natural protective barriers. It is better, soap-free preparations to use.
Furthermore can Condoms During sexual intercourse, prevent pathogens from being carried into the vagina and causing inflammation there.
If there are known problems with the natural vaginal environment, you can Döderlein bacteria (Lactic acid bacteria), which are prophylactically inserted into the vagina in capsule form, help to strengthen the protective mechanisms of the vagina and to maintain the natural flora.
In this way, incipient inflammation is warded off from the start.
Also is a healthy and balanced diet With adequate exercise important to strengthen the Immune system.