Consequences of alcohol
Synonyms in a broader sense
Alcohol abuse, alcohol addiction
General
Consumption of alcohol is omnipresent in every society. Excessive consumption of alcohol (Alcohol abuse) can lead to alcohol dependence. Both long-term alcohol abuse and alcohol dependence can lead to various neurological disorders, which should be listed here.

Alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse is understood to mean the use of alcohol which can lead to physical and psychological damage due to excessive consumption of alcohol in an inappropriate manner.
To clarify when the consumption of alcohol is to be classified as abuse, the following example shows:
The Maximum daily dose of alcohol is included for men 20-24 g Alcohol a day, for women 10-12 g per day.
This dose should not be consumed every day. For example, a beer has 4.5% alcohol by volume = 4.5 grams of alcohol / 100 ml of liquid. The maximum daily dose would then be 0.5 to 0.6 l. A Alcohol abuse would then be available from a dose of more than 24 g (for men) daily.
Alcohol addiction
In contrast, alcohol addiction is caused by:
- the desire for more alcohol (development of tolerance)
- Withdrawal symptoms
- unsuccessful control of consumption and
- by the superior position of alcohol over other activities and behaviors
characterized.
Read more on the topic:
- Alcohol addiction
- Alcohol withdrawal
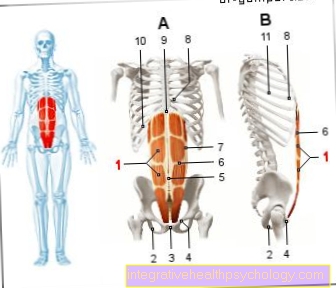
Illustration Consequences of alcohol on the organs
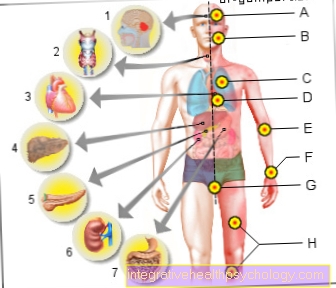
Consequences of alcohol
at the individual organs:
- Decrease in size of the cerebellum
atrophy
Decrease in brain volume
Cerebral cortical atrophy - Oropharynx cancer
Esophageal cancer - Disease of
Cardiovascular system - Alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver
- Inflammation of the
pancreas
Pancreatitis - Kidney pain, chronic
Inflammation (caused by alcohol) - Stomach and intestines
Inflammation of the mucous membranes
gastritis
Symptoms:
A - progressive dementia,
epileptic seizures,
Ataxia (impaired movement coordination)
B - facial flushing,
Skin temperature increase,
Premature aging of the skin,
Articulation disorder
C - accelerated breathing rate
D - palpitations, high blood pressure,
Myocarditis,
Risk of stroke, obesity
E - nerves - tremors, tingling,
Impaired motor skills
F - accelerated heart rate,
Skin - pimples and eczema
G - genital organs,
mild erectile dysfunction
to impotence
H - Alcoholic Myopathy
(Muscle fibers decompose),
Paralysis of the legs
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Simple drunkenness

The simple alcohol intoxication is characterized by psychopathological and neurological Symptoms. A psychological change after consumption of alcohol depends on the type and amount of alcohol, on the respective situation and the personality of the drinker. After a low dose of alcohol, the drinker is in an excitation stage (easy excitability). If you continue to drink alcohol, your consciousness will become clouded. In severe cases, there is increased sleepiness or a coma. Gaps in memory (amnesia) after high doses of alcohol can occur, also commonly called Film tear designated.
The neurological symptoms are intention tremor (trembling during targeted movements), poor articulation (slowed down, halting = Blanket in the mouth), Gait and standing ataxia (impaired movement coordination when walking or standing = Run lashing lines or drive by car) and pathological nystagmus (eye movement disorder). You may also feel dizzy (see also: Dizziness with alcohol) and palpitations (see also: Palpitations after alcohol) come.
