Use of local anesthetics during pregnancy
- Surface anesthesia
- Epidural anesthesia for vaginal delivery
- Advantages and disadvantages of epidural anesthesia
- Epidural anesthesia for a planned caesarean section
- Planned caesarean section under spinal anesthesia

First of all, local anesthesia can be divided into 2 forms:
- the surface anesthesia
and - the infiltration anesthesia
Surface anesthesia
With surface anesthesia, an area of the mucous membrane is sprayed or brushed with the local anesthetic. This leads to a blockage of small nerve endings that are superficial. The surface anesthetics include lidocaine 2-4% and mepivacaine 2%.
A specialty is the EMLA cream, which is a mixture of the local anesthetics lidocaine and prilocaine. After the exposure time, the cream with the active ingredients penetrates the skin and blocks the nerve endings there.
Read more on the topic: Emla cream
Infiltration anesthesia
In infiltration anesthesia, the active ingredient is now into the skin (intradermal), in the Subcutaneous fatty tissue (subcutaneous) or in the muscle (intramuscularly) injected. Here the nerve endings are blocked again. Infiltration anesthetics include:
- Mepivacaine 0.5-1%
- Bupivacaine 0.25-0.5%
- Levobupivacaine 0.25%
- Lidocaine 0.5-1%
- Prilocaine 0.5-1%
In the case of infiltration anesthetics, a Addition with adrenaline used so that the local anesthetic stays in the tissue longer and does not spread as quickly.
Examples of the application of local anesthesia would be one Suture or a Visit to the dentist.
What now in the pregnancy plays a role is that different fat solubility of the Medication. Local anesthetics with high fat solubility could quickly the placenta (the placenta) happen. It also depends on how high it is Protein binding in the body of local anesthetics is: All the more lower the protein binding is even more so lighter the local anesthetic is transferred to the placenta and thus to the child.
For these reasons, a local anesthetic is preferred for pregnant women high protein binding and low fat solubility.In general, however, one could do so in investigations no harmful effect of local anesthetics on the unborn child, these are just precautionary measures.
If on the other hand there is a incorrect application of the local anesthetic comes into the vessel, the situation looks quite different. By a Injection into the vessel of local anesthetics is the risk of Complications much higher.
As already mentioned, adrenaline is often added to local anesthetics. This is also with one Pregnancy possible. However, you should try one if possible low dosage to be selected (1: 200,000).
However, a Injection into the vessel definitely be avoided. An injection of adrenaline into the blood vessel can cause a Contraction of the uterine vessels trigger, which provide the child with essential nutrients. Also are during pregnancy not to use two adrenaline derivatives. It is a matter of Norepinephrine and Felypressin. The following local anesthetics can be used during pregnancy:
- Articain
- Bupivacaine
- Etidocaine
Prilocaine and mepivacaine oppose it advisedly apply.
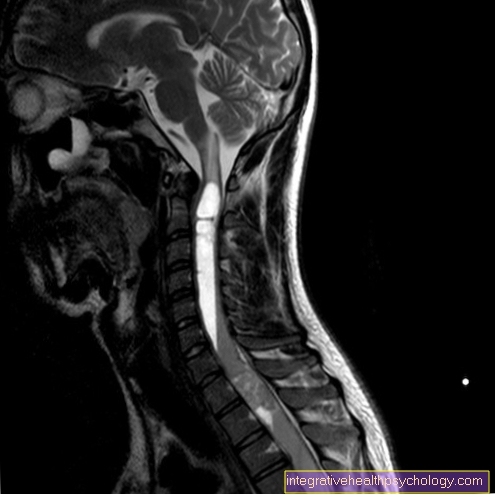
Local anesthetics in epidural anesthesia in pregnant women
Basically the epidural anesthesia (PDA) takes place with same technique as well as epidural anesthesia for non-pregnant women. However, there are a few special features that should be observed in pregnant women.
It is recommended to do one during the PDA for pregnant women rapid hydration through a vascular access. It has been found that approx. 80% the given liquid quickly out of the vessels into the tissue trespass. Since PDAs, especially pregnant women, often lead to a severe drop in blood pressure comes through the PDA, you give it liquid Dear during the PDA instead of in front of the PDA. The drop in blood pressure comes through that Blockage of the sympathetic nervous system caused by the medication of the PDA.
The pregnant woman is usually seated or lying on her left side. The Puncture for the PDA develops in pregnant women more difficult than in non-pregnant patients. Due to the hormonal changes in pregnant women are often Water retention in the tissue In addition, the fabric and band structures are usually softer and looser. That's how it is waning resistance at puncture through the loosened tissue harder to locate. The risk of incorrect punctures is therefore increased. Therefore, the PDA puncture in pregnant women should be done by one experienced anesthetists be performed.
As local anesthetics are used here Bupivacaine and ropivacaine administered. These local anesthetics have optimal criteria for not transferred to the child become.
Epidural anesthesia for vaginal delivery
The special feature of vaginal delivery is that the local anesthetics are only used in low dosage administered so that only the Blocked nerve fibers for pain and temperature but the patient is still active their muscles can use to give birth through a Abdominal press to support.
The local anesthetic is always in the Pauses in labor administered. This is important as the Local anesthetic can rise uncontrollably through the spinal canal due to the pressure of labor!
Sometimes too Additions of sufentanil used. This results in a better pain relief. The maximum dose is here 30 µg.
To Reduction of pain during opening pains one normally blocks the transmission of pain from 10 thoracic vertebrae to 1 lumbar vertebral. This will be approximately 6-8 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine or 0.2% ropivacaine needed.
To Reduction of pain associated with expectoral labor becomes the transmission of pain from the 10th thoracic vertebra to the 4th sacral vertebra blocked. One uses approx. 12 ml 0.25% bupivacaine or 0.2% ropivacaineThe pain therapy with the local anesthetics bupivacaine and ropivacaine lasts about 2 hours on. If necessary, more must be administered after 2 hours.
Advantages and disadvantages of epidural anesthesia
The PDA creates a painless birth guaranteed. In addition, the PDA is advantageous for a Birth from breech position, Premature birth, (Diabetes), EPH gestosis (triad of high blood pressure, water retention, high protein excretion), multiple pregnancies, with pulmonary or Heart disease in pregnant women and in diseases where too much pressure during the birth process would be disadvantageous.
Basically, vaginal delivery is done with a PDA not done at:
- Clotting disorders
- Allergies to the local anesthetics
- Inflammation at the puncture site
- System infections
- Shock such as dehydration
- Suspected increased intracranial pressure
- Changes in the spine such as ossification and adhesions
- CNS disorders
There are also specifically for vaginal delivery Contraindications to a PDA, such as a emergency caesarean section. Because with an emergency caesarean section everything has to be done go much faster, so you choose one here general anesthetic.
The disadvantages of having a PDA in vaginal delivery must also be considered. With the PDA, the Length of birth extended become. It also occurs in pregnant women more common to complications with PDA puncture. It can become one severe drop in blood pressure come what a Reduced blood flow to the uterus and thus can become a danger to the child.
Epidural anesthesia for a planned caesarean section
With a planned caesarean section, you usually block the transmission of pain through a PDA from 4th thoracic vertebra to the 4th sacral vertebra. One uses for this approx. 18 ml of 0.5% bupicaine or 0.75% Rupivacaine. Both Sensation of pain and temperature switched off as well as the motor skills of the muscles. The muscles of the abdominal wall for the caesarean section are completely slack. High concentrations of anesthetics are not allowed; here, too, additional sufentanil can be used for more targeted pain reduction.
When administering the medication, make sure that the deep sacrum segments are also reached. For this purpose, the doctor usually gives the first half of the dose to the seated pregnant woman. The patient should then remain seated for about 5-10 minutes. As a result, the local anesthetics sink better into the deep sacrum segments.

