Inflammation of the vocal cords
definition
The vocal cords, the colloquial term for vocal folds, are elastic ligaments that form part of the larynx (the entrance to the windpipe). They consist of the glottis, the actual vocal cord (Vocal ligament) and a muscle (Vocalis muscle). They are important for voice training: The inflowing air causes them to vibrate, tones are created and speech formation is possible. The inflammation of the vocal cords can be divided into an acute and a chronic form. The inflammation is considered chronic as soon as it lasts longer than 3 weeks. The inflammation of the vocal cords is also called laryngitis (laryngitis) called.
Read more on this topic at: Laryngitis

Symptoms
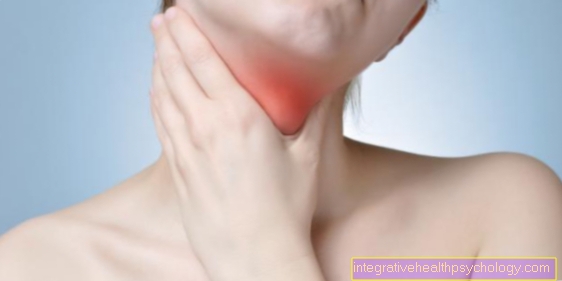
There is pain in the larynx area and a scratchy throat with an urge to cough and difficulty swallowing. In addition, there is hoarseness with a rough voice and even speechlessness (Aphonia). Occasionally, a fever can occur. In the chronic form, the symptoms last for at least 3 weeks to months. If reflux is the cause, it leads to dry cough, which occurs mainly at night, and heartburn.
Pseudo croup shows similar symptoms, with a barking cough and shortness of breath due to constricted airways leading to fear of suffocation.
Read more on this topic at: Pain in the larynx and symptoms of inflammation of the vocal cords
Shortness of breath
Vocal cord inflammation can spread to the entire larynx. The symptoms worsen and the strong swelling of the larynx mucosa can, in very rare cases, lead to breathing problems. The larynx forms the entrance to the windpipe, which is why swelling in this area can shut off the air supply and cause shortness of breath. This is a potentially life-threatening complication that needs immediate medical attention.
causes
The acute form is usually a descending infection of the upper respiratory tract (nose or throat) that spreads to the vocal cords. In most cases, viruses are the cause, but infection by bacteria is also possible. The most common pathogens are cold viruses (Rhino or adenoviruses), Influenza viruses (Haemophilus influenzae) or pneumococci (Streptococcus pneumoniae). Furthermore, a strong vocal stress can lead to irritation of the vocal cords.
If acute vocal cord inflammation is inadequately treated, chronic vocal cord inflammation can result. Furthermore, smoking, a dusty environment, the wrong voice technique or the overloading of the voice (e.g. with singers or teachers) as well as a chronic inflammation of the neighboring organs can lead to chronic inflammation.
The backflow of gastric juice into the esophagus (reflux) can also be the cause of a special form of laryngitis.
A form of laryngitis that occurs mainly in young children is pseudocroup (Subglottic laryngitis). This is an inflammation that can lead to severe swelling of the vocal cords. The cause is a viral infection with additional infection by bacteria.
Vocal cord inflammation is so contagious
Vocal cord inflammation is caused either by mechanical irritation, when the voice is stressed by long or loud talking, or by infection. Vocal cord inflammation from overuse is not contagious, whereas an infection is usually caused by bacteria or viruses and can easily be passed on to other people.
Often times, flu or other upper respiratory diseases, such as pneumonia or whooping cough, also lead to an infection of the vocal cords.Coughing or sneezing is a common symptom associated with these diseases. The pathogens get into the air with the ejected secretion and can be transmitted to other people by means of droplet infection and cause vocal cord inflammation. Sick people should be aware of the risk of infection for their fellow human beings and adhere to strict hygiene rules. This includes washing your hands thoroughly, keeping your distance from other people and only coughing or sneezing in tissues. Shaking hands should also be avoided during the duration of the illness.
therapy
First of all, the patient should spare his voice and speak only a little and quietly. However, whispering should not be used, as this puts additional strain on the vocal cords and does not, as assumed, protect them. In addition, it is advisable to refrain from smoking, alcohol and hot spices. Warm drinks and steam inhalations can also be recommended for the dry feeling and pain. Expectorants can help against the mucus.
If the inflammation is bacterial, an antibiotic should also be prescribed. If there is inflammation of the sinuses or airways in addition to inflammation of the vocal cords, these should also be treated.
If the inflammation is based on an incorrect voice technique, treatment by a speech therapist can be useful. This helps to improve the vocal technique and thus avoid renewed irritation of the vocal cords.
