Lymph node swelling in the groin - how dangerous is it?
introduction
Lymph nodes can be found all over the body. They are connected to one another by lymphatic channels and together with the lymphatic organs form the lymphatic system. A swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin can indicate a wide variety of diseases. Attention must be paid to the differentiated symptoms of benign and malignant diseases.

Causes of swelling of the groin lymph nodes
While lymph nodes in the neck or head area can already be enlarged in the case of a banal infection, such as a cold, this type of disease is no longer the cause of inguinal lymph nodes. However, this does not mean that cancer must be expected immediately. Slight inflammation can also be the cause and heal without any further problems. It is important that the patient has a feeling for his own body and that he mentally documents changes and communicates them to his family doctor when the opportunity arises. In the event of swelling that progresses rapidly or tenderness to pressure, a doctor can be consulted at any time in order to initiate further diagnostics.
In general, swollen lymph nodes can easily be roughly classified into most likely benign versus malignant based on a few criteria. The appearance of a painful swelling within a short period of time, as well as a temporal association with trauma or inflammation in adjacent parts of the body suggest a benign change. In contrast, a slowly increasing swelling without pain and possibly developing adhesions with the surrounding tissue structures are indicative of a potentially malignant swelling.
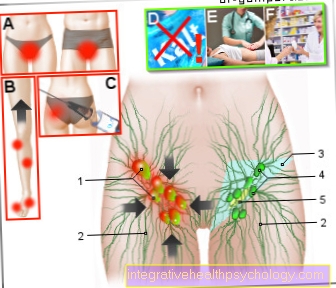
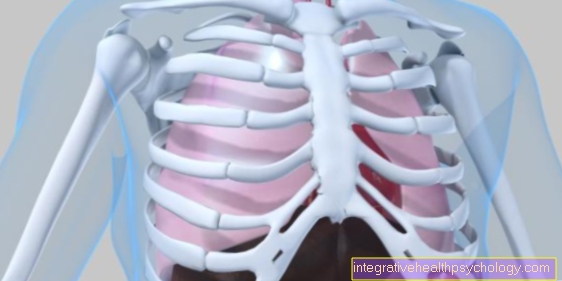
Swelling of the lymph nodes
in the bar
- Inflamed lymph node
- Lymphatic vessels -
Vasa lymphatica - Groin area (light blue) -
Inguinal region - Inguinal lymph nodes -
Nodi lymphoidei inguinales - Inguinal canal (yellow) -
Canalis inguinalis
Causes:
A - infections
Man (inflammation of the glans,
of the epididymis)
Woman (inflammation of the vagina,
the external genital organs)
B - injuries
with a contaminated wound
blood poisoning can occur
C - swelling after vaccination
(e.g. buttocks after tetanus vaccination)
Treatment:
D - The regions concerned
should not be refrigerated
E - medical massage,
manual lymph drainage
F - taking Schüssler salts,
Antibiotics, antivirals
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Lymph node swelling in the groin after an operation
An operation always poses a high risk of infectious diseases, as there is a large entry point for pathogens into the body depending on the size of the skin incision made. Pathogens have a wide area to penetrate the body, especially after major orthopedic operations that are performed with long cuts in the skin.
In hospitals, inflammation with resistant bacteria is the main focus. Despite the high hygiene requirements, the number of illnesses after operations is very high. Years of development have resulted in pathogens that are resistant to a large part of the common antibiotics. Lymph nodes in the groin region are mainly localized in inflammation in the legs. Major operations that encourage swelling of the lymph nodes are hip or knee operations.
Are you interested in this topic? For detailed information, see: Lymph node swelling after surgery
Lymph node swelling due to shingles
Shingles is a viral disease caused by the so-called "varicella-zoster virus". Shingles is a reactivation of the chickenpox disease. Those affected suffered from chickenpox in childhood or adulthood and the virus is stored in the body for life. In old age, in particular, the likelihood increases that the viral disease will recur in the form of shingles and lead to other symptoms that are limited to a specific part of the skin. This is accompanied by severe malaise, pain, swollen lymph nodes, and skin symptoms. Nowadays children are often vaccinated against chickenpox, which means that shingles is also less likely.