Withdrawal of the dose leads to a decrease in the severity of psychological and neurological symptoms. In particularly severe cases it is necessary to induce vomiting or to do a gastric lavage so that the alcohol gets out of the stomach.
Pathological drunkenness
This psychosis (Disturbance of mental functions) is particularly due to a reduced tolerance to alcohol (e.g. due to brain diseases, etc.). The psychosis sets in suddenly and is usually only very brief (less than 1 hour). Psychomotor excitement, outbursts of anger, later states of exhaustion or sleep and, after waking up, gaps in memory occur.
Emergency assistance is provided to the patient by a doctor Benzodiazepines (Sedative) or Butyrophenone administered.
Nervous system diseases
Withdrawal psychosis (delirium tremens)
Delirium tremens occurs in acute withdrawal after prolonged heavy consumption of alcohol.
The patients mostly report tremors of their hands (relieved by drinking alcohol), increased sweating, irritability, restless sleep and sometimes occurring hallucinations for some time. These symptoms are known as predelir. In addition, morning seizures (withdrawal convulsions) may occur, the exact cause of which must be clarified.
The alcohol delirium, which occurs approx. 2-3 days after the interruption of the alcohol intake, is then characterized by the following symptoms:
- Jumpiness
- coarse shaking (tremor)
- incomprehensible language
- Disturbance of attention
- Disorientation
- psychomotor restlessness
- Hallucinations (illusions, hallucinations)
- Suggestibility
Vegetative symptoms of alcohol delirium are:
- Dilation of the pupils
- sweat
- Facial flushing
- Accelerated pulse (> 120 beats per minute)
- accelerated breathing rate
- sharp fluctuations in blood pressure
Some vegetative symptoms of the alcohol withdrawal delirium are life-threatening and must be treated in the intensive care unit. The delirious syndrome described can also occur with other diseases (head injuries, inflammation of the brain, etc.). EEG and other additional examinations (laboratory values, etc.) may be used for diagnosis.
Therapeutically, clomethiazole capsules and vitamin B1 are often administered in the Prädelir, alternatively also carbamazepine. If the predelirium develops into full delirium, clomethiazole is administered by infusion.
Clonidine is also given when the vegetative symptoms are severe. If symptoms of restlessness are in the foreground, butyrophenone and tranquilizers (sedatives) can be used.
Read more about this: Alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol hallucinosis
In contrast to the withdrawal delirium, psychopathological symptoms and less vegetative symptoms are in the foreground in alcohol hallucinosis. So the patients are often awake and oriented. After the psychosis there are usually no gaps in memory.
The following symptoms occur:
- anxious excitement
- acoustic hallucinations (Hallucinations)
- Escaping or suicidal acts as a result of the hallucinations
The psychotic symptoms initially appear at night until the full psychosis breaks out, which can last for a few days. After treatment with appropriate medication (Neuroleptics) the symptoms decrease.
The patient must be admitted to a psychiatric clinic for treatment. There he is in an emergency with e.g. Butyrophenone medicated.
Alcohol-related Korsakov psychosis
This clinical picture occurs after many years of alcohol abuse or coexists with one Wernicke encephalopathy (see below) (or emerges from it). The disease can also occur after alcohol delirium.
Korsakov's psychosis is characterized by:
- wrong orientation about oneself and the place
- inability to memorize or learn something
- Confabulations (made up and mismatched statements)
Although the Korsakov psychosis is with Vitamin B1 treated, but without any significant treatment success.
Alcohol-related polyneuropathy
(poly = many nerves are affected; Neuropathy = damage to the nerve endings)
This disease, which affects only a small number of alcoholics and occurs after years of alcohol abuse, is the Malnutrition (Lack of Vitamin B1) the cause of the malfunction.A malfunction of the liver and changes in the blood count (lack of magnesium, lack of blood platelets, etc.) are usually also detected.
