Fatigue fracture in the metatarsus
General information on fatigue fractures
A Fatigue fracture is a Broken bone (fracture) caused by overuse of the corresponding bone.
Very often this type of fracture affects the Metatarsus and is noticeable through pain.
For a lot of general information on this topic, please also read our topic: Fatigue fracture
Definition of a fatigue fracture in the metatarsus
A fracture that is not caused by a sudden external trauma to the bone, but by overloading the bone, is called a stress fracture.
This bone fracture usually develops over a longer period of time by exceeding the individual load limit of the bone, with small fractures (Microfractures) train. These can then develop into larger fractures.
There are two types of fatigue fracture, namely the stress fracture and the insufficiency fracture. A stress fracture is the stress fracture of a healthy bone, which often occurs in competitive athletes.
In the case of an insufficiency fracture, the bone is already damaged by osteoporosis or bone tumors, for example. As a result, it is no longer as resistant and can easily break when exposed to stress.
In general, the bone is overloaded when it is repeatedly stressed too much, too long or incorrectly and on one side. The metatarsus is therefore one of the most common bones affected by a fatigue fracture, as it is constantly exposed to high stresses from running.
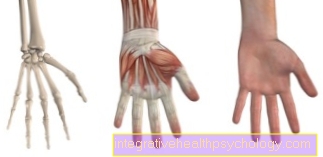
The five metatarsal bones (Metatarsal bone), which are located between the toes and the tarsal bones.
The metatarsus is involved in the formation of the arch of the foot and is important for the shock absorption of the body during vertical forces such as running.
The most common metatarsal fracture occurs on the second, third, or fourth metatarsal bones and is then called March fracture designated. This name has its origins in the military sector, as the break often occurred in untrained soldiers after long marches. If the fracture affects the fifth metatarsal, it will Jones fracture called.
Read more about: Fatigue fracture of the heel
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is dr. Nicolas Gumpert. I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- Lumedis - orthopedic surgeons
Kaiserstrasse 14
60311 Frankfurt am Main
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see Lumedis - Orthopedists.
Causes of a fatigue fracture in the metatarsus
The causes of the fatigue fracture of the metatarsus are, on the one hand, overloading of the metatarsal bones due to overuse. On the other hand, there are some factors that reduce bone stability and thus promote fatigue fractures.
The metatarsus is stressed while running. Extreme conditions such as
- a sudden extension of the running distance to more than 32 kilometers,
- a new running technique,
- Increasing the running speed,
- Bump and a hard surface of the path or
- sudden changes in the weight to be carried, for example due to weight gain or a heavy backpack.
Since it is the task of the metatarsus to absorb and cushion vertical forces on the body, the metatarsal bones are also heavily stressed when jumping. This can also lead to fatigue fractures during long jumping exercises. Runners, basketball players and dancers are particularly affected.
One of the causes that lead to poor bone stability is osteoporosis as one of the main factors. In this case, less bone substance is built into the bone and bone degradation predominates, so that the bone becomes porous and prone to fractures even under low stress.Older women are often affected by osteoporosis, who after the menopause form a reduced amount of the female sex hormone estrogen, which is essential for bone metabolism and thus for stable bones.
Read more on the topic: What kind of pain occurs with osteoporosis?
Furthermore, fatigue fractures in the metatarsus are caused by foot misalignments such as the arches foot (Pes excavatus), which can result in incorrect loading, which then leads more quickly to bone wear and consequently to fracture.
Another risk of a fatigue fracture are drugs that negatively affect bone metabolism, leading to brittle bones. The best known drug that has osteoporosis as a side effect is cortisone.
Malnutrition, eating disorders or unbalanced diets can also lead to reduced bone formation, as there is too little building material for the bones due to the insufficient absorption of nutrients.
Finally, there are diseases of the musculoskeletal system and the bones, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Paget's disease or rickets caused by vitamin D deficiency, which weaken the bones structurally and thus promote bone fractures, as is also the case with bone tumors or bone metastases in cancer Case is.
Symptoms of a fatigue fracture in the metatarsus
In contrast to a bone fracture caused by an accident, which is characterized by sudden severe pain and often loss of function in the affected extremity immediately after the trauma, a fatigue fracture of the metatarsus develops only gradually and thus also its symptoms.