Lymph node swelling after an insect bite
An insect bite from mosquitoes or horseflies usually causes mild symptoms at the site of the bite. The poison that is passed on to humans causes reddening with itching in most cases. In some people, an insect bite can lead to hypersensitivity reactions or even anaphylactic shock. Severe redness, general symptoms and circulatory problems can be the result.
If there is swelling of the lymph nodes, this is an indication of a pathogen infection as a result of the insect bite. As a result of the bite, the insect breaks through the intact skin barrier, just like a minor injury. This allows bacterial or other pathogens to find their way into the body and lead to inflammation, which is noticeable in swollen lymph nodes. In most cases the inflammation is not threatening, but a doctor should be consulted as blood poisoning can develop.
Lymph node swelling from shaving
Shaving itself does not pose a health risk to the body. However, shaving with sharp blades can always lead to minor injuries to the skin. The bleeding is a sign that the skin has been broken and the body's protective barrier has been broken. Using an aftershave minimizes the risk of minor infections caused by pathogens. These are alcoholic solutions that have a disinfectant and antibacterial effect. If there is nevertheless a small inflammation, the surrounding lymph nodes can swell.
Lymph node swelling after vaccination
Nowadays there are vaccinations against numerous diseases, above all against typical childhood diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella or chickenpox. The majority of vaccinations are given in infancy, when the immune system is mature enough to produce antibodies. Vaccines are injected into the muscle, which stimulates the body to produce antibodies against certain components of a virus. In response to the vaccination, the lymph nodes near the puncture site, which is often on the thigh in children, can swell. The swelling can be classified as harmless and will recede in a short time.
To find out more about this topic, read our next article at: Lymph node swelling after vaccination
Lymph node swelling after a tick bite
In the vast majority of cases, tick bites are harmless. Only a small part of the ticks are carriers of a bacterium, which is transmitted to humans via the bite. The bacteria can cause what is known as “Lyme disease”, which should be treated urgently as it can lead to serious damage in the long term. If a tick bite results in circular reddening around the puncture site and swelling of the lymph nodes, a doctor must be consulted. In this case, the doctor will immediately prescribe an antibiotic against the bacterium.
For more detailed help on diagnosis, see How can you recognize Lyme disease?
Abscess in the groin with a swollen lymph node
An abscess is characterized by an encapsulated inflammation of the tissue. Pathogens and immune cells of the body can be found inside the capsule. The abscess receives a palpable covering through the capsule. Typically abscesses in the performance as well as lymph node swellings can appear as painful palpable "nodes".
An abscess in the groin is often preceded by a superficial infection of the skin, from which the abscess can develop. But also an abscess of individual intestinal loops that advance into the inguinal canal (inguinal hernia, inguinal hernia) can present itself as an inguinal swelling.
This topic could also be of interest to you: Abscess in the groin - causes and treatment
What are the symptoms of swollen lymph nodes in the groin?

Lymph node swellings of all kinds can also occur in healthy people. Sometimes there are anatomically permanently enlarged lymph nodes that can be ascribed to individual development.
The symptoms of a lymph node swelling are based on whether the underlying disease is benign or malignant. In the case of infections, in this case benign, patients report persistent pain and / or tenderness (tenderness). The swelling can appear both on the left and on the right. The lateral weighting provides information on the location of the infection or whether a malignant tumor exists, as these usually only develop on one side.
General symptoms of the disease can go hand in hand with the lymph node swelling, such as fever, fatigue, headache, body aches and malaise. If there is a malignant tumor disease of a lymph node, so-called B symptoms ("B" because of B-cell lymphoma) often occur. The patient should report constant fever, excessive night sweats and unwanted weight loss.
Read more on the topic: Lymph node pain, swelling of the lymph glands
1. Infections:
In contrast, in most cases an inflammatory disease is the cause of painful swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. Frequently there are infections of the genitals. Both men - with inflammation of the glans (Balanitis) or the epididymis (Epididymitis) - as well as women - with an inflammation of the vagina (Vaginitis) or the external genital organs (Vulvitis) - affected. The inflammation is triggered by a wide variety of pathogens: bacteria, viruses and fungi. Sexually transmitted diseases play a special role in this. The best known bacterial infections are chlamydial infections, syphilis (caused by Treponema pallidum caused) and gonorrhea Gonorrhea (by Neisseria gonorrhea caused). Having a fungal infection with Candida albicans is more of a condition that affects many older people. If the skin is not properly cared for and the skin is constantly damp, the fungus can implant itself and also cause lymph node swelling as the body tries to defend itself.
