Blue spot won't go away - what can I do?
introduction
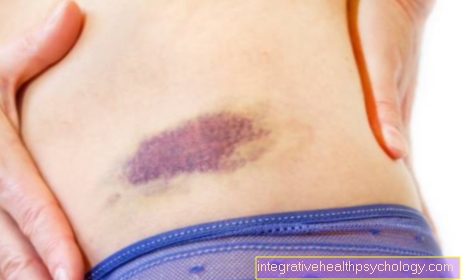
Everyone knows it, whether it is for oneself or for a child: after a knock, a blow or after falling it hurts and it develops bruise. Such a stain is nothing more than blood in the tissue under the skin. Blood leaks through the rupture of small vessels and presses on the surroundings - this is why a bruise is often painful. In technical jargon, blue spots are called "hematomas". They usually go away within 1-3 weeks and change color several times by then. If the stain has been present for significantly longer than 6 weeks, this is usually harmless, but it can also be an indication of several diseases.
Reasons why the bruise does not go away
There can be several reasons why a bruise does not go away in about 3 weeks. Some of them are completely harmless and only a cosmetic problem, others should be taken seriously and clarified by a doctor. It should be emphasized that the harmless causes are much more common are. A doctor should be consulted if a bruise does not go away within approximately 2 months.
If there is a lot of blood under the skin from an injury, it may take longer to break down. Especially after operations or severe injuries such as a car accident, you should therefore expect the bruises to be visible for a little longer. Occasionally, parts of the blood pigment in the skin cannot be broken down and remain visible for years.
However, if the bruise grows and remains painful for a long time, this can also affect one Bleeding in the injured area indicate.
If bruises occur unusually often and remain visible for a long time, an increased bleeding tendency may be the cause. This is usually triggered by taking medication such as aspirin and marcumar, but it can also be caused by Bleeding disorder that change the composition of the blood.Liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, the "von Willebrand-Jürgens syndrome" and "hemophilia A or B" are typical here. It should also be noted that some tumors can look like a bruise. These are, for example, the hemangioma or the black skin cancer on hand or toe nails. If the bruise looks unusual and has been growing for weeks or months, a doctor should therefore be consulted.
What can I do about bruises?
Basically, the breakdown of blood under the skin can rarely be accelerated. That is why it is important to do the so-called immediately after an injury PECH rule to use: rest, ice, compression and elevation. That means: pausing the sport, because a larger blood flow from the movement can enlarge the bruise and worsen other injuries. Then the injury should be covered with ice wrapped in a cloth to reduce blood flow and pain. If not too painful, applying pressure to the injured area can also reduce the size of the bruise. If an arm or leg is injured, it should be elevated.
There must be bruises behind which are very large bruises occasionally surgically removed become. This is important because bruises can form permanent swelling under the skin or become infected.
Is a Taking medication the cause of the bruise, it should be checked whether the drug is necessary and which Dose set correctly is. If this is the case, long-term visible bruises can only be prevented by preventing injuries.
Frequently becomes Heparin ointment Used to accelerate the breakdown of bruises, but effectiveness is controversial. Home remedies such as arnica and calendula ointments or homeopathic remedies can also be tried, but are rarely effective. If the bruise hurts a lot, pain-relieving ointments such as diclofenac can help.
diagnosis
Various means are used to diagnose long-standing bruises. At first it is important to inquire whether a corresponding violation has taken place or not. Spontaneous bleeding is an indication of a bleeding tendency. The question of what medication you have taken is also important, as some active ingredients weaken blood clotting and can lead to long-lasting bruises.
The bruise can be examined more closely with an ultrasound machine if a large hematoma, tumor, or internal bleeding is suspected. However, it is especially important that Blood test: it can be used to determine whether blood clotting lasts longer than in healthy people and whether or which blood proteins are missing. This is the only way to make it clear which disease is present.
Concomitant symptoms
A completely normal phenomenon with bruises is that Tenderness. He usually gets better within a few days.
If the bruise is aggravated or caused by another disease, further symptoms can appear. If there is an increased tendency to bleed, for example Joint bleeding with pain and movement restrictions occur in the affected joint. Bruises can appear without a corresponding injury. Large bruises can be caused by minor injuries. Also Bleeding from the gums or nose May occur.
In the form caused by low platelet counts, it is typical that small bruises appear all over the skin.
At Tumors growth can be observed within weeks or months. Sometimes the bruises are streaked with small vessels or slowly grow above the skin level. To step Circulatory problems or impaired consciousness after injuries to the abdomen, chest or head, should urgently consulted a doctor as this may be an indication of internal bleeding.