If the cause of the inflammation is a dusty environment, for example at work, exposure should be reduced as much as possible, for example using breathing masks.
If you have reflux, you should take medication that inhibits acid production in the stomach.
The pseudo croup should definitely be treated as an inpatient in order to be able to monitor the shortness of breath. Antibiotics against the bacterial infection are necessary. If there is a risk of suffocation, the introduction of a breathing tube into the windpipe (Intubation) or a tracheotomy (Tracheotomy) become necessary to secure ventilation.
When do i need antibiotics?
Vocal cord inflammation can be caused by an infection, with viruses or bacteria usually causing the disease. Viral infections can only be treated symptomatically, whereas antibiotics must be taken in the case of bacterial infections. If a vocal cord inflammation lasts more than three weeks or if the symptoms have not improved after two weeks, a doctor must be consulted. The doctor examines the vocal cords, takes a smear and can determine whether the inflammation is bacterial and whether antibiotics are needed.
These antibiotics help best
The antibiotic that is used to treat vocal cord inflammation depends on the type of bacterium causing it. A common pathogen is the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, which is treated with beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillin G or cephalosporins such as cefaclor, cefuroxime or cefatriaxon. Sprays containing the antibiotic fusafungin work locally on the inflamed vocal cords and can be used to treat vocal cord inflammation. In the case of drug therapy with antibiotics, it is important that a doctor prescribes the appropriate agent and that the patient strictly adheres to the type and duration of use, as otherwise severe side effects or resistance can develop.
When do i need cortisone?
In severe infections and if the patient does not respond to antibiotic therapy, it may be necessary to take preparations containing cortisone. Cortisone is an extremely effective endogenous hormone that has a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Due to numerous side effects, however, it may only be used carefully and only on a doctor's recommendation.
Read more about this topic at: Side effects of cortisone
Inhale
Inhaling is a great way to speed up healing of vocal cord inflammation. Herbal tea made from medicinal herbs such as Icelandic moss, chamomile or marshmallow root is particularly suitable for this. The hot tea is placed in a bowl and inhaled under a towel for about 15 minutes. A saline solution can also be used for inhalation. To do this, put a tablespoon of salt in a bowl of hot water and dissolve it while stirring. Inhaling the hot vapors moisturizes the dry vocal cords and has a beneficial effect.
homeopathy
Vocal cord inflammation and the associated hoarseness can be treated homeopathically. The choice of homeopathic medicines is made according to the cause of the inflammation and the accompanying symptoms. Globules with the active ingredients Allium cepa (kitchen onion), Argentum nitricum (silver nitrate), Phosphorus and Ammonium bromatum (ammonium bromide) are used. Doctors and pharmacists help decide which globules are best for each patient.
Also read the article: Vocal cord inflammation - symptoms.
These home remedies can help
There are some old and time-tested home remedies that can help cure vocal cord inflammation. A simple tip is to drink enough fluids, preferably in the form of warm herbal teas. Freshly brewed teas made from chamomile, Icelandic moss or marshmallow roots have a healing effect and soothe the inflamed vocal cords. Drinking moisturizes the mucous membranes and vocal cords and relieves irritation. However, the tea should not be drunk too hot in order not to damage the vocal cords further. The consumption of alcoholic beverages should be avoided during the duration of the illness. Cold drinks are also taboo if you have vocal cord inflammation, as is milk due to its mucus-forming effect.
Instead of drinking the herbal tea, it can also be used for inhalation. Gargle solutions also help fight vocal cord inflammation. You can use salt water, herbal teas or diluted tea tree oil for this. Neck wraps made of quark have a cooling effect and help reduce swelling in the inflamed neck area. The cool quark is spread directly onto a kitchen towel, the towel is then wrapped and wrapped around the neck. Warm potato or onion wraps also have a beneficial effect on the inflamed vocal cords.
More on this: Home remedies for vocal cord inflammation
onion
Onions are a medicinal plant and are often used for vocal cord inflammation due to their anti-inflammatory effects. The essential oils contained in the onion kill bacteria and speed up the healing process. To do this, a raw onion is cut into fine cubes and poured over with hot water. You can sweeten the brew as you like. Honey is best suited for this, as it also has an antibacterial and germicidal effect. The brew is left to steep in the refrigerator for several hours and can then be drunk.
Duration of a vocal cord inflammation
The duration of vocal cord inflammation depends on the severity of the inflammation. Usually, vocal cord inflammation is harmless and lasts for one to two weeks. A slight irritation or overuse of the vocal cords is cured within a few days if the voice is spared. In severe cases, however, it can take several weeks for the vocal cords to heal completely and for the patient to be able to speak again without any problems. Complications are also possible, which further delay the healing process. These include shortness of breath or high fever, including the transition to chronic laryngitis (laryngitis) is possible. In such cases, a doctor must be selected immediately, as otherwise the complete loss of the voice can occur.