Read more on the topic: Lymph node swelling after surgery
In addition to the pathogens already mentioned, there are infections in which not only the inguinal lymph nodes are specifically affected, but can also be involved. Viral childhood diseases such as rubella, measles or chickenpox, combined with various other symptoms (mostly skin changes), can lead to swelling of the lymph nodes in the body. Another viral pathogen can also cause swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin - a herpes infection.
Many people think that herpes can only develop on the lip, but this is wrong. The so-called cold sore (Herpes labialis) is caused by the herpes simplex virus 1, whereas genital herpes (Genital herpes) is mainly caused by the less common herpes simplex virus 2.
This leads to swelling of the lower genital organs, itching, discharge and possibly other general symptoms of the disease.
Not only bacteria and viruses can cause swelling of the lymph nodes: Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan, is transmitted by cats, among other things, and triggers the symptoms of toxoplasmosis.
The disease usually only develops when the immune system is already weakened. This is why the pathogen is particularly widespread among people infected with HIV.
Please also read: Symptoms of toxoplasmosis
During pregnancy, the disease is particularly dangerous for the unborn child. Toxoplasmosis causes severe brain damage, blindness and other organ damage in the fetus.
Please also read: Infections in pregnancy
An HIV infection (human immunodeficiency virus) is known to affect the patient's immune system and is mainly transmitted sexually, but also through contaminated needles or blood transfusions (the latter actually no longer occurs in industrialized countries these days). Immediately after the infection, the patient may have swelling of the lymph nodes, which, however, in combination with the other flu-like symptoms are usually not interpreted as a sign of an HIV infection.
In the final stage of an infection, which is often long-term, AIDS will eventually develop (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). As part of the complete destruction of the immune system, the patients are very susceptible to infection. The infections in turn lead to swelling of the lymph nodes in the body.
Please also read: Lymph Node Swelling - What Evidence Is There It Is HIV?
2. Injuries:
Injuries also activate the immune system and lead to an enlargement of the corresponding lymph node. In the case of inguinal lymph nodes, these can be injuries from the foot to the level of the groin, including the entire leg. A sharp or pointed object, such as a nail or shard, was often stepped on when the foot was injured. A contaminated wound can cause blood poisoning (sepsis), which affects almost all organ systems and causes the body to collapse in its functions if no antibacterial treatment is used. One consequence of sepsis is lymphangitis - the inflammation of the lymph vessels and, subsequently, the lymph nodes. This is also accompanied by swelling.
3. Lymph node swelling after vaccination:
Lymph node swelling has been observed more often as a late consequence of vaccination. This can occur on the neck, in the armpits (lymph node swelling in the armpit), but also in the groin. The reason for this is that modified living or dead pathogens or pathogen components are administered to the body against which the immune system has to independently build defense cells. Since the lymph nodes in the region are stressed, a vaccination in the buttocks (e.g. tetanus vaccination) can lead to lymph node swelling in the groin. The swelling should be assessed by a doctor, but it will usually go away on its own.
4. Cancer:
If the lymph node swelling develops quickly and is not painful when pressed, this can indicate a malignant disease. The tumor can arise directly in the lymph node, as is the case with Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Tumor diseases in which massive numbers of immune cells are flushed out into the lymph nodes are symptomatically different, as in acute and chronic leukemia or cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. In addition to these primary tumors, almost every malignant tumor disease can metastasize to adjacent, but also to more distant lymph nodes. This generally worsens the prognosis. Read more on the topic: Lymph node cancer
5. Differential diagnosis:
Since other reasons for swelling in the groin must be ruled out in order to strengthen the findings of a swollen lymph node, a differential diagnosis must be carried out for hernias. Hernias describe the breakthrough of abdominal viscera through the abdominal wall, between muscles or ligaments. The two relevant soft tissue hernias in this case are the femoral hernia (the contents of the hernia under the inguinal ligament) and the inguinal hernia (the contents of the hernia above the inguinal ligament).
