Tick bite during pregnancy
Unfortunately, even during pregnancy you are not necessarily spared from tick bites. Ticks are usually found in tall grass or forests, waiting for warm-blooded mammals - in this case humans - to bite into.

The tick scratches the skin of the affected person with its jaw claws and then sinks its sting (hypostome) into the wound. Before they start eating, namely the Blood sucking begins, the tick releases various secretions into the wound with its saliva. Then she starts sucking blood.Tick bites are particularly feared by expectant mothers during pregnancy, as ticks are known to cause certain diseases such as Lyme disease or TBE can transfer.
How dangerous is that for my baby?
Many expectant mothers fear tick bites during pregnancy. The reason for this is that Fear of infectious diseasesthat can transmit ticks. In our latitudes, these are above all Lyme disease and the Early summer meningoencephalitis (short: TBE). How great the risk to the unborn child is depends on various factors.
The longer the tick is on the body and can suck blood, the more likely it is that diseases will be transmitted to the mother. Borreliosis in particular is feared because, unlike TBE, there is no vaccination against it. In addition, the Transmission of TBE much less likely than Lyme disease. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that ticks that carry the TBE virus only live in certain areas of Germany; on the other hand, the probability of transmission is generally 30%. So not every sting leads to an infection.
It is now considered certain that the Borreliosis is transmitted to the unborn child through the placenta can be. However, it is not possible to say exactly how high the risk is. Overall, it is rated as very low, but transmission can sometimes lead to severe malformations in the child. The most common are abnormalities of the heart, nervous system, musculoskeletal system and skin. Liver malformations are also known.
Since damage to the child cannot be ruled out, there is a need for rapid action in the event of a tick bite during pregnancy.
Lyme disease
The Lyme disease provides the most common tick-borne disease in Europe. Transmission to the child is very rare, but in principle it is possible. It is therefore important that the Remove tick as soon as possible. You can remove the tick yourself from the pharmacy with suitable pliers or you can consult a doctor who will remove the tick properly. This measure is the most important to prevent infection and harm to the child from Lyme disease.
If there are already signs of borreliosis transmission, in the form of an roten skin changes around the puncture site (Erythema migrans), the doctor starts with an immediate one Antibiotic therapy. This is not to be seen as prophylaxis, but as therapy against the infection. The ring-shaped reddening of the skin occurs no earlier than seven days after the bite. A slight reddening immediately after the tick bites is not a sign of Lyme disease. In pregnancy the antibiotic is used Amoxicillin recommended for therapy. Therapy with Cefuroxime or penicillin be performed.
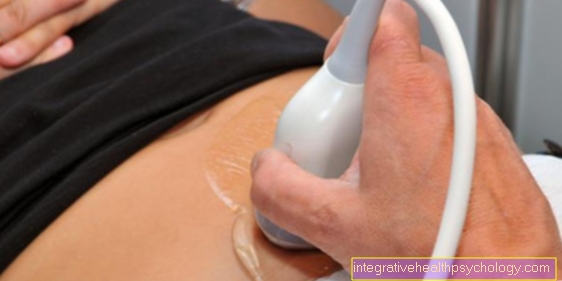
When infected with Lyme disease in the In addition to antibiotic therapy, a differentiated ultrasound examination is carried out in early pregnancyto detect malformations in the child. In addition, umbilical cord blood should be drawn for further examinations after the birth. If abnormalities are found in the newborn, an examination of the mother cake is recommended. If you are unsure, in the 6-7 Further blood tests should be carried out on the child at the age of 10 months. Should be here If no antibodies against the borreliosis pathogen are found, transmission during pregnancy is excluded. Overall, transmission to the newborn and damage from borreliosis is very rare and unlikely if the expectant mother is treated quickly.
TBE
TBE is a Inflammation of the meninges and brain tissue caused by virusestransmitted by ticks. In Germany, there is an increased risk of TBE transmission only in certain regions - especially in Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg.
There is one for TBE Vaccinationto be done if living in areas at high risk of transmission. Even if you are pregnant you can get vaccinated if you live in a high-risk area.
In pregnancy the ROverall, the risk of an infection with TBE is rather low. In addition, the disease is asymptomatic in 90% of those infected. TBE is usually not transmitted to the unborn child. Unfortunately, should the pregnant woman develop symptomatic illness, there is no curative therapy. The course of the disease, which usually heals by itself, must be awaited. Only the use of antipyretic drugs and painkillers is possible.