The disease can also be treated with medication, which can shorten the duration, but in many cases drug therapy is not necessary. In the case of severe inflammation of the vocal cords that persist for more than three weeks, however, drug treatment with antibiotics is necessary, as otherwise there is a risk of the disease becoming chronic. In the case of chronification, treatment is only possible to a limited extent and those affected usually suffer from persistent voice problems.
Read more about this topic here: Duration of a vocal cord inflammation
How long will you be on sick leave?
The length of time you are on sick leave depends on the cause and severity of the vocal cord inflammation. In the case of acute inflammation, the patient is on sick leave for several days, if the healing is slow, the sick leave can be extended. If the cause of the inflammation of the vocal cords is an infection, the person concerned will be put on sick leave until the infection has healed and there is no longer any risk of infection. The length of the sick leave also depends on the profession. People who only have to speak a little while working are more likely to go back to work than people in professions that require a lot of talk, such as teachers or call center employees.
When can I do sports again?
If you have vocal cord inflammation, heavy physical activity and strenuous sports should be avoided. If the cause of the disease is an infection, you must not do sports for the entire duration of the disease, as the infection can damage the heart muscle. If there is mechanical irritation, light sports such as yoga or a walk in the fresh air may be practiced. Those affected should, however, make sure that the vocal cords are kept warm and that cold air does not worsen the symptoms.
How long do I have to be silent?
With a vocal cord inflammation, the voice must be spared. However, this does not mean that those affected should whisper, as this puts even more strain on the vocal cords than when speaking. It is best not to speak at all, if necessary, but speak in a voice that is as normal as possible. The silence should be kept for as long as necessary. Usually the symptoms improve after a few days and those affected can slowly speak normally again. It can take several weeks for a vocal cord inflammation to completely heal and during this time the voice should not be overused.
forecast
The prognosis for vocal cord inflammation is good. Therapy should be started as early as possible and the vocal cords should be spared as much as possible. Damage to the Vocalis musclewhich closes the windpipe when swallowing and is also involved in voice production. Vocal cord inflammation, like colds, is contagious because the virus can easily be spread to other people and the surrounding area through an existing cough.
If the hoarseness persists for more than 4 weeks and therapy does not help, the presence of a tumor or tuberculosis must be ruled out by a doctor.
Complication: vocal cord nodules
A dreaded complication of vocal cord inflammation are vocal cord nodules, also known as screaming or vocal cord nodules. These are changes in the vocal folds that are caused by the previous inflammation. Vocal cord nodules are particularly common in people who talk a lot and often suffer from inflammation of the vocal cords. The nodules lead to hoarseness and difficulty speaking. An ENT doctor diagnoses the disease with a laryngoscopy (Laryngoscopy). It is possible to treat the vocal cord nodules with speech and voice therapy from a speech therapist. In rare cases, surgical removal of the vocal cord nodules can also be considered. The elevations are removed microsurgically using a laser.
Read more on this topic at: Vocal cord nodules
diagnosis
The vocal cords can be examined using the larynx mirror (indirect laryngoscopy). A small mirror is pushed over the open mouth to the back of the throat. The doctor can then assess the larynx from above. In direct laryngoscopy, instead of a larynx mirror, an endoscope is used that is pushed forward to the larynx. The advantage of this method is that, in addition to the examination, samples can also be taken. This is particularly useful if symptoms persist for more than 4 weeks and a tumor needs to be clarified.
In acute vocal cord inflammation, both examination techniques reveal evenly red and swollen vocal cords that are covered with thick mucus. If the inflammation is chronic, thickened and reddened vocal folds and dry mucous membrane, including the larynx, are noticeable. In the pseudo croup, however, the vocal folds are only slightly reddened.
Find out more about the topic here: Swollen vocal cords
How is vocal cord inflammation different from laryngitis?
The vocal cords are part of the vocal folds in the larynx. Voice overuse or infection can cause inflammation of the vocal cords. If the pathogens spread to the entire mucous membrane of the larynx when the vocal cords are infected, this is called laryngitis (laryngitis). The hoarseness and cough worsen and there is also a sore throat or difficulty swallowing. In rare cases, laryngitis causes breathing difficulties or even shortness of breath. Most of the time, both vocal cord and laryngitis are harmless and do not require drug treatment. If you become infected with bacteria, your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic.
Read more on this topic at: Laryngitis