Read more on the topic: Lymph nodes swollen and Chronic swelling of the lymph nodes.
Lymph node swelling with a rash
A rash that is accompanied by swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin is a typical constellation of symptoms that indicate inflammation caused by the pathogen. A variety of pathogens can cause skin rashes.The exact appearance of the rash can often provide clear information as to whether it is a fungal disease, a bacterial infection or an infection with typical childhood diseases.
A measles rash can almost always be distinguished from chickenpox or a fungal attack by the skin symptoms.
In a disease like measles, the entire skin is usually affected and enlarged lymph nodes can be felt in the groin as well as on the neck, armpit and shoulder.
In the case of local infections with certain pathogens, for example caused by small wounds, the enlarged lymph nodes are located in the lymphatic drainage area of the rash. In the case of swollen lymph nodes in the groin, the legs or genitals are often affected by rashes.
Lymph node swelling with fever
Fever is often the first symptom of infections with certain pathogens. It is accompanied by chills, aching limbs, weakness and fatigue. In particular, diseases such as chickenpox, measles, glandular fever and other viral infections are associated with a high fever and swollen lymph nodes. Such an infection often occurs within a few hours to days and usually resolves on its own within a maximum of two weeks.
If fatigue and slightly elevated temperatures occur over several weeks, as well as unilaterally painless lymph nodes in the groin, a doctor should be consulted. These can be early symptoms of a possible malignant disease.
Lymph node swelling with pain
Lymph node pain is a typical sign of inflammatory reactions. In the event of an acute infection, the pathogens are recognized in the lymph nodes and produce antibody cells. In doing so, they swell to twice or three times their size and release inflammatory substances that cause pain when touched. After several days with the infection healing, the pain in the lymph node stops. If he does not do this for a long time, you should consult a doctor for clarification.
Read our next article on this below: Pain in lymph nodes in the groin
Lymph node swelling without pain
A swollen lymph node in the groin that is not painful is not necessarily a sign of a malignant disease. Infections can also lead to non-painful lymph nodes. A fatty tumor can also occur. Such a lipoma is completely painless and feels like a lymph node from the outside.
Localization of the lymph node swelling
Unilateral swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin
Unilateral swelling of the lymph nodes does not necessarily indicate a malignant disease. In the case of infections and inflammations, the lymph nodes often swell in general and therefore on both sides. However, since the lymph nodes are not always evenly distributed or palpable in the body, unilateral swelling does not rule out inflammation. In the case of painful swelling of the lymph nodes, in particular, an inflammation on the respective side must be considered, which can spread to the other side over the course of hours and days.
Unilateral lymph nodes, which swell unnoticed and painlessly for a few days to weeks, can also indicate a malignant disease of the lymphatic system. However, the specificity for such a disease is not particularly high. This means that although lymph cancer often manifests itself as swollen lymph nodes, on the other hand, swollen lymph nodes rarely mean lymph cancer.
Benign tumors that cause punctiform swelling in the groin are also rare. Often these originate from the fatty tissue and represent a completely harmless fatty tumor. In technical terminology, they are referred to as "lipoma".
For a precise diagnosis, a tissue sample is taken from the lymph node with a biopsy in order to reliably rule out a malignant disease. In the case of malignant diseases of the genital organs, the lymph nodes can also swell. In these cases, the cancer can spread through the lymphatic system like an inflammation. Since the lymph nodes of the groin are large lymph stations in many parts of the body, they are less affected by such colonization than the lymph nodes near the organs. Such a malignant disease is only very rarely suspected in the case of unilateral swelling of the groin.
Bilateral lymph node swelling
A bilateral, symmetrical swelling is very typical of an inflammation. Inflammations that lead to swelling of the lymph nodes are triggered by pathogens such as bacteria or viruses. There are large lymph node stations in the groin, which collect all the lymph from the legs, genital area, pelvis and groin region. All genital organs, legs, skin and many other structures can be affected by the inflammation. Some of the pathogens flow from the inflammation region via the lymph to the groin lymph nodes. These are often palpable even in healthy people and are up to 1 cm in size.
