Anti-inflammatory drugs
Synonyms
Anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs
Areas of application and mode of action
Anti-inflammatory drugs are different drugs that have in common their anti-inflammatory effects. Since inflammation is a very complex process for the human body that has been well investigated, there are various starting points among the drugs that in the end all suppress or alleviate the inflammation.
Due to the different points of attack, there are big differences when which anti-inflammatory drug is the right one. Inflammation is the body's most uniform response to various triggers such as Pathogens, poisons or foreign body.
The inflammation is caused on the one hand by the tissue itself, by being so-called Tissue hormones as an alarm signal and so that immune system alarmed and on the other hand by activating the immune system with the help of various immune cells distributed throughout the body, the phagocytes (= Macrophages), the Dendritic cells in the skin or Lymphocytes (to the white blood cells), which lurk for foreign substances and are activated by them and then fully develop their function. The sending of messenger substances to alert the body's own immune system leads to the flooding of many other immune cells with the bloodstream, which then accumulate at the site of the event and cause the visible inflammation in order to dissolve the foreign body, remove it and kill the bacteria that have penetrated with the foreign body.
If these defense cells die in the process, the result is a mixture of living and dead cells and the remaining foreign body components pus and the inflammation around the foreign body. Through this defense mechanism, the body wants to work the foreign body out of the body.
The classic signs of inflammation are:
- Redness (= lat: rubor)
- Swelling (= lat: tumor)
- Overheating (= lat: calor)
- Restriction of functionality (= functio laesa).
The expansion described here as being localized can, if the inflammation is very severe, expand through the bloodstream into the entire body and can be life-threatening Blood poisoning (= Sepsis) cause.
Different groups and their side effects
One distinguishes so-called steroidal from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (= Anti-inflammatory drugs) and these in turn from herbal Active ingredients.
Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Steroids play a prominent role in our body. Our bodies can make a wide variety of steroids that ultimately result in the Sex hormones (e.g. testosterone), the Glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol) or the Mineralocorticoids (e.g. aldosterone) can be assigned. Cortisol has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Common to all is theirs basic chemical structurewhich by the arrangement of the molecules as steroidal referred to as. The most famous steroidal molecule in the body is this cholesterol from which all these steroids among other things in the Adrenal gland our bodies are formed. The problem here is the excessive range of effects of the steroids in the body. the glucocorticoids like cortisol are commonly referred to as our body's stress hormone. In addition to reducing inflammation, mobilizing energy reserves and providing the body with energy, it suppresses the immune system and improves mood. Each steroid can be individually chemically imitated and administered to the body as a tablet, but the selected drug will always have the effect on the entire system rather than the desired effect on any one of these systems.
Due to the broad effect, it can be used at Allergies, Asthma, bronchitis, Multiple sclerosis, rheumatism, hepatitis, Rashes, after transplants, kidney disease or autoimmune diseases.
If cortisol is used as an anti-inflammatory, the effect on all other systems must always be accepted. The unwanted effects range from Obesity on the trunk of the body through energy redistribution, osteoporosis, muscular dystrophy, Skin changes, Stomach and intestinal ulcers up to high blood pressure.
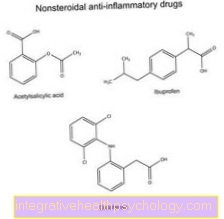
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are also used Anti-inflammatory drugs called.
They include the very well-known active ingredients Acetylsalicylic acid (e.g. Aspirin®, ASS®), Ibuprofen (e.g. Nurofen®, Neuralgin®) Naproxen (e.g. Dolormin®) and Diclofenac (e.g. Voltaren®).
Non-steroidal because they are chemical no steroid backbone, so doesn't have the typical look of steroids.
You will like the name Anti-inflammatory drugs indicates at rheumatism and other inflammatory joint diseases like the rheumatoid arthritis, the ankylosing spondylitis or also the gout used. Here comes above all Diclofenac for use.
The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs act on the Formation of hormonesthat are released in the event of an injury around the immune system to alert that Prostaglandins. The enzyme that plays a role in its formation is called Cyclooxygenase. Since the prostaglandins also at fever and Pain Playing a role, these drugs also have an excellent effect on fever and pain.
The side effects arise from the role of the Cyclooxygenases in other processes in the body, above all the Formation of gastric mucus. Normally there is a balance of different fluids on the inside of the stomach lining. On one side there is aggressive stomach acid, from hydrochloric acid and which the body needs to digest food so that it can then be used by the body in the intestine. Since the stomach acid would also digest its own stomach wall, the acid on the other side is opposed to the protective gastric fluids that are supposed to prevent this self-digestion. Because acids are best with basic To neutralize liquids are this consists of a great deal bicarbonate liquid, one Lye. This balance enables the food components to be properly digested while protecting the gastric lining on the inside of the stomach.
And it is precisely here in the production of the protective bicarbonate film of the gastric mucosa that cyclooxygenase and prostaglandins play a decisive role. If one now inhibits this formation with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, this equilibrium is thrown out of joint and it becomes proportionate much more stomach acid Formed as bicarbonate and the stomach acid can attack the stomach wall.
The patients then often complain Indigestion, nausea or stomach pain.
If the process progresses, one emerges Stomach- or Duodenal ulcer, which in extreme cases can be life-threatening Gastric perforation can lead.
This main side effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can occur after just a few ingestion. For this reason, patients at risk should always have a so-called Stomach protectione.g. one Proton pump inhibitors, take in addition.
Patients who Acetylsalicylic acid take, as these also have the properties of our Platelets changed so that they can no longer clump together. With acetylsalicylic acid, the risk of bleeding is increased enormously. Another not negligible side effect of taking it over a long period of time is the harmful effect on it heart and Kidneys. Patients with problems and diseases of one of these organs should only take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs after consultation with a doctor or on medical advice. This also applies to patients with Lung disease, since the inhibition of cyclooxygenase also leads to the preponderance of other substances Alveoli change and thus make breathing more difficult and in extreme cases one in asthmatics Asthma attack can trigger.
Herbal anti-inflammatory drugs
Herbal anti-inflammatory drugs are often very good alternative to chemically manufactured tablets, not least if the inflammation is only very slight. Their effectiveness is based on mechanisms similar to that of chemical preparations. Not infrequently, the chemical preparations even have their origin in the plant world, e.g. the Acetylsalicylic acid in willow bark extract. Those from the vegetable sector have proven themselves Teufelskrelle, ash, rose hip, trembling aspen and the Stinging nettle. Also Turmeric, oregano, rosemary, ginger and Green tea have anti-inflammatory effects and, when incorporated into the diet, can help improve inflammation.
Dosage forms

Due to their versatility, anti-inflammatory drugs can be obtained in many different forms. Above all the classic Tablet or Capsule shape.
This is great for most patients. Patients are excluded here Gastrointestinal diseases, since absorption from the intestine can be disturbed here.
Offer an alternative to tablets Effervescent tablets to dissolve or drops be.
For children too have Suppositories proven.
There is another optimal form for skin diseases: Creams, gels or Anoint.
You avoid all side effects that every drug inevitably brings with it, and apply the anti-inflammatory drugs directly to the place where it happens, the skin. Known applications are the gels e.g. With Diclofenac (Voltaren®), which are regularly used for sports injuries. Also normal skin diseases are like acne, Eczema or sunburn, all of which are associated with inflammation, are easily treated with no side effects in the body.
For severe inflammation like the extremely painful one rheumatic thrust Most preparations are also available as Solution for injection for direct injection into the muscle or one vein. With this form of administration, on the one hand, larger amounts can be introduced into the body and, on the other hand, the effect occurs many times faster.