Planned caesarean section under spinal anesthesia
First of all, it can be said that the trend towards spinal anesthesia for planned caesarean sections increased in recent years In principle, one strives for that same heights of nerve blocks as with the PDA. Here one takes as a local anesthetic approx. 2.5-3ml 0.5% bupivacaine.
The disadvantage here can be a rapid drop in blood pressure by applying it directly into the Spinal canal be. To prevent this drop in blood pressure, be approx. 1000ml electrolyte infusion administered during spinal anesthesia. You can also use the drug Akrinor use to quickly get the drop in blood pressure under control.
Again, there are complications and disadvantage for the pregnant woman. In spinal anesthesia, the most common symptom after spinal puncture can be the postspinal headache come.
Another point here is that Risk of rapid drop in blood pressurewhich is more likely with spinal anesthesia than with PDA. Other very rare complications are Cranial nerve disorders, Spinal cord injuries (The puncture is usually placed under the spinal cord, so that a spinal cord injury is practically impossible!) spinal anesthesia too high (when the anesthetic flows too far up the spinal canal), Bruising and Infections of the region.
Epidural anesthesia for vaginal delivery
The special feature of vaginal delivery is that the local anesthetics are only used in low dosage administered so that only the Blocked nerve fibers for pain and temperature but the patient is still active their muscles can use to give birth through a Abdominal press to support.
The local anesthetic is always in the Pauses in labor administered. This is important as the Local anesthetic can rise uncontrollably through the spinal canal due to the pressure of labor!
Sometimes too Additions of sufentanil used. This results in a better pain relief. The maximum dose is here 30 µg.
To Reduction of pain during opening pains one normally blocks the transmission of pain from 10 thoracic vertebrae to 1 lumbar vertebral. This will be approximately 6-8 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine or 0.2% ropivacaine needed.
To Reduction of pain associated with expectoral labor becomes the transmission of pain from the 10th thoracic vertebra to the 4th sacral vertebra blocked. One uses approx. 12 ml 0.25% bupivacaine or 0.2% ropivacaineThe pain therapy with the local anesthetics bupivacaine and ropivacaine lasts about 2 hours on. If necessary, more must be administered after 2 hours.















.jpg)