If the lymph node recognizes a certain pathogen, it produces numerous defense cells to fight the infection. The lymph nodes swell on both sides within a few hours or days and are painful.
Even if there is no noticeable infection, the lymph nodes can swell symmetrically due to pathogens. After the inflammation subsides, the large lymph nodes may persist in some people. In the course of the inflammation, they encapsulate and lose the opportunity to shrink despite the infection has subsided. Such swelling is not a cause for concern.
Diagnostics of swollen lymph nodes
The first diagnostic tool for any superficial lymph node problem is a physical exam. If possible, the lymph node is palpated. A lymph node that is not enlarged due to a malignant change should be painful, move easily with pressure, and be soft in texture. On the other hand, a tumor in the lymph node appears rather immovable with a hard consistency and is also not tender to pressure. In order to underpin an infection, the classic inflammation parameters can be checked by a laboratory test of the blood.
In addition to scanning, the doctor can do an ultrasound scan. This is inexpensive and does not burden the patient with radiation. Swelling of deeper lying lymph nodes cannot be palpated and becomes increasingly difficult to visualize with ultrasound as it gets deeper. Better imaging methods must now be used, such as computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). If the suspicion of a malignant disease is confirmed, a biopsy of the lymph node concerned is carried out. Tissue is taken intraoperatively and then examined microscopically in the pathology department.
Read more on the subject at: Lymph node biopsy
How do you feel the lymph nodes in the groin?
It is usually not difficult to feel the lymph nodes in the groin. If the lymph nodes are somewhat swollen, they can be felt as small "knobs" under the skin. The swollen lymph nodes usually feel rubbery or like a somewhat hardened node. They should slide against the skin under the fingers.
Often there is not only swelling of a single lymph node, but many of the lymph nodes (often on both sides) can be felt in the groin. The swollen lymph nodes are also often tender on pressure.
What is the normal size of the lymph node?
Lymph nodes in the groin are usually about half an inch to one centimeter in diameter. Often, not swollen lymph nodes can be felt in the groin.
From a size of over one centimeter, one speaks of swollen lymph nodes, and often not only a single lymph node is swollen, but instead several lymph nodes on both sides are affected. It can also lead to the feeling that several of the lymph nodes are connected and cannot be clearly separated from one another with the fingers. After the swelling has subsided, this should be possible again.
Therapy of lymph node swelling in the groin

1. Conventional:
The treatment of swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin depends on the cause using conventional approaches. In the event of an infection, antibiotics or antivirals can be used to kill the pathogen and support the immune system. The affected areas should not be cooled, even if the body is likely to be warmed up at this point (common consequence of inflammation). In the case of a malignant tumor disease, surgical intervention is often indicated in which the affected lymph node or nodes are completely removed. Chemotherapy can also be used to attack the cancer cells and to increase the success of surgical therapy. The relapse rate has been shown to decrease with additional medication.
2. Homeopathy:
As an alternative medicine, various forms of treatment are suggested. On the one hand, the topic of medical massage is very important. Manual lymph drainage should be carried out independently or by a non-medical practitioner. A brush is used to brush the skin of the lower extremities towards the chest and try to increase the lymphatic drainage. Another technique based on massage is acupuncture massage according to Penzel, in which the procedure is carried out without needles, but with reference to acupuncture theory. From a nutritional point of view, it is recommended to completely and increasingly to avoid sugar, eggs and milk and to eat whole foods, fruit and vegetables. For followers of the homeopathic philosophy, taking Schüssler salts or aromatherapy is also an option. If this type of treatment does not result in therapy, please consult a doctor.
Home remedies for swollen lymph nodes
If there is swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin, home remedies can be used to cool the affected area. This includes simple cold packs as well as quark or cabbage compresses. Above all, the cold relieves pain that may be associated with the lymph node swelling.
Treating the underlying disease with home remedies also makes sense. Infections or abdominal complaints are often the cause of the lymph node swelling. These can be treated symptomatically with a hot water bottle on the stomach and a sufficient amount of water to drink (teas such as sage, herbal, inger, peppermint tea) or even liquid intake through food (soup, broth).