That’s often the case during bone overload first Pain symptoms in the metatarsal area noticed, but they disappear again when idle.
Because the pain in the early stages only when loaded of the foot, they are often ignored and not taken seriously. If the affected foot continues to be stressed, the initially only stress-dependent pain remains later also in rest phases persist, and gradually lead to that any footfall painful and thereby avoided. This is what ultimately happens with a fatigue fracture creeping to the decrease of the resilience of the metatarsus and thus to the Loss of function of the foot.
The pain described here is called dull tenderness characterized in the foot area. Occasionally, symptoms such as swelling, reddening, overheating and bruising occur as a side effect of the fatigue fracture (Hematomas) in the area of the metatarsus.
diagnosis
The diagnosis The fatigue fracture in the metatarsus is difficult due to the gradually developing and often unspecific symptoms, and is therefore often diagnosed relatively late.
First in the anamnese tries to narrow down the cause of the pain by asking specific questions. Here it is of interest since when the pain persists, whether it is only under pressure or already in peace occurs and whether a initiating trauma underlying.
In the subsequent physical exam the doctor pays attention Signs that indicate a fracturesuch as axial misalignment and abnormal mobility of the metatarsus or whether bone rubbing (Crepitations), Swelling, redness, or bruising.
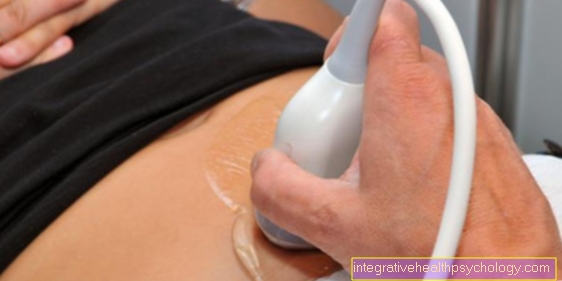
The next step in diagnostics is that Imaging. First will be a X-ray image made, with which the bone fracture can at best be proven, or a Exclusion of other causes occurs, such as the exclusion of a rheumatic diseasewho may have similar pain symptoms.
Often, however, a fatigue fracture is just in the early stages X-ray not clear, which is why procedures like the Computed Tomography (CT) that Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a Scintigraphy which enable a good and usually reliable diagnosis.
therapy
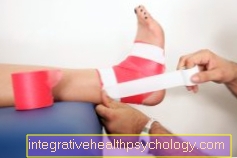
The therapy of the fatigue fracture of the metatarsus is mostly conservative, that is without surgery.
The most important measure here is Protection of the foot, on the one hand by strict Avoidance of any burden, on the other hand also through Immobilization of the metatarsus in a cast or a so-called Forefoot relief shoe.
During the rest period, mostly four to six weeks continues, the bone can regenerate and thus stabilize again.
If the fracture has a organic cause like for example osteoporosis the underlying cause must be adequately treated to prevent further bone fractures (see also: Therapy osteoporosis).
To symptomatic treatment the pain come Painkiller, cooling and Put up of the foot to use. Additional measures such as Lymphatic drainage, Kinesio tapes or physical therapy have a positive effect on the healing of fatigue fractures and acceleration of bone regeneration.
If the diagnosis is very late or if the metatarsal fracture is severe and in which no treatment is achieved by immobilization, can in individual cases also one operative therapy the fracture by fixing the fragments with wires and screws with subsequent immobilization in the plaster of paris.
forecast
Generally, the metatarsal fatigue fracture has one very good prognosis, as it usually occurs within six to eight weeks under adequate therapy uncomplicated and complete healing comes.
prophylaxis
The most important measure to prevent a fatigue fracture in the metatarsus is Avoidance of overload.
So it is essential to yourself to warm up before exerciseTo increase training sessions slowly and gradually, and after that sufficient rest breaks in which the body can regenerate.
Are also important matching running shoes with shock-absorbing properties that relieve the metatarsus. Also should Painthat are warning signals for the body, taken seriously and be clarified by a doctor.
Lie Risk factors for the development of a fatigue fracture, such as osteoporosis, these must be treated adequately.



.jpg)