Alcohol-related neuropathy usually starts with tingling, paresthesia and pain in the feet and lower legs. These appearances then expand further into the arms. In severe cases it can lead to paralysis legs come.
With sufficient nutrition, Vitamin B1 therapy and appropriate physical treatment can become alcohol-related Polyneuropathy partially regress within several weeks or months.
Wernicke encephalopathy
In general, Wernicke encephalopathy is a syndrome that occurs particularly in chronic alcoholism, but also in a range of other diseases. The disease occurs in alcoholics due to malnutrition, since alcoholics "feed" almost exclusively from alcohol. The associated thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency leads to bleeding and vascular damage in numerous parts of the brain. The onset of the disease is acute and can also occur as a life-threatening complication in delirium tremens.
If the disease is not treated with high doses of vitamin B1 in a timely manner, it will be fatal in a few days. Even with appropriate treatment, the death rate is 10-20%.
The most noticeable symptoms are:
- Eye muscle and eye paralysis
- Pathological nystagmus (eye movement disorder)
- impaired coordination of movements in the trunk, gait and stance
- psychological disorders (hallucinations, states of excitement, indifference and drive disorder)
- Pupillary disorders
- Korsakoff syndrome
- vegetative symptoms (sweating, tremor, increased pulse rate)
Cerebellar atrophy
Long-term alcohol abuse sets between the ages of 50 and 60. Year of life one atrophy (Decrease in size) of the cerebellum.
The hallmark of this disease is one in particular Ataxia (impaired coordination of movements) of the legs available. The patient's gait is changed, i.e. the corridor is legs apart, later staggering.
The arms can also be affected. The typeface is also slightly shaky. The disease lasts for 10-20 years.
The therapy is limited to the administration of vitamin B1.
Read more on the subject at: Cerebellar atrophy
Cerebral cortical atrophy
This reduction in brain volume, which occurs in younger and middle age, is due to chronic alcoholism. Symptoms are progressive dementia (Decrease in mental performance), epileptic fits and delusions of jealousy. This reduction in brain volume is reversible if the patient remains abstinent, i.e. If no more alcohol is consumed, there is no renewed increase in brain volume.
Alcohol embryopathy / alcohol during pregnancy
This is to be understood as a malformation of the embryo that has arisen from the mother's chronic alcohol abuse during pregnancy.
Physical and mental deformities of the child can occur. The birth weight of these children is e.g. below that of healthy children.
These children are also small and underweight later on (up to the age of 7). Malformations are especially that Internal hydrocephalus (Enlargement of certain brain structures) as well congenital heart defects.
Please also read our topic: Alcohol during pregnancy
Alcohol in adolescence
The consequences of alcohol should not be underestimated, especially in adolescence. This is because the body and especially the brain are still developing in adolescence and can be more easily influenced by external factors. Long-term behavior is also shaped in adolescence.
After drinking alcohol, the acute effects and consequences of alcohol such as mood enhancement and relaxation become apparent. But the general ability to criticize and self-assessment are negatively influenced.
The direct consequences of alcohol in adolescence are therefore frequent conflicts that are often violent. The increased self-assessment leads to further dangerous behavior. Around 30% of traffic accidents among young people aged 15-20 are related to alcohol. Sexual assault in adolescence is also often associated with alcohol consumption.
More serious consequences of alcohol in adolescence are, however, the long-term consequences. These affect both the body and psychological development. People who drink alcohol regularly and in large quantities in adolescence are at a higher risk of developing mental health problems.
The brain is affected, which can lead to attention, concentration and learning difficulties. School performance can suffer. As the disease progresses, the risk of developing alcohol dependence or other addictive behavior for other drugs increases. Due to the addiction, duties and rules are disregarded, which makes successful integration into working life more difficult.
The development of a depression can come later. Since alcohol is also often abused in adolescence as an escape from reality, it can happen that important behaviors are not learned.
This includes dealing with people, expressing feelings and strategically solving problems.