Causes of tick bites
Human blood is a food source for ticks, so they sting too. The Pregnancy is not associated with an increased risk of a tick bite. S.walks in fields, tall grass or in the forest pose a particularly high risk of a tick bite. There are ticks on blades of grass and wait for an animal or human to brush the blade of grass. With their sensory organs they perceive vibrations, body heat and fragrances. Seasonal consists an increased risk depending on the region for a tick bite. You should therefore be careful, especially in so-called endemic areas. You can protect yourself with sturdy shoes and long socks. Long pants also help protect yourself from a tick bite.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of a tick bite falls not particularly difficult. Most of the time the tick is still on the body and can be seen with the naked eye. During pregnancy, the tick should be removed as soon as possible. If you remove the tick yourself, keep it in a jar. It may be needed for further research.
After removing the tick, the doctor may run one Blood collection to detect antibodies against pathogens that the tick is transmitting. Since the antibodies are sometimes only formed with a delay - after about 2 to 3 weeks - the blood collection usually has to be repeated after 6 weeks.
First of all, the focus is on physical examination of pregnant women. The doctor looks at the area around the tick bite. There, in about 50% of Lyme disease infections, the so-called Wandering redness (Erythema migrans). It is a red skin lesion that spreads in a ring around the tick bite. This however, occurs no earlier than 7 days after infection.
If you suspect a Transmission in early pregnancy, additional ultrasound exams are doneto find harm to the child. If the suspicion persists, will blood taken from the umbilical cord after birth and further investigated.
accompanying symptoms
Tick bites do not always lead to discomfort and are usually symptom-free. The sting as such is not painful and is usually only noticed during a targeted search for the tick. Since the tick bite can lead to the transmission of infections, accompanying symptoms are possible.
The Borreliosis is usually transmitted asymptomatically at first. After a few days, however, the so-called occurs in 50% of those affected Wandering redness (Erythema migrans on). Occasionally the wandering redness is accompanied by a slight itching. Only in very rare cases are Concomitant symptoms such as fever, malaise, headache and fatigue available. Later stages of Lyme disease only become symptomatic after months and therefore cannot be regarded as accompanying symptoms of a tick bite.
An infection with TBE runs in pregnancy completely asymptomatic in over 90% of cases. In very rare cases it can Fever and flu-like symptoms 2 to 4 weeks after the tick bite come. A subsequent fever-free interval with a subsequent renewed increase is typical. This process is called biphasic.
What to do if you get a tick bite during pregnancy
First of all, you should try not to get caught in the first place or to discover it as quickly as possible. So after a walk in the forest, field or tall grass - especially during pregnancy - you should look carefully for ticks on the body. A careful search is recommended, especially if you live in high-risk areas. This way, ticks can be found quickly and do not go unnoticed on the body. The longer the tick has time to suckle, the higher the risk of infection.
After the tick has been found, it should be removed as soon as possible. Remove The tick only with suitable pliers from the pharmacy and avoid squeezing or pressing them. After that is a Cleaning the puncture site with disinfectant recommendable. After removing the tick, you should get one Consult a doctor and have yourself examined. If Borrelia is suspected, antibiotic therapy is carried out immediately Amoxicillin.
When do i need antibiotics?
Antibiotic therapy after a tick bite is necessary if the Suspected Lyme disease in the pregnant woman consists. This results from indications in the blood test or the physical examination. One sign is the so-called wandering redness (Erythema migrans). However, since such a skin mark can only be seen in 50% of Lyme disease infections, Lyme disease cannot be reliably excluded or confirmed. If there is an increased risk of Lyme disease, therapy with Amoxicillin carried out. The decision is to be made individually for each pregnant woman.
In some cases, the tick can be examined in order to be able to make a risk assessment. In this way it can be determined whether the tick has Borrelia or not. In reality, however, this examination is rarely carried out as it is rarely useful. The duration of the tick's attachment is also used to assess the risk. If the tick is removed within a few minutes or hours, the risk of transmission is very low. This is usually only increased after 6 to 24 hours of adhesion.
forecast
It usually consists of a tick bite only a low risk of harm to mother and child during pregnancy. Most feared is an infection of the unborn child with Lyme disease. However, if the mother is treated quickly with antibiotics, the risk of harm to the child is almost zero. Therefore, if you get a tick bite during pregnancy, you should initially remain calm. A Rapid removal of the tick and antibiotic therapy - in the case of borreliosis - reliably prevent damage to the child and mother.




.jpg)