An injury to the leg, for example, can also trigger swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin, which is better treated with cooling home remedies.
When do I need antibiotics?
Antibiotics are drugs that are given as tablets or intravenously to treat bacterial infections. In the case of other infectious diseases, for example viral diseases, they are ineffective or can even lead to undesirable side effects. Antibiotics should only be prescribed if a doctor has a justified suspicion of a bacterial disease with a high degree of certainty. An example of such a disease is the "erysipelas" or the "wound rose". It often affects the leg and is caused by bacteria. When the pathogens rise, the lymph nodes in the groin can swell. Immediate high-dose antibiotic administration is necessary.
Antibiotics can be counterproductive for certain viral diseases that are associated with swollen lymph nodes. In the case of glandular fever, for example, the administration of ampicillin can trigger a hypersensitivity reaction of the skin. This leads to a widespread rash on the skin.
Homeopathy for lymph node swelling
Many healing plants can be used in homeopathy for swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. These are often taken in the form of tea, sometimes also as a powder.
Plants such as:
- peppermint
- incense
- lemon
- oregano
- Licorice root
- Red clover
These plants can clear the build-up of lymph and thus reduce the swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin. Accompanying symptoms such as pain and fever can also be treated with homeopathic remedies if necessary, but you should make sure that the substances taken are compatible with each other.
Duration of a swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin
The duration of lymph node swelling depends on its cause. In the case of short viral infections, the disease and the swelling of the lymph nodes can heal within 2-3 days. Some viral diseases take up to several weeks to heal, for example Pfeiffer's glandular fever.
Bacterial diseases can also last for different lengths of time. An antibiotic is often prescribed after a few days.
In exceptional cases, after the infection has healed, the lymph node swelling may persist. The swollen lymph node "encapsulates" and does not recede. There is nothing to worry about.
Long-standing enlarged lymph nodes that are not caused by inflammation can occur in malignant lymphoma. The duration cannot be estimated here. Sometimes the lymph nodes have to be irradiated or shrunk with medication. The duration depends on the type of illness and the success of the treatment. which accelerates healing. About 2-3 days after starting the medication, the symptoms improve and the swelling also decreases.
After vaccination, swelling of the lymph nodes can appear as a late consequence one to four weeks after the administration and also last for a few days. A doctor should always be consulted with new lymph node swelling. If the swelling persists for a long time, i.e. weeks or even months, the corresponding lump must be examined further.
Read more at: Duration of lymph node swelling
Patient groups
1. Women:
A painful swelling of the inguinal lymph nodes in a woman indicates an inflammation of the genital organs or an injury to these or the lower extremities. The inflammation of the vagina (Vaginitis) or the external genital organs (Vulvitis) are possible diseases that should be checked.
2. Children:
Every day children come into contact with new germs against which they have not yet formed defense cells. However, the fact that they do not contract all kinds of pathogens over and over again means that their immune system is actively developing. This can lead to the spread of the pathogens into the lymph nodes and these swell. Often the disease does not manifest itself in the first place and there is a short-term swelling.
Lymph node swelling can also occur after vaccinations, which are often carried out in the first few years of a person's life. The child is presented with part of a pathogen that cannot lead to inflammation, but still stimulates the body to produce antibodies.
If a painless, swollen lymph node develops in the groin over a long period of time without a trigger, it should also be observed here how it develops. If in doubt, a biopsy must also be carried out on the child in order to rule out a malignant "lymphoma", as this can also occur in children.
3. Pregnant women:
In the case of lymph node swelling during pregnancy, the cause should be found out. Some diseases that involve lymph node involvement are caused by pathogens that can be harmful to the unborn child.
Infectious diseases such as chickenpox, rubella, cytomegaly, herpes and chlamydia are particularly dangerous. The list of very dangerous diseases is much longer, with some more and some less threatening. For this reason, women of childbearing potential should be vaccinated against the most common childhood diseases if possible before pregnancy. Vaccination or infection during pregnancy can cause serious harm to the unborn baby.
Read more on the topic: Infections in pregnancy
What are the reasons for a swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin in children?
