Atrioventricular node
Synonyms

AV node, Atrial ventricular knot, Aschoff-Tawara knot
definition
The AV node is part of the heart's conduction system. This still consists of the Sinus node, the His bundle and the Tawara thighs. The AV node forms that after the sinus node secondary pacemaker center in this system and forwards the excitation to the bundle of His, which is then divided into the two tawara limbs. The regulation of the heart rate is the primary function of the conduction system.
anatomy
The AV node is in the so-called Koch triangle located, which is in right atrium in the vicinity of the Atrial septum is located. Macroscopically (that is, “with the naked eye”) it is difficult to distinguish it from the surrounding structures. Both nerve tracts from the Sympathetic originate as well as nerve tracts from Parasympathetic nervous system come to the AV node and thus regulate its function. His Blood circulation the AV node usually receives from the Coronary artery dextra.
Figure AV node
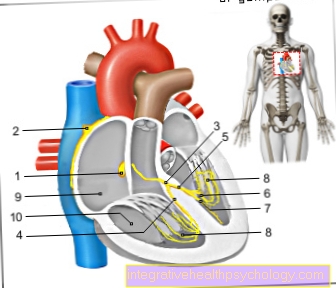
- AV node
(= Atrial-ventricular node)
Nodus atrioventricularis - Sinus node -
Nodus sinuatrialis - Tribe of
Excitation conduction system -
Atrioventricular fasciculus - Right thigh -
Crus dextrum - Left leg -
Crus sinistrum - Rear thigh branch -
R. cruris sinistri posterior - Front thigh branch -
R. cruris sinistri anterior - Purkinje fibers -
Rami subendocardiales - Right atrial -
Atrium dextrum - Right ventricle -
Ventriculus dexter
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
histology
Cardiomyocytes are specific heart muscle cellswhich form the AV node. These are compared to the cells of the Working muscles (Myocardium) poor in heart Myofibrils and Mitochondria.
function
The function of the AV node is Forwarding the excitement of Sinus node to that His bundle. As the excitement of the Heart muscle cells not simply walking over the connective tissue of the heart skeleton in order to excite the cells of the ventricular muscles, the AV node is required. This is the only one that transmits electrical connection between Atria and Chambers the excitement. He induces one delaywhich is important for heart function. This delay will too atrioventricular conduction time called (AV time) and is important for that contraction the atria and the ventricles of the heart coordinated expire. in the EKG is this delay as PQ interval readable.
Pathophysiology
Should the Sinus node can no longer fulfill its function, the AV node the task as primary Rhythm generator take over. The heart rate is then only 40-60 beats per minute.
The time delay can last too long or fail completely, which leads to the clinical picture of the so-called AV blocks comes. A distinction is made between three grades. At the AV block 1. Degree is that Transition period between atrium and ventricle extended. This is visible in the ECG as a longer PQ segment (> 200 ms). Mostly the patients have no symptoms and it does not require treatment.
In the second degree AV block, the conduction of excitation fails partially. There are two forms of this: With Mobitz type I (Wenckebach block), the transition time (= PQ interval in the EKG) becomes longer with every cardiac action until a transition fails at some point. After the transition fails, the PQ interval is suddenly extended from the beginning (Wenckebach periodic). This form of AV block generally has a good prognosis.
With 2nd degree AV block type Mobitz II the transition time is in principle not extended (no increased PQ interval in the ECG), but every second, third or fourth atrial contraction is not passed on to the ventricle. The prognosis is less favorable than that of the 2nd-degree AV block, as the probability is greater that a 3rd-degree AV block will develop.
At the AV block 3. Degree, too total AV block called, the transition between the atrium and chambers of the heart has completely failed. Beat atrium and chamber completely uncoordinated independent of each other. The Chamber can Substitute rhythm develop, which then independent of the Sinus rhythm running. As a rule, however, this is not enough for the body oxygenated blood to supply. There is no connection between the P wave (Atrial excitation) and the QRS complexes (Ventricular excitation).
The opposite case, one accelerated transition between atrium and ventricle, lies with Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome in front. This comes from an additional (=accessory) Pathway between atrium and ventricle. Via this additional conduction path, the excitation can be conducted from the chamber back into the atrium and thus renewed excitation in the ventricles via the AV node induce. That makes the picture of a circular motion and a seizure occurs Tachycardia (the heart beats too fast). The sudden occurrence of a very high pulse (often 150 to 230 beats per minute), which ends just as abruptly.