Duration
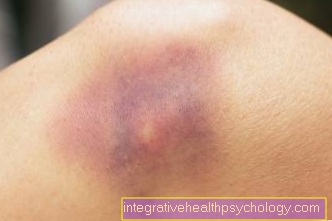
Bruises develop slightly differently from person to person. They usually disappear within, depending on their size 1 to 3 weeks. The smaller they are and the deeper they are, the faster they are no longer visible. Particularly large bruises can still occur up to 2 months be visible for a long time. Occasionally, part of the blood pigment under the skin cannot be broken down and remains visible as a brownish-reddish spot for years.
Bruises in a joint can also be felt or visible for a very long time if they are not treated properly. The color shows how far the breakdown of a bruise is. In this way it can be estimated how long it will still be visible. Are they red-dark bluishthen they are relatively fresh. After that they will brown-blackish. Then take one green-dark green color what a speedy healing means. Shortly before they are completely broken down, the spots are yellow-brownish.
In the case of blood coagulation disorders, the stains can be visible for longer, but do not have to be. Most of the time there are many or large bruises, but they go away within a few weeks. If bleeding occurs days or weeks after an operation, the bruise will last longer.
Blue spots in babies / children / toddlers
There are bruises in children very often. They play a lot, are often very clumsy and fall, often bump into each other or otherwise hurt themselves. Usually the bruises will go away on their own within the next 1-3 weeks. The smaller and deeper the bruise, the faster it is no longer visible. Larger bruises may still be visible 8 weeks after the injury, as large bruises take longer to clear. As a parent, you usually don't have to do anything except wait and see because of the bruises. They are usually completely harmless and shouldn't be a cause for concern.
What is important, however, is the Examine the wound and the bruise in the event of an injury. For example, if the child was playing with something sharp like a pencil or wood, something could be stuck in the wound. If they complain of very severe pain or if they keep their arm or leg in a relieving position for a long time, muscles or even bones can be injured. If the child bumped himself or herself at greater speed or otherwise injured himself a little more, the PECH rule (Break - ice - compression - elevation) to prevent the resulting bruises from becoming large and to alleviate the pain: sport and movement should be paused first. During the break you should cool the injury and apply some pressure to the injury with the cool pack. Care should be taken not to apply ice directly to the skin, but rather to place it in a cloth. The injured limb can then be elevated.
If the bruise has already been visible for a few weeks, natural remedies or homeopathics such as arnica or Traumeel are often applied as ointments to the bruises to make them disappear more quickly. However, the effectiveness of such agents has not been proven.
Is a bruise not gone after more than 8 weeks or if it enlarges, in a few cases a tendency to bleeding or even an leukemia exist. However, these are less apparent from the time it takes for the bruise to disappear than from other symptoms. These include the appearance of bruises without adequate injury, frequent gum and nosebleeds, bleeding in the joints, the appearance of small, punctiform hemorrhages all over the skin, fatigue, weakness, and the frequent occurrence of infections. Should these signs appear in addition to the bruises, a See pediatrician.
Localization of the bruise
Arm / upper arm
The arms and hands are our main tools in everyday life and during sports, and are often bumped, cut or otherwise injured. The resulting bruises usually disappear within a few weeks. If it takes much longer to heal, this can also be a sign of an increased bleeding tendency - especially if the bruises are unusually large and other spots appear without explanation.
If the bruise is caused by a fall on the arm, an accident, or a bruise at high speed and the arm is very painful, it should be checked to see if the arm is broken. Elderly people with osteoporosis are particularly prone to fractures of the upper arm. In addition, in old age we move less and can sometimes tolerate pain better. Therefore, it occasionally happens that a broken bone is discovered several weeks after the injury.
If there are no symptoms that indicate a dangerous cause of the bruise, you can wait 2 months before consulting a doctor. If the bruise hurts a lot when you apply pressure, you can take pain-relieving medication such as ibuprofen or diclofenac as a tablet or apply ointments containing diclofenac.
Leg / shin
The leg, especially the shin, becomes very large frequently bumped into objects and therefore often shows bruises. The skin on the shin is very thin and lies practically directly on the bone. This is why the bruise that leads to the bruise is often very painful: it presses directly on the very sensitive periosteum. As long as the swelling and the stain persist, pain is not uncommon. If the stain does not look unusual and appears without any further symptoms, you can wait 8 weeks before seeing a doctor.
Stand up severe pain in the foreground and is particularly evident when the leg is moved or stressed, it should be checked whether the Injured bone is. The same applies to the treatment of bruises on the leg as to the rest of the body: the most effective means is to wait and see. Heparin ointment or natural remedies such as arnica, comfrey ointment or Traumeel can be tried, but often do not work. If the appearance of the stain disturbs, make-up can be used to cover it. If the bruises and swelling remain very large or painful, a small operation to remove the blood clot under the skin may be necessary.