In children, swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin is not unusual at first.Typically, the lymph nodes swell when defense mechanisms (immune system) or repair mechanisms are taking place in the body. In children who are getting bruises on their knees and shins at the age they are learning to walk, swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin is normal.
Even if the immune system is activated after a vaccination in the thigh, a swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin can occur in the child. Most of the time, the lymph nodes in the groin are chronically enlarged, especially in physically very active children, and this can regress after childhood.
Do you have anymore questions? Read our next article at: Lymph node swelling in the child
Frequently asked questions about swelling of the groin lymph nodes:
Can that be an indication of cancer?
A swelling of the lymph nodes can in principle also be an indication of cancer. Typically, there is then no swelling of the lymph nodes on the same side in the groin. Instead, a single lymph node is affected or there is swelling of the lymph nodes in the immediate vicinity.
Further indications that cancer could be the cause of the swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin would be a severe hardening that accompanies the swelling. Even if the lymph node is not tender on pressure, this can be an indication of cancer.
Especially when there is no other explanation for the lymph node swelling (injury to the legs, feet, skin diseases, diseases in the abdominal cavity), cancer should also be considered. In addition, lymph nodes that continue to grow and whose swelling does not stop after a while and tend to regress are suspicious of cancer.
Can that be an indication of HIV?
HIV is a disease of the immune system caused by the human immunodeficiency virus. Particularly at the beginning of the disease, i.e. during the initial infection, there can be severe swelling of the lymph nodes. However, the cervical lymph nodes are primarily affected.
Then there is a long (months to decades) phase without symptoms in the disease with HIV. Only in the final stage can a generalized (occurring anywhere on the body) lymph node swelling become noticeable. This can also affect the groin region.
Do you have anymore questions? Read our next article below: Symptoms of HIV
Can you exercise if you have swollen lymph nodes?
Whether it is possible to exercise with swollen lymph nodes depends on the accompanying symptoms.
In the event of exhaustion, a slight or high fever and accompanying symptoms that may indicate an underlying disease, rest should be observed first. Sports activities can usually be carried out after vaccinations or in good general condition. However, if you have any doubts about your health status, it is advisable to consult a doctor first.
Which doctor treats lymph node swelling?
In the case of typical symptoms of infection and painfully swollen lymph nodes, a doctor can first be consulted. This can find the first indications of infectious causes or increased activity of the immune system. If necessary, he will perform an ultrasound of the swollen lymph node in order to assess the structure. If the family doctor suspects a malignant cause of the lymph node swelling, he can refer the affected person to a specialist depending on the underlying disease.
The pediatrician is also a good contact for children and toddlers, especially if there is a suspicion of a viral childhood disease.
If there is a suspicion of lymphoma or another malignant disease, the family doctor can refer the patient to a hospital for a biopsy of the lymph node, ideally to an oncology ward. A decision about further therapy has to be made there.
Anatomical excursus
The lymphatic system is responsible for the immune defense by forming the defense cells and allowing them to mature. The former is carried out in the primary lymphatic organs (thymus and bone marrow), the latter in the secondary lymphatic organs, which also include the lymph nodes (also spleen, tonsils and special sections of the intestine such as the appendix). In the lymph nodes and in the lymphatic system, substances that circulate in the blood through the body are checked and hazardous substances are filtered out and rendered harmless. The lymphatic channels finally end in the left and right venous angles. Lymph nodes are therefore intermediate stations in the overall system.
Inguinal lymph nodes or also inguinal lymph nodes are both superficial and deep. Lymph channels from the legs flow into them (lower extremities), from the genital area, the buttocks and from the skin and subcutaneous tissue (Kutis and Subcutis), which is located below the navel. The most noticeable lymph node due to its size is the deep Rosenmüller lymph node. He lies in the Lacuna vasorum, an anatomical gap under the inguinal ligament through which blood vessels and nerve cords reach the thigh.
Read detailed information on the subject: Lymphatic organs
Recommendation from the editor
You can find more information on the subject in the following articles:
- Lymphangitis
- Lymph nodes swollen
- Lymph node swelling in the groin
- Pain in the lymph nodes of the groin
- Lymph node swelling in the neck
- Swelling of the lymph nodes

.jpg)