In the long term, the consequences of alcohol can cause psychological as well as organic damage, especially to the liver, kidneys and nervous system. The rule here is that the earlier the consumption of alcohol is started in adolescence, the greater the damage.
All of these consequences of alcohol in adolescence are possible and represent a risk. The probability of measurable consequences occurring naturally depends strongly on the age of the first contact and the amount of alcohol consumed. The majority of adolescents do not experience any long-term consequences, even if they have occasionally consumed alcohol in adolescence.
You might also be interested in this topic: Alcohol intolerance
Drink driving
The effects of alcohol can be seen in many areas, but in a few aspects of life the effects of alcohol are more devastating than at the wheel.
It must be said in advance that one not looking for the least amount of alcohol at the wheel should have. The consequences of drink-driving are also related to the amount consumed.
Initially, the alcohol does one Overconfidence at the same time Loss of attention and ability to react. Speeds and distances become Not more correctly assessed. As a result, there are more accidents and injuries as a result of drink-driving.
The responsiveness decreases measurably below the permitted alcohol limit of 0.3 ‰ or 0.5 ‰ without any noticeable driving uncertainty. So you should leave the car before.
The risk of accidents is particularly high between the ages of 18-25, as they are still an inexperienced and risk-averse age group.
If you drink more alcohol, it will eyesight and the general judgment impaired. You are then no longer able to drive a car. Drunk driving almost always results in property damage or personal injury.
In addition to the health consequences of drinking and driving, driving under the influence of alcohol has other personal consequences. There are clear rules and levels of punishment, which are related to the alcohol level and interference with road traffic.
The consequences of drink driving range from one Fine until Loss of driving license. From a legal point of view, you can drive a vehicle up to an alcohol level of 0.3 ‰ without consequences.
In the range of 0,3-0,5‰ Driving is permitted as long as there is no accident or other hazard to road traffic.
However, if the ability to drive is restricted, ab 0.3 ‰ a fine as well as points in Flensburg or even the withdrawal of the driving license can be the consequences of drinking and driving.
Driving with a level of 0,5-1,1‰ is classified as an administrative offense and, depending on the number of violations, punished with up to € 1,500, 2 points in Flensburg and a 3-month driving ban.
At over 1,1‰ The consequences of drinking and driving are even more severe now that it is a criminal offense. From 1.6 ‰ you have to have one medical-psychological examination (MPU) in order to regain the driving license.
It is important to know that alcohol has an individual effect and is broken down in each person. Before driving a vehicle, it is best to refrain from alcohol in order to safely avoid the above-mentioned consequences of drinking and driving.
Alcohol combined with drugs
The specific consequences of alcohol and drugs combined are of course always dependent on the drug consumed. The amount consumed also plays a significant role in the expected consequences.
However, when consumed in large quantities or for a long time, the effects of alcohol and drugs are extremely negative.
In most cases, the effects of alcohol and drugs not only add up, they multiply. That is, both the risk in one Dependency to slip that increases exponentially as well physical consequences of alcohol and drugs more pronounced could be. The burden on internal organs such as the liver, pancreas and kidneys is already enormous from one substance and, depending on the substance, is also increased.
Simultaneous consumption of drugs and alcohol puts even more stress on these organs, which is the case with frequent or heavy consumption Fatty liver, Cirrhosis of the liver, malignant tumors and Organ failure can lead.
The nervous system, i.e. both peripheral nerves and the brain, can also be significantly damaged as a result of alcohol and drugs. For example, peripheral nerve damage and memory disorders can occur
Other consequences of alcohol and drugs are the unpredictable acute effects of intoxication. The effects of alcohol alone are known to most people and are more predictable than when drugs are additionally taken.
It can too acute psychotic states (Drug psychosis) come, some of which have to be treated in hospital.
Also are legal consequences Expect alcohol and drugs as most drugs are illegal. The consumption and especially the possession of drugs can result in severe fines or imprisonment.